If you’re managing a modern supply chain, you know that a delayed or incorrect order doesn’t just hurt operations. It damages customer trust and creates friction across procurement, warehousing, and logistics — that’s where supply chain order management becomes mission-critical.
This isn’t just about paperwork or shipping labels. Order processing in supply chain management involves coordinating inventory systems, and teams to accurately and on time move every order from capture to delivery.
Whether you call it supply order management or SCM order management, the goal is to streamline your order flow, reduce costs, and enhance visibility.
As more companies invest in these integrated order-to-delivery systems, the benefits are becoming increasingly apparent. According to Deloitte’s 2025 survey, manufacturers that utilize connected systems, such as automation and real-time analytics, are achieving greater agility, productivity, and workforce performance.
These results highlight how a well-structured order management process drives both operational and strategic gains.
In this guide, you’ll learn what order management means in the supply chain, how the workflow functions, and how to choose the right tools.
- What Is Order Management in Supply Chain?
- Supply Chain Order Management Workflow
- Importance of Order Processing in Supply Chain Management
- Key Technologies & Systems for SCM Order Management
- Optimization Strategies for Supply Order Management
- Core Features to Look for in Supply Chain Order Management Tools
- Top Order Management Software Providers
- Challenges in SCM Order Management and How to Solve Them
- How to Choose the Right Order Management Software
- How Order Management Differs by Industry
- Summary
- Frequently Asked Questions on Supply Chain Order Management
- List of Resources
What Is Order Management in Supply Chain?
Order management in the supply chain is the end-to-end process that handles how customer orders are received, validated, routed, fulfilled, and delivered across every link in your supply network.
You’re not just tracking one order. You’re coordinating multiple departments, systems, and locations to ensure every sales order flows smoothly from demand to delivery. That includes capturing orders from different channels, such as e-commerce, EDI, and retail.
In a supply chain context, order management sits at the intersection of procurement, inventory control, warehouse operations, transportation, and customer service. It’s what connects planning with execution.
Let’s check the differences below on Order Management Vs Fulfillment Vs Order Management System (OMS).
| Aspect | Order Management | Order Fulfillment | Order Management System |
What it is |
End-to-end process of managing customer orders |
Physical handling on picking, packing, and shipping |
It is a software that controls and automates the order management process |
Scope |
Covers the full cycle |
Focused only on logistics and delivery |
It supports integration with ERP, WMS, CRM, and TMS for centralized control |
Main focus |
Coordinating, validation, inventory, routing, and exception handling |
Movement of goods |
It helps in automating, visibility, and tracking across all the systems |
Tools involved |
Automatic or manual workflow |
Warehouse transport tools |
Cloud-based platforms like Kladana, Netsuite, SAP, Oracle, etc |
Who uses it |
Ops leads and supply chain managers |
Logistic teams and warehouse staff |
Teams from the supply chain, IT, and Operations |
Supply Chain Order Management Workflow
Managing an order across your supply chain isn’t a single task. It’s a coordinated workflow involving multiple systems, teams, and checkpoints. Here’s how a typical supply order management workflow unfolds:
Step 1: Order Capture and Validation
The process begins from the moment an order is received, whether it’s through an online store, sales team, or customer portal.
- Orders can come from multiple channels such as eCommerce, ERP, mobile sales app, etc
Order Management System checks for:
1. Duplicate orders
2. Customer information
3. Payment terms
4. SKU-level accuracy
Step 2: Inventory Check and Reservation
Once validated, the system checks stock availability across all possible fulfillment nodes.
- An order management system or ERP checks inventory across all warehouses
- It reserves stock for confirmed orders
- It flags out low or out-of-stock items
- It applies allocation logic, such as FIFO, customer priority, and region, among others.
Step 3: Order Routing and Fulfillment Assignment
The OMS determines the best locations to fulfill the order based on:
- Inventory availability
- Customer location
- Shipping cost and delivery speed
Step 4: Shipping, Delivery & Returns
- Shipping details are generated and passed to the carrier via the Transportation Management System or Application Programme Interface
- OMS updates the tracking numbers and estimated date of delivery
- Customers receive shipping details through email or SMS
If returns occur:
1. OMS triggers RMA (Return Merchandise Authorization)
2. Return instructions and labels are sent to the customer
3. Returned items are restocked or flagged for inspection
Step 5: Post-Delivery Analysis
After delivery, the final step is about performance monitoring and continuous improvement, such as:
- OMS track records on delivery confirmation and status
- Track OTIF (on-time in full), delivery accuracy, and exceptions
- Data fed back into forecasting and procurement systems
- Captures customer feedback and rate of return
📘 Recommended Read: Want to improve upstream planning too? Check out Raw Materials Inventory Management to see how raw stock levels can impact your entire order cycle
Importance of Order Processing in Supply Chain Management
Order processing is one of the most influential levers in your entire supply chain. It drives speed, accuracy, and visibility across operations, but neglecting this process can create bottlenecks, stockouts, and unhappy customers.
Here’s why it matters.
1. It Shortens the Fulfillment Cycle Time
Faster order processing means faster deliveries. By automating key steps like:
- Order validation
- Stock allocation
- Fulfillment routing
You can minimize touchpoints and eliminate delays. This shortens the time from order receipt to final delivery.
📌 Faster order processing = faster cash flow and higher customer satisfaction.
2. It Improves Order Accuracy
A streamlined order processing makes sure that each order is verified against real-time data before fulfillment. It significantly improves accuracy and reduces manual errors like incorrect SKUs, lead returns, and lost revenue.
3. It Enables Demand-Driven Planning
Every processed order is a live signal for planning. When your order system is connected to inventory and procurement, you can forecast demand more accurately, schedule replenishments smartly, and avoid overstocking or stockouts
📊 Better data = smarter inventory and purchasing decisions
4. It Directly Impacts Customer Satisfaction
Nowadays, customers expect their orders to arrive quickly with complete visibility. A well-managed order process ensures early confirmation, precise fulfillment, and real-time tracking. This helps build a reliable delivery experience that builds trust and loyalty.
5. It Powers Post-Delivery Insights
Order management doesn’t stop at delivery. But by tracking KPIs like OTIF, return rates, and delivery accuracy, you gain valuable insights into performance gaps. It helps you optimize forecasting, logistics, and inventory control.
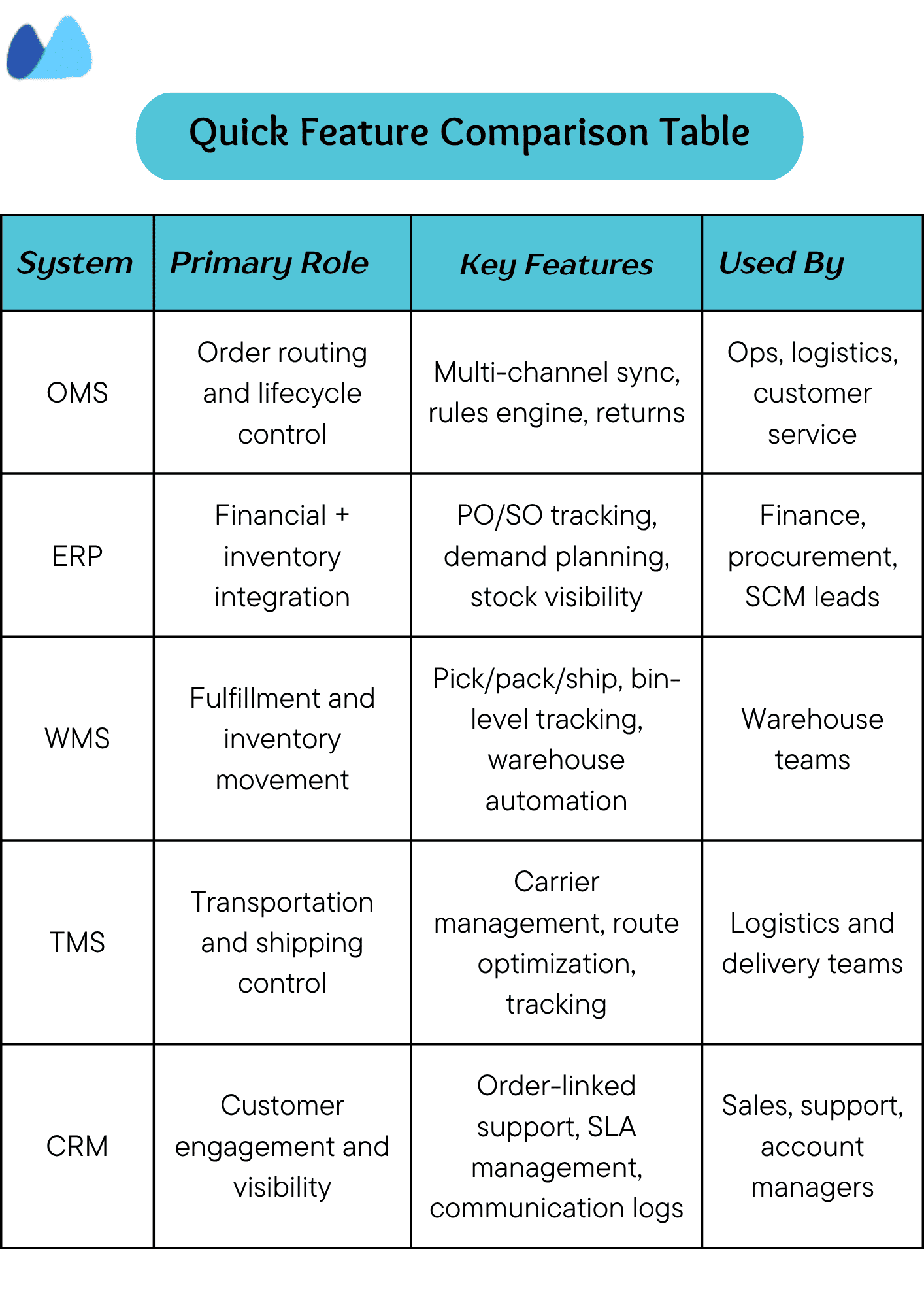
Key Technologies & Systems for SCM Order Management
You can’t manage orders efficiently at scale without the right technology stack. Manual processing always leads to delays and frustrated teams. Modern SCM order management relies on integrated digital systems that coordinate every step, from order capture to delivery and returns.
According to Mordor Intelligence, the global multichannel order management market is projected to reach $4.26 billion by 2025 and is expected to grow further to $6.82 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 9.87%. This growth indicates the rising adoption of Cloud Order Management Systems to streamline omnichannel sales and fulfillment.
Here’s a breakdown of the core systems that will help you power today’s order workflows.
1. Order Management System
An order management system automates order routing, applies business rules, and validates data to ensure accuracy. You use this to control how orders are captured, processed, and fulfilled across all channels, such as:
- Automate your order validation, allocation, and routing based on predefined rules
- Syncing your inventory and order statuses to prevent overselling
- Consolidating your orders from online and offline channels and B2B portals in one place
- Helps you in managing returns and exchanges through structured workflows
- Tracks your order performance and flags exceptions automatically
2. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
Your ERP acts as the backbone. You rely on this system to connect your order data with inventory, procurement, finance, and operations, such as:
- Syncs your sales order with inventory levels to prevent stockouts
- Generates your purchase order automatically when stock thresholds are reached
- Updates your finances and invoices as soon as orders are processed
- Tracks your vendor performance and delivery timelines alongside order status
- Enables multi-department visibility into each order’s progress and cost impact
📘 Recommended Read: Use our free purchase order templates to manage your POs
3. Warehouse Management System (WMS)
You use this to manage how orders are picked, packed, and shipped from your warehouse, such as:
- Assign your pick-lists to warehouse staff based on order priority and location
- Optimizes your storage, bin selection, and picking routes to reduce handling time
- Updates your order status as items are picked, packed, and dispatched
- Integrates with your barcoding or RFID systems for accurate stock movement
- Tracks your stock levels by batch, expiry, or serial numbers across multiple locations
4. Transportation Management System (TMS)
You depend on this to plan, execute, and track the movement of goods from the warehouse to the customer, such as:
- It helps you to select the most cost-effective carrier or delivery route based on SLAs
- It automatically generates shipping labels, waybills, and dispatch documentation
- It syncs and updates your delivery status with your order management or customer portal
- It tracks shipments across regions and resolves delivery exceptions faster
5. Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
You use this to connect customer interactions with order-related data and service workflows such as:
- Linking each order to its customer profile, communication history, and service level
- It helps to track your support tickets, delays or issues against specific orders
- It helps to coordinate with your sales or account teams to manage high-value customer expectations
- It helps to automate your follow-ups, feedback requests, and delivery confirmation
- It helps sync your order insights with marketing campaigns or loyalty programs
Here’s a quick comparison table on key technologies and tools.
Optimization Strategies for Supply Order Management
Having tools like supply chain order management or ERP in place is only the beginning. To move ahead, you need to optimize how those systems are used.
Here are key strategies to help you elevate your supply order management process.
🔂 Automate Approvals and Order Routing
If you work manually, you have to deal with a high risk while working in high volume or at multiple locations. Instead, use workflow tools that automatically:
- Approve low-risk orders
- Route orders to the nearest fulfillment center
- Flag exceptions
🤖 Leverage AI/ML for Demand Prediction
Predictive analytics helps you forecast demand and allocate stock where it’s needed most. Modern systems can analyze:
- Historical order data
- Seasonal trends
- Regional sales behaviour
- Supplier lead times
💹 Track KPIs to Drive Continuous Improvement
You can’t improve what you don’t measure. Set up dashboards with critical metrics like:
- OTIF rate
- Average order cycle time
- Inventory turnover ratio
- Return rate and root causes
📌 Tip: Track KPIs by channel such as B2B, D2C and market place to isolate performance issues.
⏭️ Align Logistics, Procurement, and Inventory Teams
Order management doesn’t work in silos. You have to connect departments using integrated systems and shared dashboards so that:
- Logistics knows what’s coming in and going out
- Procurement understands real-time stock consumption
- Inventory teams get alerts for reordering based on actual demand
⛔ Prevent Stockouts and the Bullwhip Effect
Fluctuations in upstream order quantities can cause major disruptions downstream, known as the bullwhip effect. You can minimize this by:
- Sharing POS and order data with suppliers
- Avoiding reactivating over-ordering during spikes
- Using safety stock and reorder point logic based on real trends
☑️ Smarter forecasting = steadier supply chain = fewer fire drills
📦 Recommended Read: Want to streamline how you route and fulfill orders across online channels? Explore this e-commerce supply chain guide for practical strategies on handling high-volume, multi-platform order flows
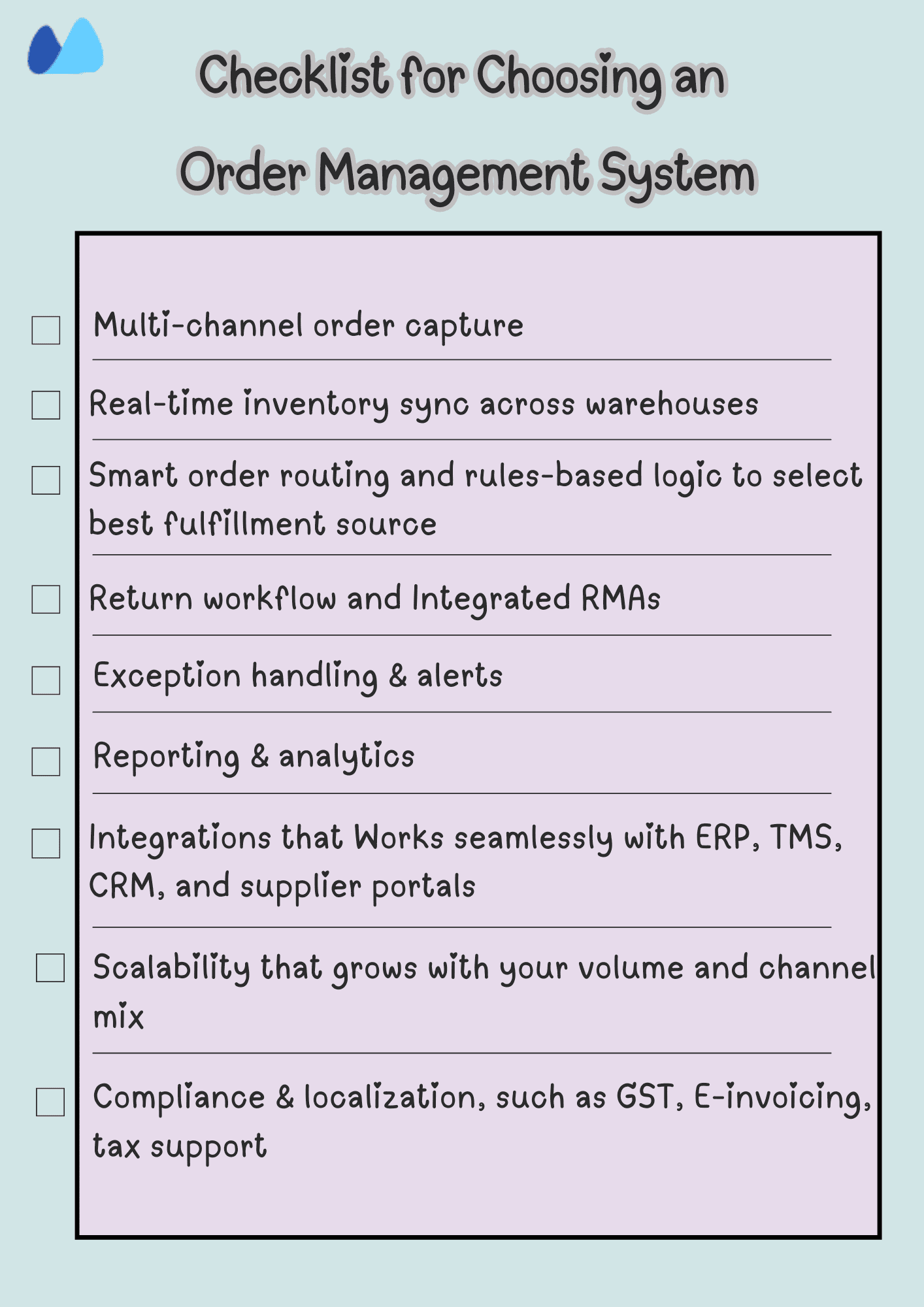
Core Features to Look for in Supply Chain Order Management Tools
Whether you’re implementing an order management, ERP order module, or a full-fledged SCM platform, be sure your solution offers:

Top Order Management Software Providers
| Software | Best For |
Kladana |
SMEs needing an all-in-one Order Management + ERP |
SAP SCM |
Enterprise-grade, global supply chain integration |
Oracle SCM Cloud |
End-to-end planning, logistics, and fulfillment workflows |
NetSuite Order Management |
Cloud-native, scalable for mid-sized businesses |
Manhattan Active |
High-volume omnichannel and retail fulfillment |
Zoho Inventory |
Cost-effective for multi-channel orders in SMBs |
Challenges in SCM Order Management and How to Solve Them
Order management in the supply chain is rarely smooth sailing. Delays, miscommunications, and data disconnects can throw your entire operation off track.
Here are the most common challenges and how you can solve them.
🚒 Delayed Shipments and Fulfillment Bottlenecks
Late deliveries don’t just upset customers, they erode trust across the supply chain.
| Why Does It Happen? | Solution? |
|
|
🧩 Siloed Systems and Data Disconnects
If your ERP, WMS, and CRM don’t integrate, then you’ll constantly battle delays and duplicated work.
| Why Does It Happen? | Solution? |
|
|
🥽 Poor Inventory Visibility
If you neglect checking your stock levels or availability, it will lead to canceled orders or emergency replenishment.
| Why Does It Happen? | Solution? |
|
|
❎ Inaccurate or Incomplete Orders
Mistakes in SKUs, quantities, or addresses are a major driver of returns and rework.
| Why Does It Happen? | Solution? |
|
|
How to Choose the Right Order Management Software
The best tool for your business depends on your order volume, fulfillment complexity, and how tightly your sales, inventory, and logistics functions are integrated
Here’s how to evaluate your options.
How Order Management Differs by Industry
| Business Type & Industry | Order Management Priorities |
Sync with BOMs, raw material reservations, and multi-level approvals |
|
Real-time inventory across warehouses, bulk order routing, channel-wise tracking |
|
Fast fulfillment, returns automation, and customer visibility |
|
Expiry management, Iot/batch-level tracking, rapid replenishment |
|
Seasonal demand spikes, SKU variants, by color/size, reverse logistics |
🚚 Streamline Order Management — No Bottlenecks, No Delays
Auto-route sales orders, approve faster, and sync fulfillment from one smart dashboard
Summary
Therefore, if your supply chain is the backbone of your business, then order management is its nervous system. It helps in processing signals, coordinating movements, and responding to exceptions in real time.
By understanding the entire cycle, from order capture to post-delivery analytics, you can eliminate delays, reduce errors, and respond faster to disruptions. Whether you manage 50 orders or 5,000, the right systems and workflows will help you scale sustainably.
Frequently Asked Questions on Supply Chain Order Management
What is order management in supply chain management?
Order management is the complete process of capturing, verifying, routing, fulfilling, and analyzing customer orders across your supply chain. It ensures the right product reaches the right customer, on time and in full.
What is the difference between order management and order fulfillment?
Order fulfillment encompasses the physical aspects of picking, packing, and shipping. Whereas order management covers everything from capturing orders to inventory checks and performance analysis.
What are the key steps in supply chain order processing?
The typical workflow includes:
- Order capture and validation
- Inventory check and reservation
- Fulfillment routing
- Shipping and delivery
- Post-delivery analysis
Which KPIs should I track to measure order management performance?
Important metrics include:
- OTIF
- Order cycle time
- Inventory turnover
- Return rate
- Exception resolution time
What benefits does effective SCM order management bring?
It reduces cycle times, improves order accuracy, enhances inventory visibility, supports real-time decision-making, and directly improves customer satisfaction.
What is the bullwhip effect?
The bullwhip effect occurs when small changes in customer demand lead to increasingly larger fluctuations in upstream inventory or production. It often results from poor forecasting, communication gaps, or over-ordering.
How do I prevent stockouts in my supply chain?
- Use predictive analytics to anticipate demand
- Set smart reorder points and safety stock thresholds
- Sync real-time inventory across all sales and fulfillment channels
- Avoid relying on outdated spreadsheets or manual systems
What technology should power SCM order management?
A modern SCM order flow should be powered by:
- Order management system
- ERP with integrated inventory and procurement modules
- WMS for warehouse-level tracking
- TMS for shipping optimizations
Can supply chain order management scale across multiple locations?
Yes. If your system supports multi-location logic. Features like centralized order routing, warehouse-specific inventory visibility, and region-based tax handling are important for scaling.
How can supply chain order management help reduce operational costs?
- Automating order validation reduces costly rework
- Smart routing lowers shipping costs by fulfilling from the most efficient location.
- Inventory sync helps avoid emergency replenishment or lost sales
- Integrated systems eliminate duplicate data entry
- Return tracking highlights recurring issues that can be fixed upstream
List of Resources
- Deloitte: Survey on Smart Manufacturing
- Mordor Intelligence: Multi-Channel Order Market Report
Read‑alikes
A Guide to Purchase Order Management: Meaning, Process, and Benefits
4 Free Purchase Order Templates with a Step‑By‑Step Guide: Excel, Word, and Google Sheets Format
Material Purchasing in Manufacturing: Process, Tips, and Tools for 2026
Purchasing Process in Business: 7 Key Steps with Tools And Examples