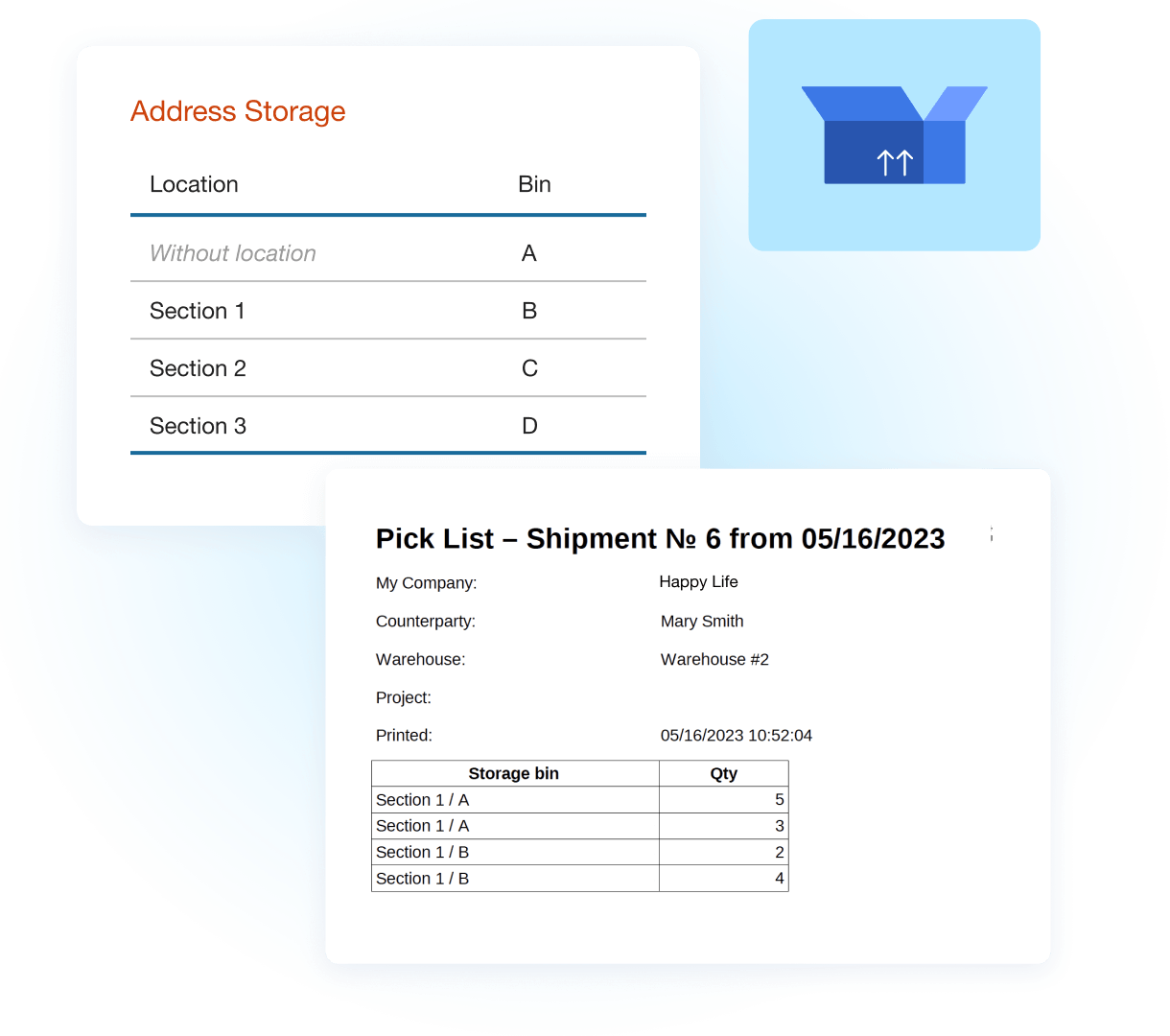
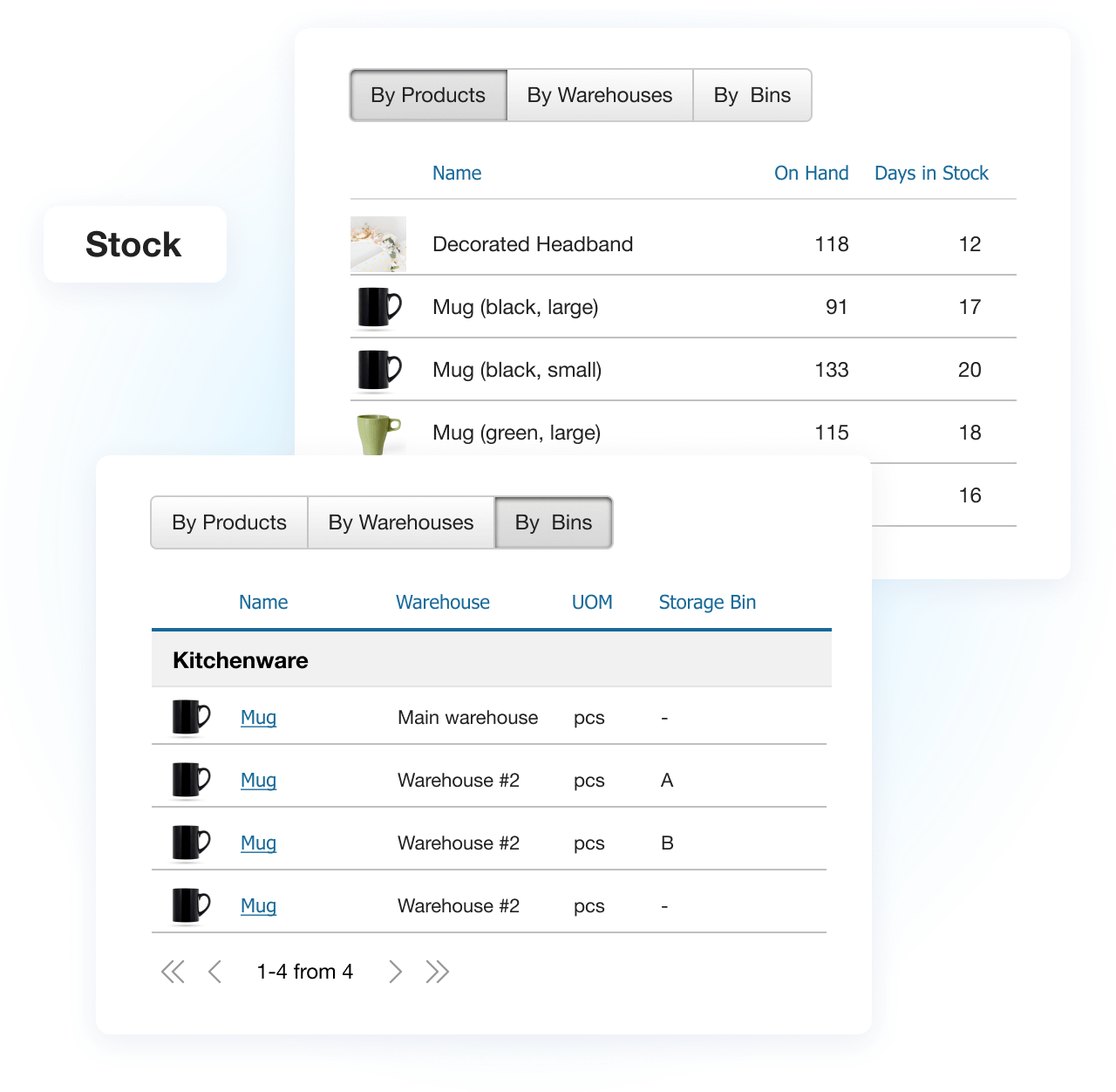
If your warehouse holds inventory, it holds potential. The question is — how well is that potential organized, traceable, and aligned with your operations? Warehouse inventory management goes beyond knowing what’s in stock. It’s about pinpointing where each item is stored, how quickly it moves, how it ties into purchase and sales orders, and how fast you can fulfill demand.
When these components — stock, storage, orders, and tracking — are disconnected, inefficiencies creep in. When they’re integrated, your operations accelerate: from receiving to picking to reordering. This visibility prevents common supply chain issues like missed replenishments, delayed deliveries, or mismatched online inventory.
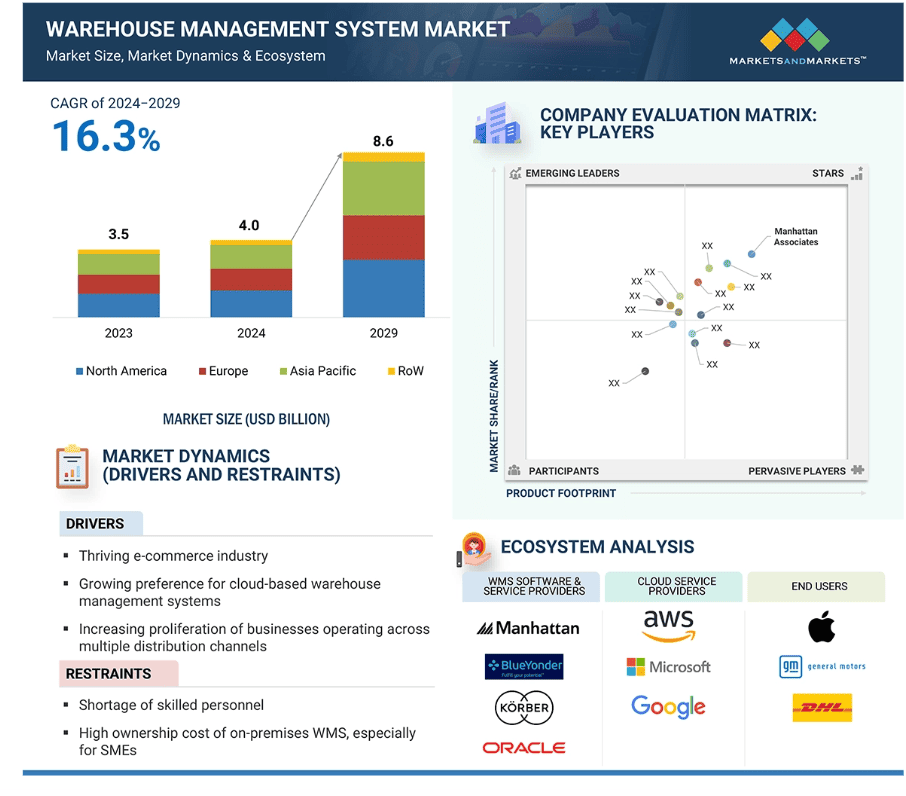
It’s no surprise the global Warehouse Management System (WMS) market — valued at $4 billion in 2024 — is projected to more than double to $8.1 billion by 2028 (MarketsandMarkets).
In this guide, you’ll learn how to manage warehouse inventory more efficiently. We’ll cover essential systems, automation tools, and real-world strategies to track and control your stock
- What Is Warehouse Inventory Management?
- How to Manage Warehouse Inventory Effectively
- Warehouse Inventory Management Systems
- Key Features of Warehouse Inventory Management
- Integration with ERP and Supply Chain Software
- Best Practices for Warehouse Inventory Management
- Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
- Warehouse and Inventory Management Technologies
- Benefits of Optimized Warehouse Inventory Management
- To Sum Up
- Frequently Asked Questions On Warehouse Inventory Management
- List of Resources
What Is Warehouse Inventory Management?
When managing inventory, most businesses focus on numbers — units in stock, reorder points, and sales. But warehouse inventory management adds another layer. It’s not only about what you have, but also where it is and how efficiently it moves through your system.
Warehouse inventory management refers to the processes, systems, and tools used to control inventory within a warehouse. It ensures that incoming stock is properly received, organized, stored, and easily accessible. It connects accurate inventory tracking with physical layout, staffing, barcode labeling, and digital tools like warehouse inventory systems.
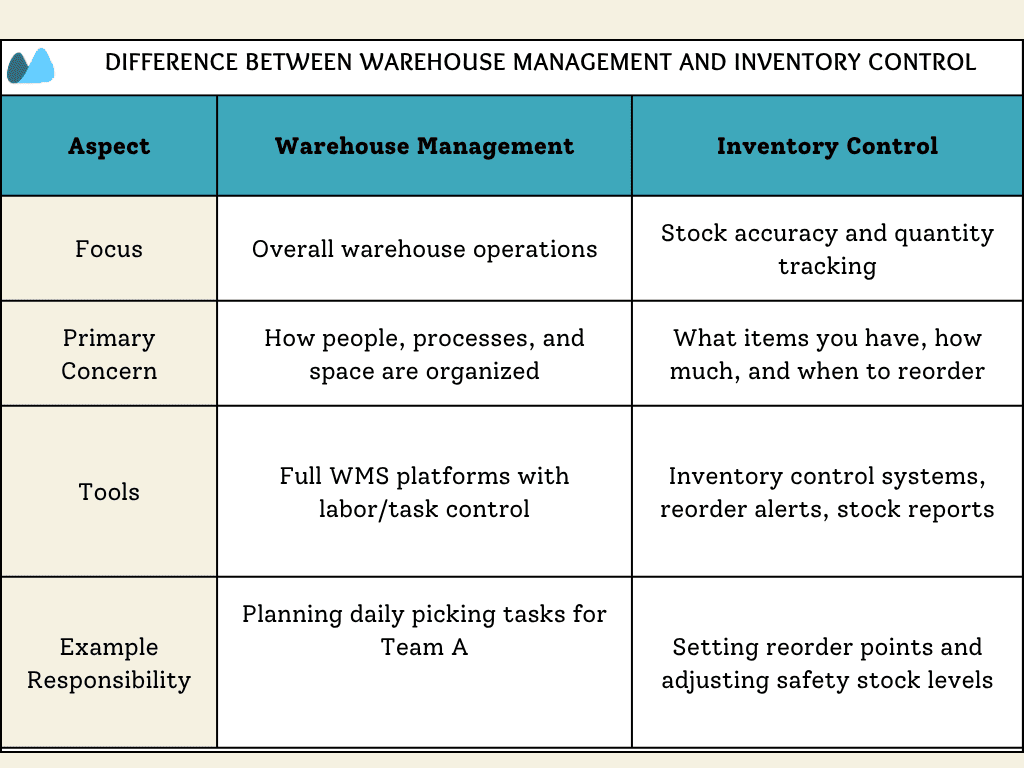
In short, it’s about syncing physical inventory movement with digital accuracy — optimizing space, reducing handling time, and streamlining fulfillment from receiving to dispatch. The table below explains how warehouse management and inventory control differ — and how they complement each other.
How to Manage Warehouse Inventory Effectively
Receiving goods into your warehouse is only the first step. The real challenge lies in managing day-to-day operations with accuracy and efficiency — without constant firefighting. Here’s a step-by-step approach to take control of your warehouse inventory management.
1. Accurate Stock Counting
You can’t manage what you don’t measure. Inaccurate stock levels affect reordering, fulfillment, and customer satisfaction. Use these two approaches to keep counts precise.
Cycle Counting
Break inventory into smaller groups and count specific SKUs on a rolling basis — daily, weekly, or monthly. This approach minimizes disruptions and flags issues early.
📌 Example: High-value or fast-moving SKUs = weekly; low-priority SKUs = quarterly.
Full Physical Counts
This is a complete stocktake, often done quarterly or annually. It’s time-consuming and may require downtime but provides a fresh baseline.
📍 Want to go deeper? Check out our full guide on how and when to count inventory effectively.
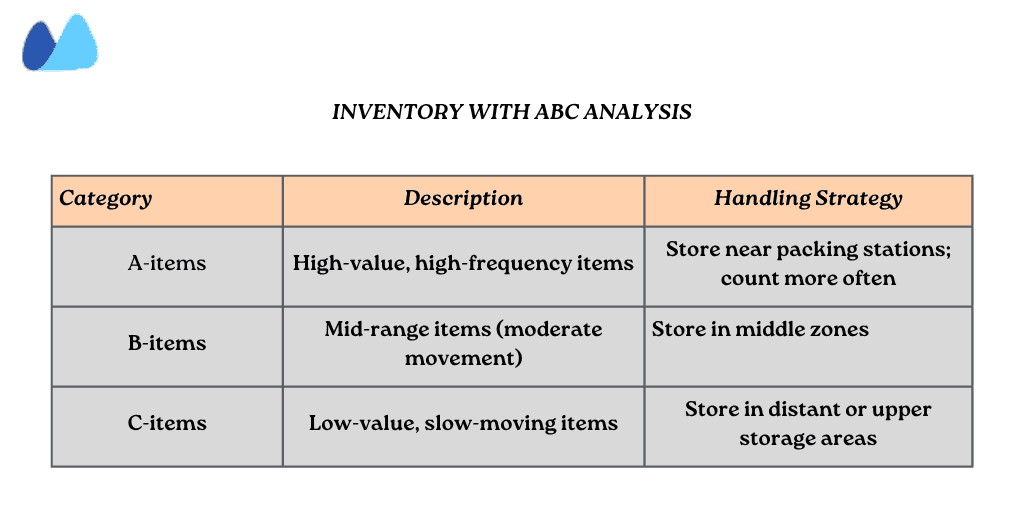
2. Classify Inventory with ABC Analysis
Not all items are created equal. ABC analysis helps you segment inventory by value and velocity, so you can manage and store it more strategically.
How ABC analysis works:
- A items: High-value, low-quantity — frequent review
- B items: Moderate value and frequency
- C items: Low value — bulk stock
📌 Pro tip: Apply these categories to physical zones in your warehouse to speed up picking and reduce travel time.
3. Implement Barcodes or RFID for Real-Time Tracking
Manual tracking is prone to errors, delays, and blind spots. Barcode and RFID systems help you monitor stock movement — from receiving to picking — in real time.
Barcode Labels
- Scan individual SKUs using handheld devices
- Cost-effective and widely compatible with inventory software
RFID Tags
- Scan multiple items at once, even without line of sight
- Ideal for large-volume or security-sensitive warehouses (but more expensive)
4. Define Storage Zones and Bin Locations
If staff constantly zigzag through aisles to locate items, your layout needs work. Create logical zones and assign bin locations to every shelf and rack. It improves space usage and speeds up picks.
Example layout:
- Zone A: Fast-moving SKUs (near shipping dock)
- Zone B: Bulky or seasonal stock
- Zone C: Overstock and returns
✅ Pair each bin with a barcode ID in your inventory system — for faster access and fewer errors.
5. Standardize Receiving and Put-Away Processes
Inventory mistakes often start at receiving. To avoid mismatches and delays:
- Scan goods upon arrival
- Match items against purchase orders
- Assign bin locations before shelving
- Label all cartons or items immediately
Warehouse Inventory Management Systems
A warehouse inventory management system (WMS) is software designed to control and optimize inventory movement inside your warehouse — from receiving and storing to picking, packing, and shipping.
But not all systems are created equal. Some WMS solutions focus solely on inventory control, while others integrate with your ERP, ecommerce channels, and logistics partners to create a seamless, end-to-end supply chain.
What does a WMS do?
A good WMS tracks every touchpoint — from scanning items at the dock to completing outbound shipments — so you always know:
- What’s in stock and where it’s located
- What’s reserved for pending orders
- What’s moving, how fast, and what’s stagnant
- What needs reordering and when
📍 Recommended Read: 20 Best Warehouse Management Systems (WMS)
Key Features of Warehouse Inventory Management
Here are the most critical WMS features and why they matter for growing businesses.
| Feature | What It Does | Why It Matters |
Real-time inventory |
Updates stock levels instantly as items are scanned |
Prevents overselling and ensures accurate stock visibility |
Order routing |
Sends pick/pack tasks to the right zone or team member |
Speeds up fulfillment and reduces handling errors |
Barcode scanning support |
Works with handheld devices or mobile apps |
Automates receiving, counting, and picking |
Stock level alerts |
Sends notifications for low or excess inventory |
Avoids stockouts or overstocking |
Bin location management |
Assigns SKUs to specific shelves or pallet spaces |
Reduces pick time and improves accuracy |
ERP integration |
Syncs with procurement, sales, and accounting |
Enables cross-team visibility and faster decision-making |
Multi-warehouse control |
Manages inventory across several locations |
Supports business scaling without losing control |
Reporting and analytics |
Analyzes SKU turnover, space usage, and operational KPIs |
Empowers data-driven inventory and warehouse planning |
Integration with ERP and Supply Chain Software
One of the biggest advantages of modern warehouse inventory management systems is their ability to seamlessly connect with your broader business tools. Instead of functioning in isolation, your warehouse becomes part of a fully integrated ecosystem that spans sales, purchasing, accounting, logistics, and planning.
According to Accenture, warehouse automation delivers full value only when it’s part of an integrated plan — one that accounts for warehouse complexity, calculates ROI, and connects systems like WMS and ERP into a human-machine workflow.
This means choosing tools that not only manage warehouse stock, but also enhance supply chain visibility and support real-time decision-making.
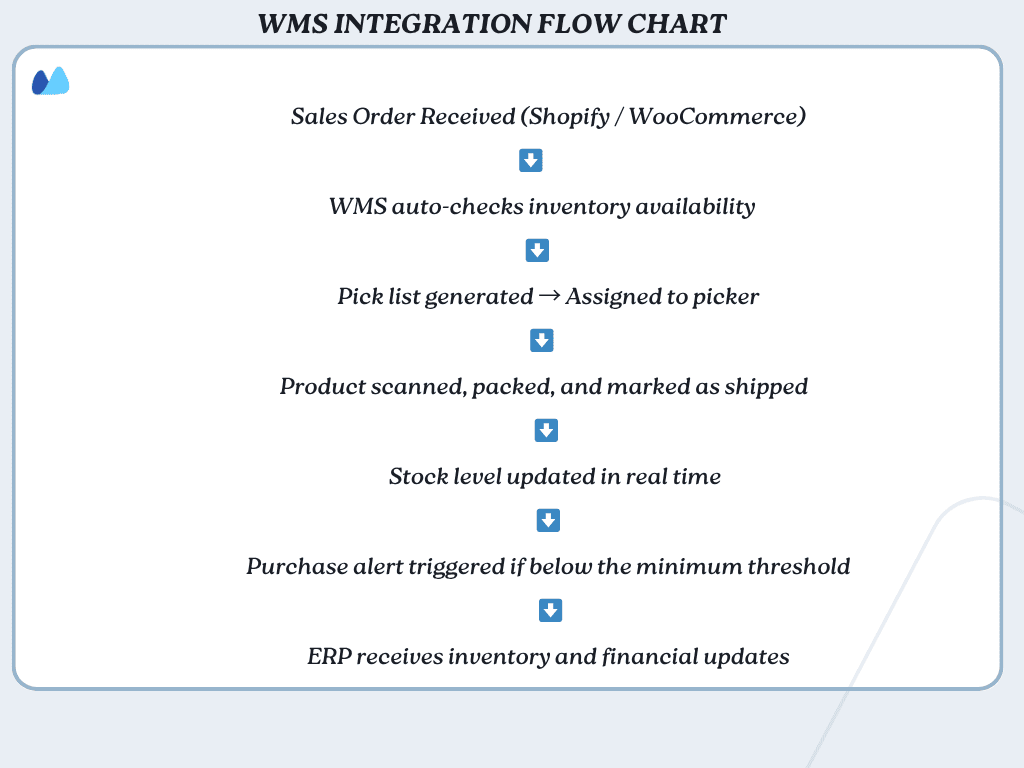
When your WMS is integrated with an ERP system, it enables:
- Real-time inventory sync for sales orders — so available stock is always accurate and reservations update automatically
- Smart procurement triggers — low stock levels can auto-generate purchase orders or supplier alerts
- Finance automation — Cost of goods sold (COGS), stock value, and fulfillment costs are reflected instantly in your accounts
📍 Real-world case study: Neytthomes, a premium carpet manufacturer, reduced fulfillment delays and stock mismatches by integrating Kladana ERP with their warehouse operations. The result? Full visibility across raw materials and finished goods, faster order processing, and better production planning.
WMS integration doesn’t stop at ERP. A warehouse inventory management system can also connect with:
🛒 E-commerce platforms (Shopify, WooCommerce )
🚚 Transportation Management Systems (TMS Management Systems (TMS)
📦 B2B order portals and vendor marketplaces
📈 Demand forecasting and inventory planning tools
The real power of warehouse and inventory management lies in integration. It’s what turns a basic WMS into a strategic hub for your entire business.
Best Practices for Warehouse Inventory Management
Once your inventory system is in place, the next step is ensuring consistent execution. Well-defined warehouse inventory management practices help reduce human error, avoid stockouts, and maintain smooth operations — even as order volumes grow.
Here are three foundational practices to follow.
1. Automate Your Reordering Process
Manual stock checks are slow, error-prone, and inefficient. Instead, set reorder points in your warehouse inventory management system for each SKU. Once stock falls below your set minimum, the system should:
- Automatically generate a purchase request
- Notify the procurement team
- Or trigger an auto-reorder from a preferred supplier
📌 Example: You set the reorder point for packing tape at 50 units and the maximum at 200. When inventory hits 49, the system notifies your buyer — helping maintain optimal stock without overordering.
2. Schedule Regular Inventory Audits
Even with barcode scanning and real-time dashboards, inventory errors can creep in due to:
- Mislabeling
- Staff mistakes
- Lost or unrecorded movements
- Theft or shrinkage
To catch discrepancies early, schedule two types of inventory audits:
- Cycle counts: Targeted, frequent checks of priority SKUs
- Full stock takes: Done quarterly or annually for total accuracy
3. Train Your Team on Inventory SOPs
The best warehouse software won’t deliver results if your team doesn’t follow standard operating procedures (SOPs). Train all warehouse staff — from receiving to dispatch — on:
- How to scan and label items
- Where and how to store goods by bin location
- How to handle misplacements or mismatches
- What to do when exceptions arise
A well-trained team is your frontline defense against inventory chaos.
Common Challenges in Warehouse Inventory Management — and How to Solve Them
Even with a strong layout and basic systems, warehouse operations can easily spiral into disorder. If you’re frequently dealing with delays, missing items, or mismatched data, you’re not alone. Below are the most common warehouse inventory management challenges — and how to fix them.
1. Stock Discrepancies
The Problem: Your system shows 35 units, but the shelf has 40— or worse, none.
| Why It Happens | The Fix |
|
|
2. Overstocking and Dead Inventory
The Problem: You’re drowning in unsold items while fast-movers go out of stock.
| Why It Happens | The Fix |
|
|
3. Inefficient Space Utilization
The Problem: You’re out of space — not because of growth, but due to poor layout and storage logic.
| Why It Happens | The Fix |
|
|
4. Manual Data Entry and Disconnected Systems
The Problem: Data lives in silos — sales uses one system, warehouse another, and finance relies on spreadsheets.
| Why It Happens | The Fix |
|
|
Warehouse and Inventory Management Technologies
Modern warehouse operations rely on digital tools and connected technologies to track inventory movement, enhance accuracy, and respond in real-time. While you don’t need to implement everything at once, knowing your options helps you prioritize what’s most valuable for your business.
Here are the essential technologies that bring visibility, speed, and control to warehouse inventory management.
1. Barcode and RFID Systems
Scanning tools form the foundation of accurate inventory tracking.
| Tool | Use Case | Best for |
Barcode |
Scanning tools form the foundation of accurate inventory tracking |
Most SMEs warehouses |
RFID |
Bulk scanning pallets or high-value goods remotely |
Fast-moving or high-security items |
📌 Tip: Pair barcode scanning with bin location mapping for real-time visibility down to the shelf.
2. IoT Sensors and Smart Monitoring
Internet of Things (IoT) devices help monitor environmental conditions and asset movement without manual input. Use cases include:
- Temperature/humidity sensors for food, pharma, or electronics
- Motion detectors for security and theft prevention
- Smart shelf sensors that detect stock depletion based on weight
📍Tip: Connect your IoT system to your WMS to trigger alerts and automated workflows.
3. Mobile Inventory Apps and Handheld Devices
Equipping staff with mobile tools allows them to:
- Scan and update stock from anywhere on the floor
- Access pick lists, bin locations, and task assignments
- Adjust inventory without returning to a desktop
This mobility improves speed and reduces bottlenecks during receiving, picking, and restocking.
4. Real-Time Dashboards and Reporting Tools
A modern warehouse inventory system should offer visual dashboards and reports that show:
- Live stock levels across bins and warehouses
- Order and fulfillment status by shift or team
- Stockouts, returns, and high-risk trends
- SKU performance, space utilization, and turnover rates
📌 Tip: Real-time data helps managers react to issues before they become problems.
5. Software Integrations to Keep Everything in Sync
Even the best technology falls short if it’s siloed. Your WMS should integrate with:
- E-commerce: Shopify, WooCommerce, Magento, Ecwid
- Accounting: QuickBooks, Tally, Xero, FreshBooks
- ERP tools: Procurement, financials, sales, and production tracking
These integrations ensure consistent data across the supply chain and eliminate double entry or communication gaps.
📍 Recommended Read: WMS for Shopify: What to Know Before Choosing a Warehouse Management System
Benefits of Optimized Warehouse Inventory Management
An optimized warehouse isn’t just more organized — it drives measurable business value. Here’s what streamlined inventory control unlocks.
1. Faster and More Reliable Fulfillment
When you always know what’s in stock, where it’s located, and what’s ready to ship, your fulfillment process becomes faster and more predictable:
- SKUs are stored by zones and bin locations, making picks faster
- Barcode scanning reduces picking and packing errors
- You can confidently offer same-day or next-day delivery without bottlenecks
2. Lower Inventory Carrying Costs
Excess stock ties up cash and occupies valuable space. With optimized inventory planning, you:
- Set reorder points to avoid overstocking
- Improve inventory turnover by focusing on demand-driven SKUs
- Reduce warehousing costs by avoiding underused storage or third-party overflow
3. Improved Customer Satisfaction
Accurate inventory data and fast, error-free fulfillment enhance the customer experience:
- Real-time visibility ensures accurate delivery timelines
- Faster processing minimizes delays and missed SLAs
- Fewer mistakes reduce returns and support issues
To Sum Up
You don’t need a massive warehouse or a large team to run a well-oiled operation. What you need is visibility, structure, and scalable tools.
From barcode scanning and bin location tracking to implementing a warehouse inventory management system that syncs with your ERP — every step brings you closer to operational clarity.
When your warehouse is optimized, decisions become faster, fulfillment more reliable, and your costs drop. You ship faster, waste less, and deliver a better customer experience — every time.
Ready to Run a Smarter Warehouse?
Track every item by bin, cut fulfillment delays, and stay in control as you grow — all in one system
Frequently Asked Questions On Warehouse Inventory Management
Looking for quick answers? Here are the most common questions about how to manage inventory in a warehouse and how modern systems help streamline the process.
What is warehouse inventory management?
Warehouse inventory management refers to the systems and processes used to track, control, and organize inventory within a warehouse. It ensures every item is accounted for from receiving to picking to shipping.
How is warehouse inventory management different from warehouse management?
Warehouse inventory management focuses on tracking product quantities and locations. Warehouse management covers broader operations like staffing, layout planning, equipment use, and warehouse workflow optimization.
How can I Improve Inventory accuracy in my warehouse?
Use cycle counting, barcode or RFID scanning, fixed bin locations, and a real-time inventory system. These strategies reduce errors and keep stock records reliable.
What is the difference between WMS and ERP?
A WMS (Warehouse Management System) handles stock movement, picking, and storage. An ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning system) covers end-to-end business processes — from finance and procurement to sales and production. Integration ensures both work together seamlessly.
Why is warehouse inventory management important in a supply chain?
It provides visibility into stock levels and locations, reduces errors, and helps prevent fulfillment delays. This keeps the entire supply chain running smoothly.
What’s the difference between cycle counting and full physical inventory counts?
Cycle counting checks selected SKUs regularly (e.g., daily or weekly), while full counts audit all items at once. Cycle counting avoids downtime and catches errors early.
What are the biggest challenges in managing warehouse inventory?
Common challenges include stock discrepancies, misplaced items, overstocking, manual data entry errors, and lack of real-time tracking — all of which impact speed, accuracy, and customer satisfaction.
How do I choose the right warehouse inventory system?
Consider your warehouse size, SKU complexity, and order volume. Look for software that supports barcode scanning, real-time updates, and integrations with your ERP or ecommerce platform.
Can warehouse inventory management help reduce costs?
Yes. It reduces stock waste, lowers carrying costs, improves space utilization, and cuts labor hours spent searching or correcting errors.
What are common Inventory KPIs?
Key warehouse inventory KPIs include:
- Inventory accuracy rate
- Order picking accuracy
- Inventory turnover ratio
- Carrying cost of inventory
- Rate of stockouts or backorders
List of Resources
- Marketsandmarkets: Warehouse Management Market Report
- Accenture Report: Warehouse Automation
Read‑alikes
Warehouse Management System in the UAE: A Practical Guide for Growing Businesses
20 Best Warehouse Management Systems (WMS): 2026 Update
What Is Lead Time in Inventory Management? Meaning, Formula, and Optimization Tips
ERP for Manufacturing Industry in South Africa: Boost Your Profits & Production Control
Top ERP Software in South Africa for 2026: Comprehensive Guide, Solutions, Pricing & Business Impact