If you’ve ever closed a sale but had to chase the money weeks later, you know exactly why the accounts receivable process matters. It’s the bridge between your revenue on paper and actual cash in the bank. The smoother this process, the faster your team gets paid.
For small businesses, the gap between invoicing and payment is costly. On average, nearly 18% of total revenue is locked up in accounts receivable at any time.
The typical AR cycle runs anywhere from 30 to 90 days, depending on industry norms and customer terms. Multiply that delay across dozens or hundreds of transactions, and your cash flow begins to feel the strain.
So, it gets important to know how the AR cycle works, where it breaks, and how to fix it. We’ll break it down here.
What Is the Accounts Receivable Process?
Accounts receivable (AR) refers to money owed to your business by customers after a credit-based sale. The accounts receivable process tracks how your business bills customers and collects payment after delivering a product or service.
The process helps:
- Keep cash flowing into your business
- Spot payment delays early
- Maintain clean books for reporting
AR vs AP: Quick Comparison
Accounts Receivable (AR) and Accounts Payable (AP) are two sides of your company’s financial operations. AR deals with the money coming in from customers, while AP handles money going out to suppliers.
Balance requires balancing, but they serve different functions and are managed by different teams.
| Feature | Accounts Receivable (AR) | Accounts Payable (AP) |
What is it? |
Money owed to your business |
Money your business owes |
Direction |
Incoming funds |
Outgoing funds |
Managed by |
Sales/Finance/AR teams |
Procurement/Accounts team |
Goal |
Get paid faster |
Pay on time without cash strain |
Cash flow impact |
Improves liquidity when collected on time |
Controls expenses and preserves vendor relationships |
Tracking tools |
Aging reports, DSO, invoice status dashboards |
Payables calendar, approval workflows, vendor portals |
Process starts with |
Customer sale or service delivery |
Supplier invoice or purchase order |
Risks if mismanaged |
Delayed cash flow, customer disputes, bad debt |
Missed due dates, late fees, strained vendor ties |
How Kladana Facilitates Your Accounts Receivable Process
✅ Quick Invoice Generation from Sales Orders — Convert confirmed sales or delivery notes into GST-ready invoices in just a few clicks, reducing lag between sale and billing.
✅ Payment Tracking Linked to Customer Accounts — Monitor incoming payments by customer, invoice, or due date so your team always knows what’s pending, collected, or overdue.
✅ Aging Reports & DSO Dashboards — Get real-time visibility into your outstanding receivables, broken down by customer or time bucket, to act before cash flow takes a hit.
✅ Excel Templates for Credit Follow-Ups — Download ready-to-use templates for payment tracking, collection calls, or credit control reviews to keep things moving.
✅ Bank Reconciliation to Close the Loop — Match received payments with invoices using references or amounts and mark them as settled—keeping your financials clean and audit-ready.
✅ Multi-User Access with Defined Roles — Let your finance, sales, and support teams collaborate on collections and follow-ups with shared visibility and role-based access.
The Full Accounts Receivable Cycle (with Flowchart)
The accounts receivable cycle covers the journey from a customer order to final payment reconciliation. Every step, from delivery to reminders and bank matching, must work without delays.
You’ll typically calculate Days Sales Outstanding (DSO) at the end of each month or quarter to monitor how healthy your AR cycle is.
DSO = (Accounts Receivable / Total Credit Sales) x Number of Days

With the AR process, you enable the:
- Cash flow forecasting
- AR performance benchmarking
- Evaluating client credit risk
- Setting team or software automation targets
An entire AR flowchart looks like this:
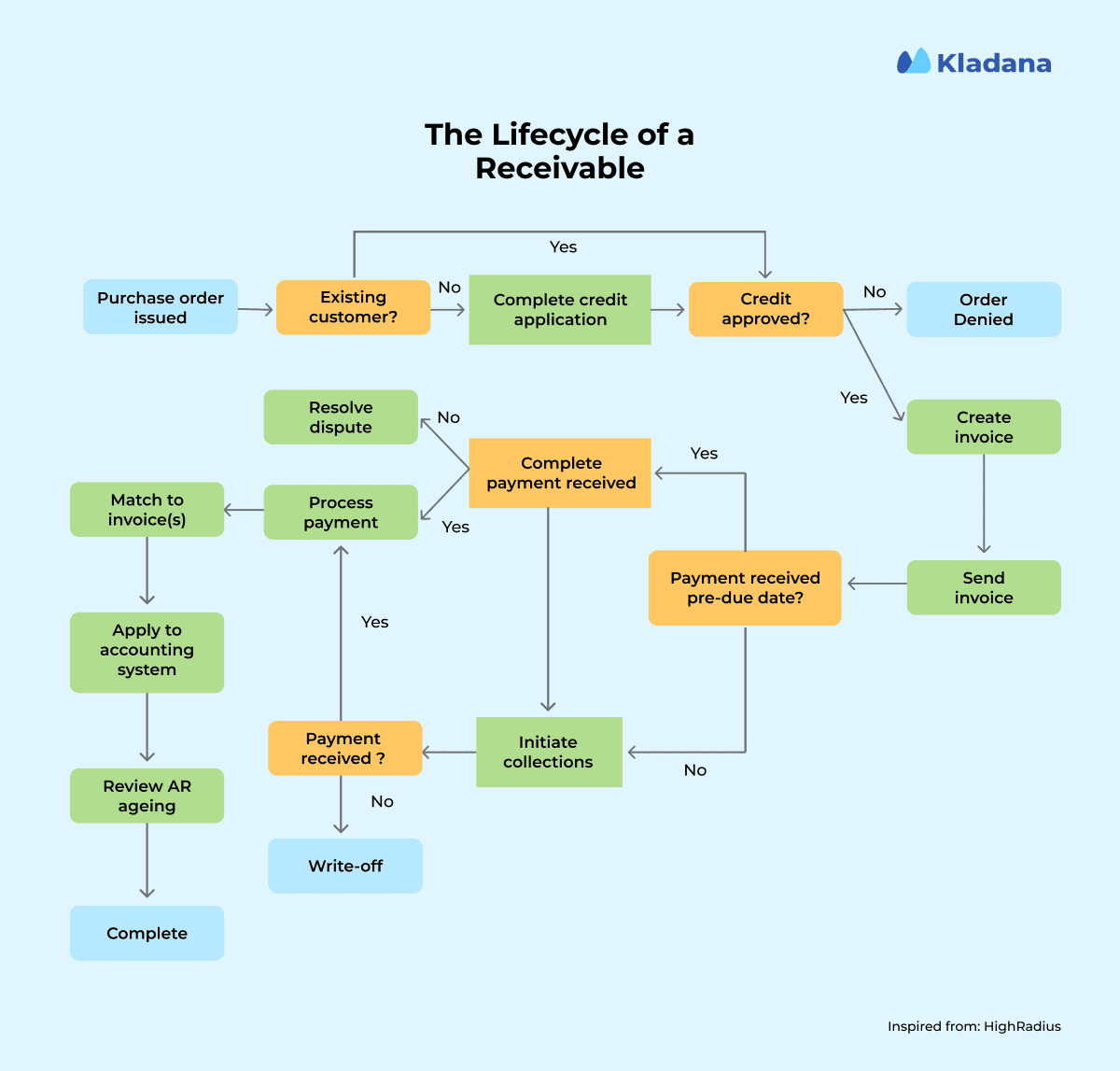
Majorly, it’ll have the following actions.
Customer places order
A formal sales order or signed agreement is received. It triggers the billing, typically including quantity, pricing, delivery timelines, and payment terms.
Invoice is generated
Based on the approved order or delivery confirmation, an invoice is prepared. Key fields include customer details, unique invoice number, line items, taxes, due date, and payment instructions.
Invoice is delivered to customer
Delays in sending invoices delay payments. Depending on the customer’s preference, this may be via email, an online portal, or integrated EDI. Some clients won’t pay until they receive an official PO match.
Tracking Payments
Once the invoice is out, the clock starts ticking. Payment terms (such as Net-15 or Net-30) need to be tracked within your AR dashboard. Some businesses set up escalation workflows (friendly reminder → formal follow-up → collections).
Follow-ups/reminders sent
AR teams (or systems) must proactively nudge clients. A common best practice: send a reminder 5 days before the due date, again on the due date, and escalate after 7 days late.
Payment is received
Through bank transfer, credit card, or payment gateway. Reconciliation begins here.
Bank is reconciled & ledger updated
The final step: link received payments with open invoices. Tools can auto-match using references or payment IDs. Once cleared, the invoice is closed, and financial reports are updated in real-time. This ensures aging reports and DSO metrics stay accurate.
Common AR Documents
With cleaner, factual documentations, you can reduce confusion, speed up reconciliation, and make audit trails more powerful. These are the core documents used during the AR cycle:
Invoice
The main billing document is sent to the customer. It lists products/services, amounts due, tax, and payment instructions.
Credit memo
Issued when you need to reduce the amount a customer owes, often due to product returns, discounts, or overcharges.
Debit memo
Sent to increase the amount owed, usually for underbilled items or additional fees post-sale.
Receipt
Proof of payment received — partial or full. It’s issued to acknowledge that the money has been credited to your account.
Statement of account
A summary of outstanding invoices and payments for a given customer over a defined period.
Remittance advice
Sent by the customer, this outlines which invoices are being paid and in what amounts — crucial for matching bulk payments.
🧮 See When Your Accounts Receivable Costs Become Profitable
Tired of wondering how AR delays are affecting your bottom line? Use Kladana’s Free Break-Even Point Calculator:
- Plug in fixed & variable costs, selling price, and current receivables
- Instantly see the break-even revenue and units needed
- Model different scenarios: delayed payments, discounts, cost spikes
- Make better decisions around invoicing policies, credit terms, or customer contracts
Steps in the Accounts Receivable Process
From setting expectations to resolving disputes, let’s break down each action in detail and highlight where teams typically lose time, money, or visibility.

1. Setting Payment Terms
The AR process starts even before you raise an invoice. When payment terms aren’t clearly defined at the contract stage, everything downstream: collections, cash flow forecasting, and even dispute resolution.
- Owner: Sales & Finance
- Manual vs. Automated: Often manual unless you’re using CRM-accounting sync
- Common blockers: Sales reps skipping payment term entries, non-standardized clauses
- Tools can help: Use default term presets in your invoicing software linked to customer profiles
2. Invoicing Accuracy
Even a minor issue like the wrong tax rate, a missing PO number, or incorrect quantity can cause a customer to hold back the payment. With accuracy being non-negotiable, invoices are based on verified data from approved quotes, fulfilled delivery notes, or validated timesheets (for services).
- Owner: AR team or billing operations
- Manual vs. Automated: Usually manual in Excel workflows, automated in ERP/AR tools
- Common blockers: Human data entry errors, mismatched units, and no approval workflow
- Tools can help: Set up rules to block invoice creation without complete sales order mapping
3. Generating Invoices
Let the process of creating the invoice be a byproduct of business activity. It’s different from the data entry task. Once the delivery is confirmed or a project milestone is reached, your system should automatically generate an invoice.
- Owner: Finance or back office
- Manual vs. Automated: Many still use Excel + PDF methods; modern tools generate invoices from order events
- Common blockers: Delivery marked complete but not invoiced, batch billing delays
- Tools can help: Use AR tools with rule-based triggers tied to shipment completion or project updates
4. Sending & Tracking Invoices
Sending invoices involves documenting and tracking who receives the invoice — Is it the procurement team, accounts team, or a shared inbox?
Without confirmation of delivery and visibility into whether it was opened or processed, you’re operating blind.
- Owner: AR team
- Manual vs. Automated: Often manual; high risk of being missed or ignored
- Common blockers: Sent to the wrong contact, attachment missing, not acknowledged
- Tools can help: Auto-send with delivery tracking, customer invoice portals, EDI options for enterprise clients
5. Recording Payments
You must match every incoming payment with its corresponding invoice. Customers may pay in bulk or forget to reference invoice numbers. Reconciliation gets cluttered fast. If you’re unable to handle it daily, your reports become unreliable.
- Owner: Accounting or AR ops
- Manual vs. Automated: Manual matching can eat up hours
- Common blockers: No payment reference, short or excess payments, bulk payment splits
- Tools can help: Auto-match by customer ID + payment amount, with exception queues for unclear entries
6. Reconciling & Following Up
You’ll have to take action if an invoice remains unpaid after the due date. However, manually chasing payments when you don’t know which ones are overdue is inefficient. Reconciliation also requires clearing out partial payments, credit memos, and bounced transactions.
Done poorly, this makes AR aging reports look worse than they are.
- Owner: AR or credit control team
- Manual vs. Automated: Manual systems often miss follow-ups or repeat reminders
- Common blockers: No overdue alert system, no tracking for partials or disputes
- Tools can help: Set follow-up logic (X days after due) and auto-reconcile partials with smart rules
7. Handling Disputes & Chargebacks
There may be disputes, such as delivering the wrong products, missing service hours, or miscommunication regarding price. What matters is how fast your team logs and resolves them.
- Owner: AR, customer success, support
- Manual vs. Automated: Mostly manual, but should be tracked in CRM or AR tool
- Common blockers: No centralized ticketing, lack of documented resolutions
- Tools can help: Use shared systems to tag disputes, assign owners, and track time to resolution
Common Challenges & How to Overcome Them
Below, we’re listing some of the common issues AR teams face + how to address them with real, workable fixes.
Late Payments & Disputes
When customers miss due dates or question a charge, AR teams lose time and momentum. Delays often stem from unclear payment terms, missing references, or disputes that are not properly logged.
How to overcome it:
- Add visible payment terms to every quote, order, and invoice
- Confirm contact details before sending invoices
- Maintain a central log of disputes with status, owner, and resolution date
Data Errors & Manual Tracking Pitfalls
Manual processes introduce mistakes that slow collections. Even a minor discrepancy between the invoice and the order can cause a delay in payment. Also, most teams only catch the issue once the customer flags it.
How to overcome it:
- Pull invoice data directly from sales orders or delivery notes
- Use invoice templates with required field checks
- Review invoices using a short approval checklist before sending
Lack of Visibility Across Teams
When sales, finance, and support are not integrated, then there can be delays in the AR timeline. For example, sales personnel may not be aware that an invoice is overdue. Finance may not know a customer is disputing a charge. And support might be unaware that the account is on credit hold.
How to approach it:
- Link your CRM, invoicing, and accounting platforms or use shared views
- Make customer payment status visible to sales and support
- Assign owners to key accounts and overdue follow-ups
Inaccurate or Delayed Reconciliation
Payments hit your bank account, but the ledger doesn’t reflect them. Teams spend hours matching deposits to open invoices, or chasing down unidentified transfers.
How to fix it:
- Use software that can auto-match payments using invoice numbers, amounts, and customer IDs
- Set up a queue for exceptions and assign someone to clear them daily
- Flag unallocated payments and review them weekly in AR meetings
Automating Your AR Process
Manual AR processes are time-consuming, error-prone, and hard to scale. Bringing in automation helps reduce the admin burden, improves accuracy, and gives real-time visibility into where your money is.
Tools like Kladana bring structure to your AR workflow by integrating invoicing, reminders, and financial reporting into a single system.
Benefits of AR Automation
You can also automate the accounts receivable process by refining the way your business handles receivables from end to end.
It’ll speed up collections and keep your books cleaner.
Key benefits include:
- Faster invoice generation from sales orders or delivery confirmations
- Automated reminders based on invoice due dates and status
- Accurate reconciliation with bank sync and payment reference matching
- Central visibility across finance, sales, and fulfillment teams
- Real-time aging and DSO tracking through built-in reports
How Kladana Streamlines AR
Kladana is a cloud-based ERP designed for SMEs that require complete control over inventory, sales, and finance in one place.
You can benefit from its AR automation feature without the bloat of large ERP systems.
With Kladana, you can:
- Sync your AR data with your accounting software and last-mile delivery tools using built-in integrations. Check out supported integrations with Kladana.
- Monitor receivables and generate real-time DSO, aging, and payment performance reports through its financial reporting dashboard.
- Simplify your documentation using downloadable Excel templates for invoice tracking, credit control, and collection follow-ups.
FAQs on Accounts Receivable Process
Time to answer a few basic questions around accounts receivable.
What does the accounts receivable process include?
It includes issuing invoices, sending them to customers, tracking due dates, following up on payments, reconciling receipts, and reporting on outstanding balances.
How long is the typical AR cycle?
Most AR cycles range from 30 to 90 days, depending on your payment terms, customer base, and industry norms.
What documents are used in AR?
Core documents include invoices, credit memos, debit memos, receipts, customer statements, and remittance advice.
Why is AR important for cash flow?
AR ties up your revenue. The longer it stays unpaid, the more it strains your ability to cover operating expenses and invest in growth.
What is the difference between AR and AP?
AR tracks money owed to your business by customers. AP tracks money your business owes to vendors and suppliers.
How can you speed up collections?
Set clear payment terms, send invoices promptly, follow up regularly, offer digital payment options, and automate reminders.
Can small businesses automate AR?
Yes. Tools like Kladana help small teams automate invoicing, reminders, reconciliation, and reporting with minimal setup.
What happens if customers delay payments?
It increases your DSO, disrupts your cash flow, and may impact your ability to meet obligations. Aging reports and proactive follow-up reduce the impact.
How does AR impact financial statements?
AR appears as a current asset on the balance sheet. If it grows too large without being collected, it weakens your liquidity position.
What’s the best software for AR management?
The best tool depends on your size and needs. For SMEs, Kladana offers AR automation, invoicing, payment tracking, and financial reporting in one place.
List of Resources
Conciliac — The importance and benefits of performing effective bank reconciliation

