When you run an internal audit, your findings are only as strong as the way you present them. That’s where a well-structured internal audit report format in Excel becomes essential. Excel gives you the flexibility to document, analyze, and track audit results — from risk ratings to action plans — in a single sheet that your management can easily review and act on.
This guide helps you understand what an internal audit report is, why Excel is the preferred tool for many audit teams, and how you can build or customize your own templates. You’ll also get free downloadable Excel formats for audit findings, compliance checklists, and action trackers that you can use right away.
By the end, you’ll know how to:
- Structure your internal audit report effectively
- Automate updates using Excel formulas and conditional formatting
- Maintain version control while meeting compliance standards
- Present findings and corrective actions with clarity
Let’s start by understanding what an internal audit report includes and how it strengthens your organisation’s governance and compliance process.
- What Is an Internal Audit Report?
- Why Use Excel for Internal Audit Reports?
- Key Elements of an Internal Audit Report — Excel Format
- Types of Internal Audit Reports
- Step-by-Step Guide: How to Create an Internal Audit Report in Excel
- Excel Templates for Internal Audit Reports
- Best Practices for Using Excel-Based Audit Reports
- Download Free Internal Audit Report Templates
- Frequently Asked Questions on Internal Audit Report Format in Excel
What Is an Internal Audit Report?
An internal audit report is a structured document that summarizes what you reviewed, what you found, and how those findings affect your company’s operations, compliance, or financial integrity. In simple terms, it’s your formal record of the audit process from objectives and scope to key observations and management actions.
You typically prepare this report at the end of an audit to communicate risks, control gaps, or process inefficiencies to management. It serves as a decision-making tool that helps leadership strengthen governance, risk management, and internal controls, ensuring regulatory compliance.
Purpose of an Internal Audit Report
- Identify gaps in internal controls, operations, or compliance
- Provide recommendations for corrective actions or process improvements
- Support accountability by tracking who’s responsible for implementing changes
- Promote transparency across departments and management levels
Who Prepares and Reviews It
As an internal auditor or compliance officer, one typically compiles the report after completing fieldwork and analysis. Once finalized, it’s reviewed by department heads, risk teams, or senior executives to ensure that findings are addressed through defined action plans.
Role in Corporate Governance
An internal audit report is more than compliance paperwork. It plays a vital role in your company’s corporate governance framework, ensuring policies are followed, risks are managed proactively, and improvements are documented for continuous monitoring.
When you use an internal audit report format in Excel, it becomes an interactive tool rather than a static document. Excel lets you track actions, assign responsibilities, and visualize risk trends over time, giving your audit function real accountability and visibility.
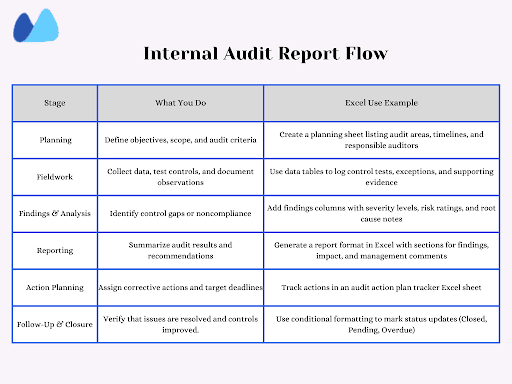
Why Use Excel for Internal Audit Reports?
When you prepare an internal audit report in Excel, you’re not just creating a table; you’re building a flexible, transparent system that keeps every audit step measurable and traceable. Excel remains the go-to tool for most internal auditors because it balances simplicity with powerful tracking features.
Here’s why using an internal audit report format in Excel works so well for you.
1. Universally Accessible
Everyone in your team, from finance to compliance, can open, edit, and review Excel files. You don’t need complex software or IT support, making collaboration easy across departments and management levels.
2. Flexible and Customizable
You can design your own audit report format, add or remove columns, or include dropdowns for risk ratings (High, Medium, Low). Excel lets you tailor the layout to match your organisation’s audit standards and reporting style.
3. Built for Tracking and Automation
With formulas, pivot tables, and conditional formatting, you can turn your simple audit sheet into a dashboard that tracks open issues, overdue actions, and closure rates.
For example:
- Use conditional formatting to highlight overdue corrective actions
- Apply COUNTIF formulas to calculate open vs closed findings
- Create dynamic charts to visualize risk severity by department
4. Compatible with ERP or GRC Tools
Suppose your organisation already uses ERP or governance systems. In that case, Excel can serve as a bridge, exporting data to or from audit dashboards, making it easier to consolidate all audit activities in one place.
5. Cost-Effective and Easy to Standardize
Unlike paid audit management tools, Excel is free and already available to your team. You can standardize a single audit findings report template across your company, ensuring everyone follows the same structure.
Key Elements of an Internal Audit Report — Excel Format
When you create an internal audit report format in Excel, every section should serve a clear purpose, from documenting what was checked to recording how issues will be fixed. A well-structured format not only makes your findings easy to review but also ensures that your audits remain compliant with IIA, ISO, or SOX standards.
Here’s what your Excel-based report should include.
1. Header & Basic Details
This top section defines the identity of your audit.
It includes:
- Company or department name
- Audit title and reference number
- Names of auditors and reviewers
2. Scope, Objectives & Criteria
Explain what the audit covers and what standards you’re using for evaluation. For example, the audit scope includes procurement and payment cycles, assessed against ISO 9001 and internal control guidelines.
3. Methodology & Approach
Briefly describe how the audit was conducted.
Include details such as:
- Sampling techniques
- Documentation reviewed
- Interviews or walkthroughs
- Control tests performed
4. Findings & Observations
This is the heart of your report — where you list all identified issues.
Columns you can add in Excel:
- Observation/Issue
- Process Area/ Control ID
- Impact/Root Cause
- Supporting Evidence/ Reference Documents
5. Risk Rating/Severity
Classify each finding’s criticality using dropdown menus (High/Medium/Low). You can even apply conditional formatting — red for high risk, yellow for medium, and green for low — to visualize priorities at a glance.
6. Recommendations & Corrective Actions
Provide your suggested fixes for each issue.
Add a column such as:
- Recommended action
- Responsible person
- Target completion date
7. Action Plan Tracker
Once management accepts your recommendations, you can update this tracker to track implementation.
Columns to include:
- Issue reference number
- Assigned owner
- Due date and completion date
- Status (Open, Closed, Overdue)
8. Follow-Up & Verification
After a set period, you’ll need to verify whether corrective actions were practical. Add a column for follow-up notes or verification date to maintain accountability.
9. Sign-Off/Approvals
End your Excel sheet with digital sign-off fields for:
- Internal auditor
- Department Head
- Compliance/Risk Manager
Types of Internal Audit Reports
Not every audit serves the same purpose. The format you choose for your internal audit report in Excel depends on the kind of review you’re conducting, such as financial, operational, compliance, or IT-based. Understanding these types helps your Excel templates capture the correct details for each case.
1. Financial Internal Audit Reports
Not every audit serves the same purpose. The format you choose for your internal audit report in Excel depends on the type of review you’re conducting, such as financial, operational, compliance, or IT-based. Understanding these types helps you customize your Excel templates to capture the correct details for each case.
Example: Account code, control description, test result, variance, and auditor remarks.
2. Operational Audit Report
This format evaluates how efficiently your internal processes run. Its key focus is productivity, resource usage, workflow gaps, and performance indicators.
Example Columns: Process Name, Observation, Root Cause, Recommendation, Responsible Team.
3. Compliance Audit Report
Ideal for organisations subject to specific regulations such as ISO, SOX, or GDPR. Its key is to adhere to laws, internal policies, and regulatory standards.
Example columns: Regulation reference, compliance status, risk level, remarks.
4. IT/Information Security Audit Report
Use this when assessing system security, data access, or backup protocols. Its key focus is cyber security risks, access control, network policies, and data protection.
Example columns: Control ID, Asset/Module, Vulnerability identified, severity, mitigation status.
5. Department-Wise or Risk-Based Audit Report
This structure works well for targeted audits such as HR, procurement, or inventory control. Its key focus is on specific department processes or on high-risk areas identified through prior audits.
Example columns: Department Name, Audit area, Control weakness, action owner status.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Create an Internal Audit Report in Excel
If you want to build your own internal audit report format in Excel, follow this simple sequence. Each step helps you design a structured, functional, and professional-looking audit sheet from scratch.
Step 1: Plan the Workbook Layout

Divide your workbook into three key sheets:
- Finding sheet — record all observations, ratings, and recommendations
- Action tracker — follow up on corrective actions
- Dashboard — summarize results using charts and metrics
Step 2: Create the Findings Table
Set up a clean data table to record your observations.
| Finding ID | Audit Area | Risk Rating | Responsible | Status |
| F-001 | Procurement | High | Purchase manager | Open |
| F-002 | Finance | Medium | Finance Head | In progress |
Step 3: Add Dropdowns for Data Validation
Use Excel’s data validation feature to add dropdown lists for:
- Risk rating: High, Medium, Low
- Status: Open, Closed, Overdue
Step 4: Apply Conditional Formatting
Make your sheet visually clear:
- Highlight high-risk cells in red
- Highlight overdue tasks in yellow
- Mark closed actions in green
Step 5: Use Formulas to Track Progress
Add formulas to calculate progress automatically:
- =COUNTIF (Status, “Closed”) ➞ Total closed findings
- =COUNTIF (Status, “Overdue”) ➞ Pending or overdue items
- =COUNTIF (Risk Rating, “High”) ➞ High-risk issues
Step 6: Link Sheets for Real-Time Tracking
Connect your findings and tracker sheets so updates sync automatically. Use cell references (like = Findings! H5) or L00KUP formulas to pull data into summary tabs.
Step 7: Protect the File
Lock formula and signature cells to avoid accidental edits. Use review ➞ Protect Sheet and set permissions for editors.
Step 8: Create a Dashboard (Optional but Powerful)
Use pivot tables or charts to visualize audit progress.
You can show:
- Total findings by risk level
- % of closed vs pending actions
- Trend of overdue findings
Step 9: Save as a Template
Once finalized, save the workbook as “Internal_Audit_Template.xlsx” so you can reuse it every audit cycle.
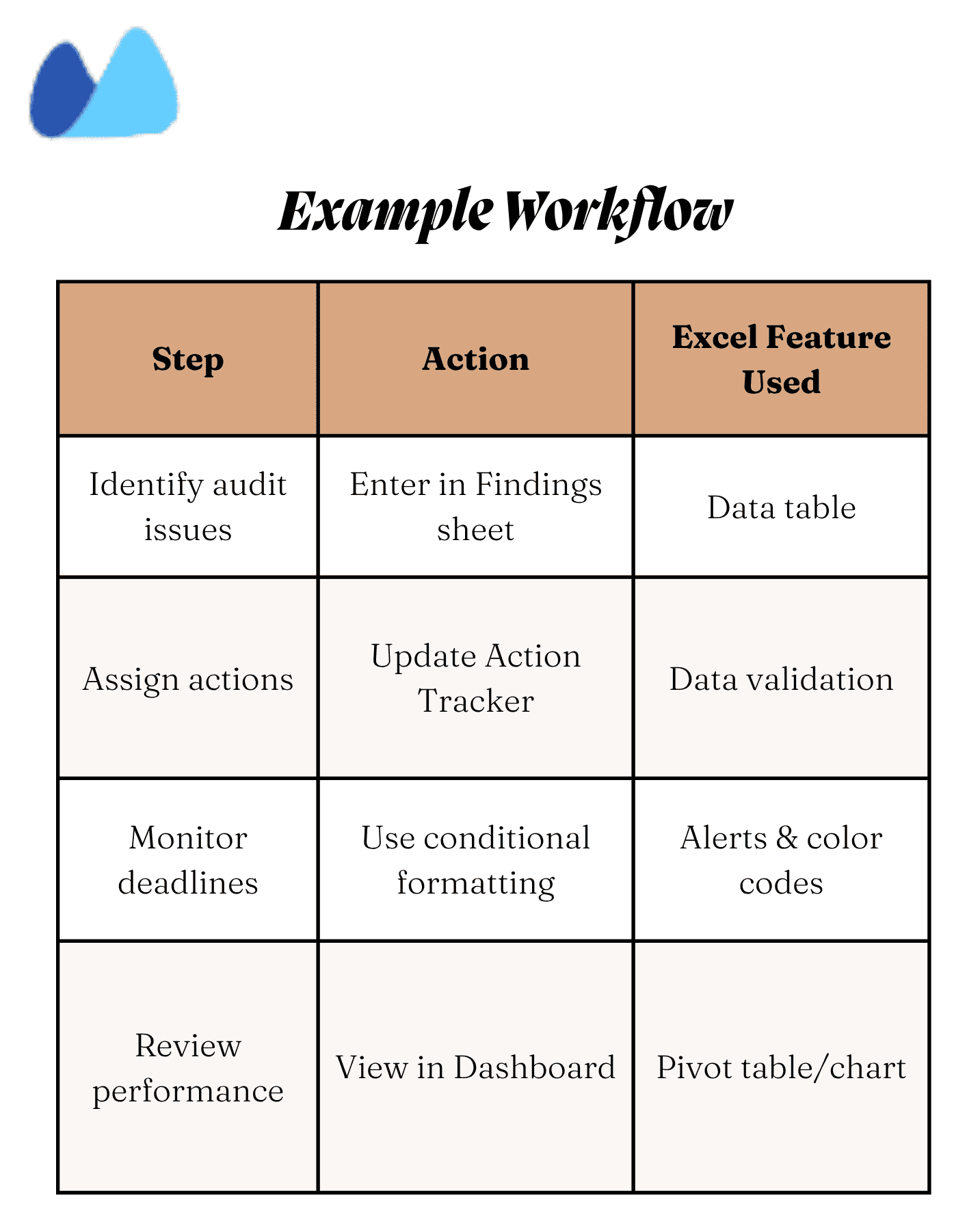
Excel Templates for Internal Audit Reports
You don’t need to start from scratch every time you perform an audit. A ready-to-use internal audit report format in Excel saves you hours of setup and helps you maintain consistency across audits. Below are the key templates you can download or recreate for your organisation.
1. Audit Findings & Recommendations Template
This is your main working sheet, where you list every audit issue, its risk rating, and the corrective action.
It includes:
- Observation/Finding
- Risk rating (High/Medium/Low)
- Recommendation
- Responsible person
- Status (Open/closed/overdue)
➡️ Ideal for auditors documenting multiple departments in a single report.
2. Risk-Based Internal Audit Report Template
If your audit follows a risk-based approach, this format helps you prioritize the areas that matter most.
Use it for: Highlighting controls or processes with the highest risk exposure.
It includes:
- Risk category (Financial, Operational, IT)
- Impact and Likelihood ratings
- Current controls
- Residual Risk score
➡️ Use color-coded cells or conditional formatting to flag high-risk areas visually.
3. Compliance Checklist in Excel
A must-have for audits aligned with standards like ISO 9001, SOX, or GDPR.
Use it for: Verifying compliance with policies, laws, or internal procedures.
It includes:
- Regulation Reference/Clause Number
- Compliance Status (Yes/No/Partial)
- Remarks/Evidence
✅ You can reuse this checklist for different audits by changing the standard reference.
4. Audit Action Plan Tracker Template
Turn your findings into measurable progress.
Use it for: Tracking corrective and preventive actions (CAPA)
It Includes:
- Finding reference ID
- Responsible person
- Target completion date
- Current status
- Current status
- Follow-up notes
📊 Link this sheet with your findings table using VLOOKUP or cell references to keep both in sync.
5. Summary Dashboard (Advanced)
For visual reporting, use charts and pivot tables to summarize all your audit data.
Use it for: Monthly or quarterly review meetings
It includes:
- Total findings by risk level
- % of actions closed vs pending
- Department-wise summary
📉 This sheet makes your Excel report presentation-ready without needing PowerPoint.
Best Practices for Using Excel-Based Audit Reports
Creating an internal audit report format in Excel is only the first step; using it effectively is what ensures accuracy, accountability, and compliance. When your report structure is standardized, you make it easier for your team and management to track progress and maintain transparency across every audit cycle.
Here are a few best practices to help you get the most out of your Excel audit reports.
1. Standardize the Format across Teams
Use one internal audit report template in Excel across all departments. This ensures everyone follows the same reporting structure, risk rating scale, and terminology, making cross-audit comparison more straightforward.
2. Maintain Version Control
Always save new audit reports with version numbers (example, Audit_Report_Q1_v2.0.xlsx). This prevents confusion between drafts and finalized reports, especially when multiple auditors collaborate on the same file.
3. Align with Global Audit Standards
Follow frameworks such as IIA guidelines or ISO 19011 to ensure your findings, ratings, and recommendations meet professional audit requirements. Add references to these standards in your Excel template to strengthen credibility.
4. Protect Sensitive Information
Your audit reports often contain confidential data. Use password protection and restrict editing access for specific sheets or cells. This keeps formulas, dashboards, and signatures safe from accidental edits or unauthorized changes.
5. Automate Follow-Ups
Set reminders or use Excel formulas to flag overdue actions automatically. For example: Conditional formatting that turns cells red when the due date is past.
6. Integrate Excel with ERP or Governance Systems
If you use ERP, CRM, or compliance tools, connect your Excel tracker to them through imports or pivot dashboards. This ensures real-time updates and centralizes all governance-related data.
7. Review and Update Regularly
Audit templates aren’t static. Review your Excel audit report format at least once a year to add new regulatory fields, update risk parameters, or enhance dashboard logic based on your company’s evolving needs.
Download Free Internal Audit Report Templates
Here are the downloadable formats you can use right away.
📘 Internal Audit Findings Sheet
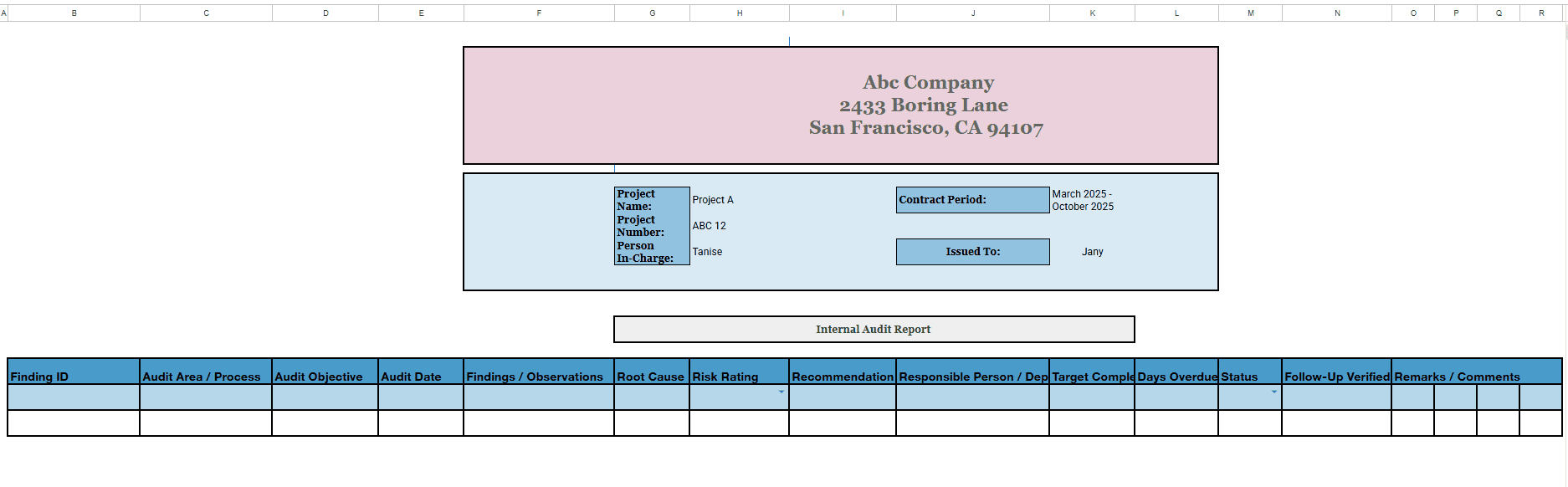
Use this sheet to document every observation, assign a risk level, and capture recommendations.
It includes:
- Finding ID and Audit area
- Observation/Issue
- Risk rating (High/Medium/Low)
- Recommendation & Responsible person
- Status tracker
📒 Summary Dashboard Template
Turn your audit workbook into a quick-view dashboard for management reviews.
It includes:
- Total findings by risk level
- % of action closed
Check the ‘Dashboard’ Sheet to explore its possibilities.
📖 Recommended Reads
- Daily Maintenance Report Format In Excel — Learn how to structure maintenance logs, track daily tasks, and manage issue reporting using an Excel-ready template
- Fixed Asset Register Format In Excel — A complete guide to recording, tracking, and auditing a company’s assets using clean, audit-ready Excel templates
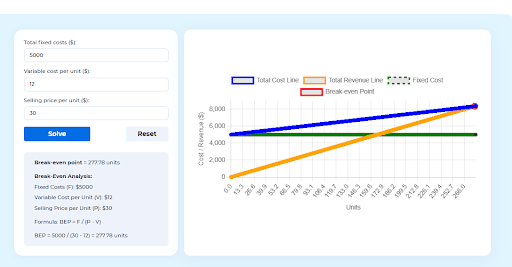
🚀 Turn Audit Insights Into Action — Calculate Your Break-Even Instantly
Make smarter cost decisions with Kladana’s free break-even calculator
Frequently Asked Questions on Internal Audit Report Format in Excel
What is included in an internal audit report format?
An internal audit report format in Excel includes key sections such as audit title, scope, objectives, methodology, findings, risk rating, recommendations, and an action plan tracker. It summarizes what was reviewed, what issues were found, and how management plans to address them.
Can Excel be used to create audit dashboards?
Yes. You can use Excel pivot tables, charts, and conditional formatting to create visual dashboards that show open findings, high-risk issues, and closure rates. It’s easy to present results to management without external software.
How do I track audit findings and actions in Excel?
Maintain a separate Audit action plan tracker sheet that links each finding to a responsible person and due date. Conditional formatting automatically colors overdue tasks and completed actions.
What are the limitations of using Excel for audits?
While Excel is flexible and cost-effective, it lacks multi-user, real-time collaboration and audit-trail controls. To overcome this, you can link Excel with your company’s ERP or document management system for secure version control.
How do I maintain confidentiality in my Excel audit report?
Use password protection and limit access to authorized users only. You can also lock specific cells or sheets, such as formulas and sign-off areas, to prevent unauthorized edits.
How can I automate my internal audit report?
Use Excel’s built-in features such as formulas, COUNTIF, and conditional formatting. For advanced automation, consider linking your Excel sheets to Power BI or using macros to create instant visual dashboards.
Can I use the same format for ISO or internal quality audits?
Yes. The internal audit report template in Excel is flexible and can be adapted for ISO 9001, ISO 27001, or internal quality audits by simply updating the compliance checklist section.
How often should I update my audit report?
You should update your Excel audit tracker every time an action item’s status changes. At a minimum, review and finalize the report at the end of every audit cycle or follow-up phase.
What’s the difference between internal and external audit reports?
An internal audit report is used within your organisation to improve controls and operations, while an external audit report is conducted by independent auditors for regulatory or financial validation purposes.
How do I share Excel audit reports with management?
Save your Excel file as a PDF summary or export your dashboard charts for presentations. You can also use cloud storage, such as OneDrive or Google Drive, to provide controlled access to management teams.
Read‑alikes
4 Free Purchase Order Templates with a Step‑By‑Step Guide: Excel, Word, and Google Sheets Format
Invoice Templates for Excel: Free Downloads, Formats & When to Use Them
Free Labour Contractor Bill Format in Excel: Templates and How to Create Yours
Fixed Assets Register Format in Excel: Free Templates & Complete Guide