When there are hundreds and thousands of products in a store, it is not always clear what is bought consistently and in large quantities, and what is not. ABC analysis will help to understand this — it is suitable for retail, wholesale and online trade. How to conduct it — in this article with examples.
What is ABC Analysis?
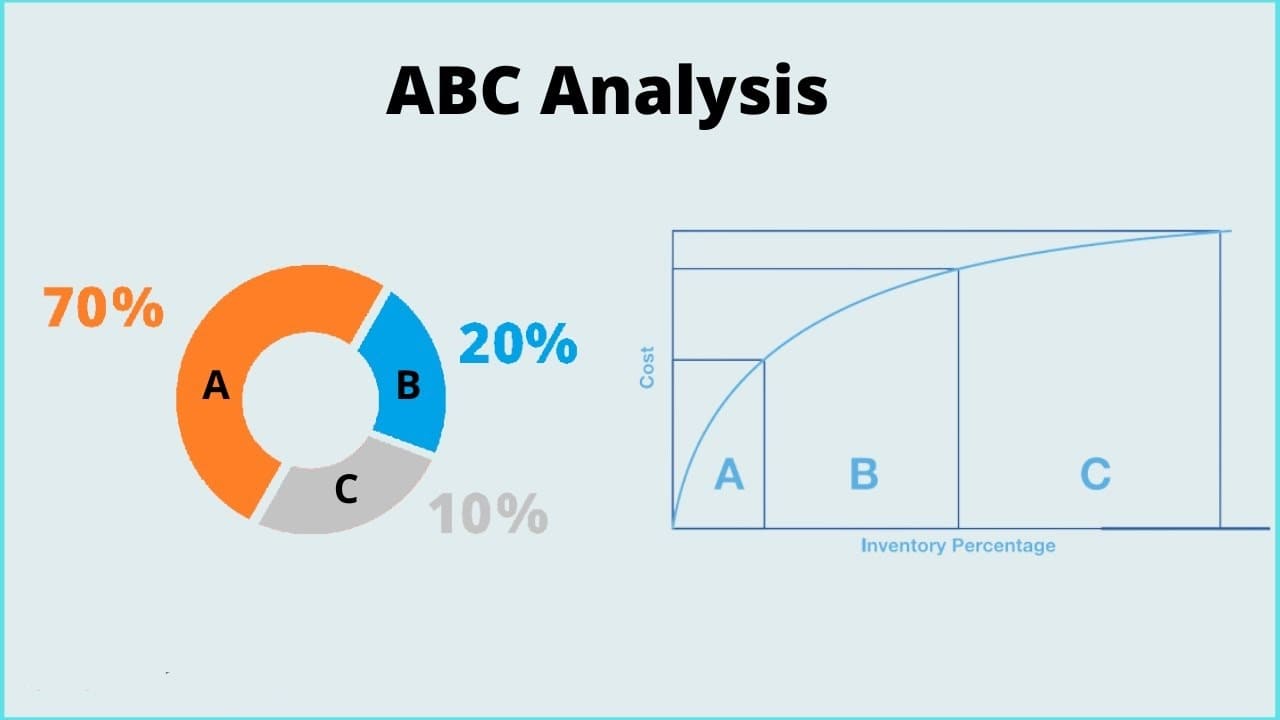
ABC analysis is used for evaluating large amounts of data. This inventory technique involves dividing stock into three main categories. Items are classified into categories depending on the value they bring:
🔤 Category A usually includes 10-20% of the stock, which brings the main value: from 70 to 80%. Managing this category is very important for maintaining and increasing business profitability.
🔤 Items from category B are moderately valuable, they occupy about 30% of the stock and carry 15-20% of the value.
🔤 Products from category C are the lowest priority. They make up about 30% of all resources and bring only about 5-10% of profit.
ABC analysis involves different targeting approaches for stock groups. This allows you not to keep an excess of low-turnover goods in the warehouse, but also not to experience a shortage of the most important ones.
This type of analysis is needed to make the right management decisions. First of all, it concerns purchasing: in what quantities and in what timeframes does a trade or production company order certain goods and raw materials from suppliers? If you don’t have this data, your processes will be in chaos, especially with assorted stock.
Advantages of ABC Analysis
There are many proven benefits of ABC analysis, from small to significant. Let’s highlight the key ones:
Better Resource Allocation
ABC analysis enables businesses to direct time, money, and effort toward the most important products. Category A items receive greater attention because of their critical role in the company’s success. This approach helps prevent understock and overstock, keeps warehouses organized, and ensures resources are focused on truly important areas.
Improved Forecasting and Control
Knowing which products sell best and bring in the most profit, businesses can more accurately forecast demand. This leads to more accurate monitoring and replenishment of stock, allowing the right products to be ordered or produced in a timely manner, not taking up space in the warehouse with excess “just in case”, but also preventing stock from running out.
Excess Stock Issues Detection
ABC analysis helps you understand which products are sitting in your warehouse for too long. Category C items take up a significant amount of space and bring in little profit. If you notice them in time, you can make an informed decision about discounting, liquidating, or bundling them with other products. This will free up physical space in your warehouse and help reduce storage costs.
Common Challenges in ABC Analysis
ABC analysis is not only about advantages and ease of assortment planning. You can’t implement this system once and for all without spending any more effort on it. Let’s consider three basic challenges of ABC analysis:
Time and effort to maintain
ABC analysis is not a one-time task. Sales trends and popularity among consumers may change: seasonally or under the influence of changing needs. As a result, products may be reassigned from one group to another. To stay ahead, analysis should be carried out frequently. Without regular checks, the accuracy of the results decreases.
Limited focus on other factors
This technique primarily focuses on the value of products and the profit they generate. The analysis is unable to predict seasonal trends and sales peaks, logistical risks, and demand fluctuations. Relying solely on the results of ABC analysis without considering other factors when making decisions about the assortment may ultimately lead to losses.
Possible misclassification of products
A product may sell poorly, but have great potential and grow in popularity in the future. If you rely solely on the results of ABC analysis, this product will be relegated to the category of slow movers and will not be able to realize its potential fully. Therefore, it’s essential to combine analysis with observation and solid knowledge of the market.
How to Perform ABC Analysis (Step-by-Step)
In this paragraph we’ll briefly list the main steps of ABC analysis.
List inventory Items & Annual Consumption Value
Start with a complete list of products. For each item, calculate its annual consumption cost. Multiply the annual sales volume by the unit price. This will give you the baseline data for your analysis.
Rank by Consumption Value
Sort all products from highest to lowest customer value. Keep the most valuable products at the top. This allows you to understand which products bring in the most profit.
Compute Cumulative %
Add value as you go down the list. Then calculate the cumulative percentage of total consumption. This will help you visualize how much each product contributes to the overall supply.
Classify into A/B/C Groups
Divide items into three categories:
- Category A items: typically the top 70-80% of total value, although they may be as little as 10-20% of total number of products.
- Category B items: around 15-25% of value.
- Category C items: the rest, often the most numerous but the smallest share.
Example of ABC Analysis Table
| SKU Code | Annual Consumption Value | Cumulative % | Category |
| SKU001 | $5,00,000 | 40% | A |
| SKU002 | $3,00,000 | 65% | A |
| SKU003 | $1,50,000 | 77% | B |
| SKU004 | $80,000 | 84% | B |
| SKU005 | $20,000 | 100% | C |
This table shows how a small proportion of goods (category A goods) can account for most of the cost, while many category C goods make a very small contribution.
ABC Analysis in ERP (Automated Approach)
How software auto-updates classifications
Conducting ABC analysis manually takes a lot of time and requires constant updates. The ERP system automates the process. It collects data after sales and stock updates, automatically recalculates the cumulative value, updates cumulative percentages, and redistributes products by category.
The business owner can be sure of the accuracy and timeliness of the data. So they are always aware of the current business situation.
Kladana Example: How ERP System Can Facilitate ABC Analysis
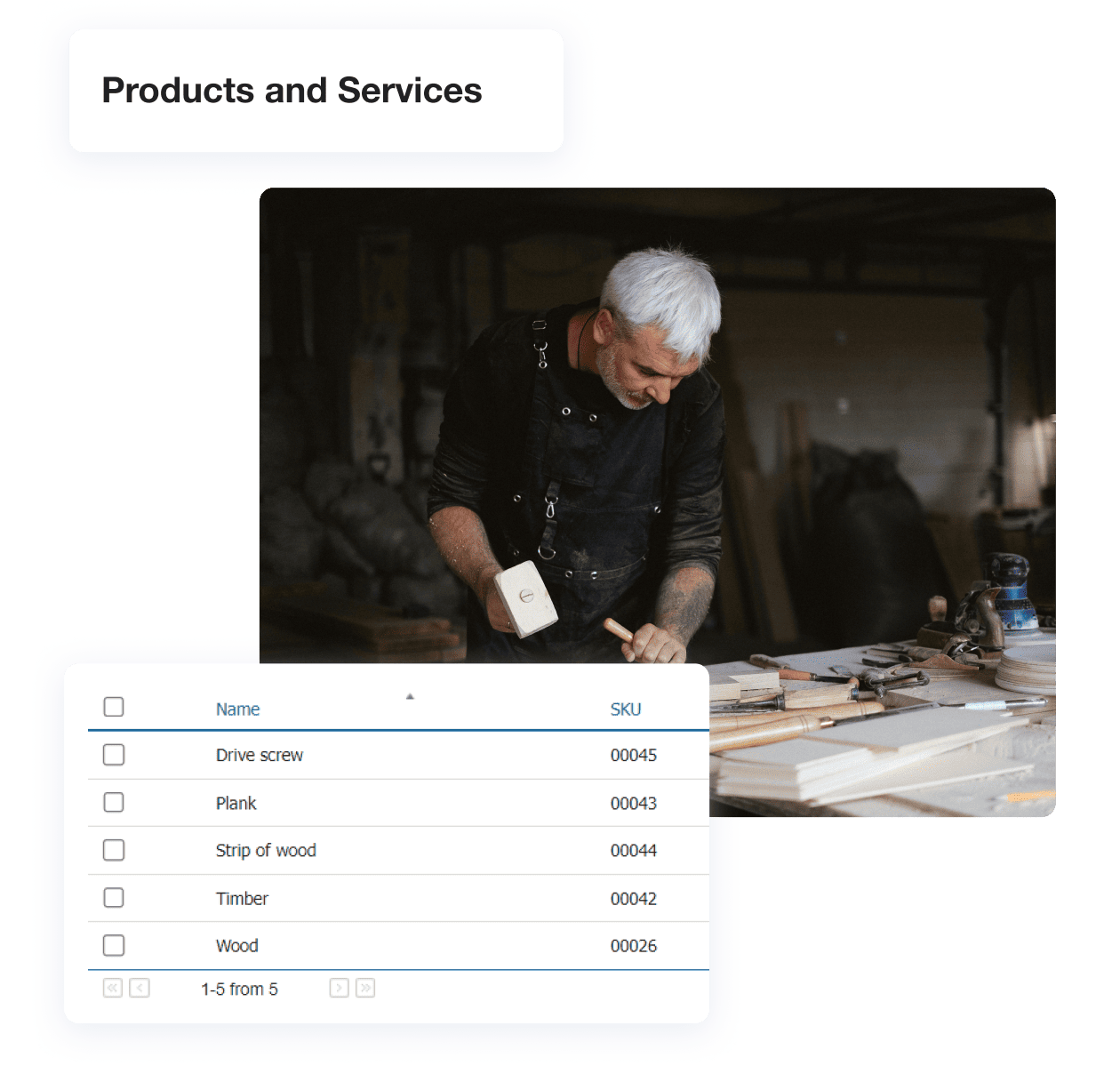
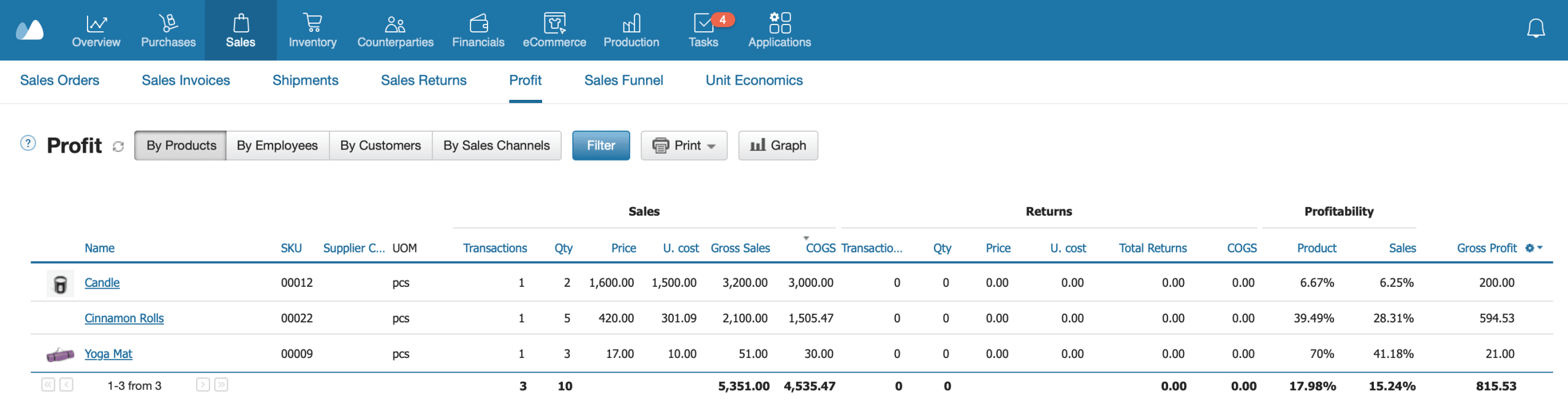
In the Sales section of Kladana, you can generate a Profit Report, filter it by products, then select Print and get it in Excel format. This spreadsheet will become your base for ABC analysis, as it will reflect all the SKUs sold during the selected period, their quantity, cost, profitability, gross profit, and other details.
After conducting ABC analysis, you can leave marks in the Inventory section for all your products, classifying them as belonging to group A, B, or C.
Using ABC Analysis Results to Improve Inventory Management
The method helps determine how to manage goods to increase store profit. The strategy depends on which group the goods belong to.
Recommendations for inventory management for small businesses based on ABC classification:
| A | B | C |
| Maintain close control of inventory levels | Control your inventory levels | Maintain basic level of inventory control |
| Achieve maximum accuracy in information tracking | Keep information tracking accurate | Maintain standard information tracking |
| Conduct inventory counts frequently | Carry out periodic inventory counts | Conduct infrequent inventory counts |
Category A goods are the most important. They must always be in stock, so maintain a safety reserve. Keep accurate records, run a partial inventory every week, and a full inventory every quarter.
Category B goods also require a high level of control and accurate record-keeping, but partial and full inventory counts can be carried out less frequently.
Category C goods require thorough analysis. You need to understand why they are in this group.
Reasons may vary: a new product did not generate the expected sales, the item is poorly placed in the sales area, or the website listing lacks a good description and photo. The key is not to rush to remove these goods from the assortment since they still help shape the store’s product range.

Get started with cloud-based solutions by choosing Kladana — an ERP tailored for small and medium-sized businesses. Now is the time to take full control of your inventory, sales, and manufacturing processes.
Frequently Asked Questions on ABC Analysis
ABC inventory analysis can significantly improve inventory management for small and medium‑sized businesses. Below are answers to some common questions SMBs may have about implementing this method.
What is ABC analysis in inventory?
ABC analysis is a method of classifying products based on their value and impact on sales. Category A items are the most valuable, B are moderate, and C bring the least profit.
How does ABC analysis help in reducing inventory costs?
It highlights the items that need strict control. Businesses spend less on storage by avoiding excess stock of low-value goods.
How is ABC analysis useful in inventory management?
It helps decide where to focus attention. High-value goods get priority, while less important items are managed with simpler controls.
How can I use ABC analysis to optimize my inventory?
Start by classifying products. Then set reorder points, safety stock, and purchase strategies for each category.
How does ABC analysis differ from other inventory management techniques?
It focuses on value-based classification, while other methods may use demand frequency, time, or stock flow as criteria.
What are the best practices for implementing ABC analysis in e-commerce?
Update data regularly, track fast-moving goods closely, and integrate the analysis with sales platforms for real-time control.
How often should ABC classification be updated?
At least once every quarter. For fast-changing industries, monthly reviews are better.
How does ERP automate ABC analysis?
ERP systems use sales and stock data to classify items automatically and update categories in real time.
Is ABC analysis suitable for seasonal businesses?
Yes, but categories should be reviewed more often to reflect seasonal demand shifts.
What types of businesses should use ABC analysis?
It works well for retailers, wholesalers, manufacturers, and e-commerce sellers managing many products.
Read‑alikes
ERP Inventory Management: 12 Benefits for Your Business in Full Guide
MRP vs ERP: A Comprehensive Guide to Business Management Solutions
Top 20 ERP Software for SMEs in India and Across the World 2026
ERP Software Boom: “It’s Becoming a Single Point of Assembly of All Business Processes”