Every product a customer orders passes through a warehouse before it reaches them. The way a warehouse receives, stores, picks, packs, and ships goods is called warehouse operations. These activities determine how fast orders are fulfilled, how accurate stock data is, and how efficiently businesses use their space and workforce.
Strong warehouse operations management is essential for supply chain success. A delay or stock error in the warehouse can disrupt the entire order cycle. On the other hand, optimized operations cut costs, improve customer satisfaction, and create room for growth. Warehouse operations are critical for efficiency, considering that warehousing typically accounts for around 23% of total logistic costs.
This guide explains what warehouse operations are, their functions, step-by-step processes, challenges, and best practices. We’ll also explore how technology like Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) and automation improve efficiency for businesses of all sizes.
- Defining Warehouse Operations
- Core Functions of Warehouse Operations
- Warehouse Operations Process Flow
- Challenges in Warehouse Operations
- Best Practices for Efficient Warehouse Operations
- Technology and Automation in Warehouse Operations
- KPIs to Measure Warehouse Efficiency
- Warehouse Operations vs Warehouse Management
- Case Example: Optimizing Warehouse Operations in an SME
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions on Warehouse Operations
- List of Resources
Defining Warehouse Operations
Warehouse operations are the set of activities that handle goods inside a warehouse, from receiving shipments to sending orders out. They cover everything that keeps stock moving in and out smoothly.
These operations are critical because they connect suppliers, storage, and customers. An error in receiving or picking can lead to stockouts, late deliveries, or extra costs. Effective warehouse operations management ensures accuracy, speed, and cost control.
Warehouses vary depending on the industry, for example:
- Distribution centers move goods quickly to retailers or customers.
- E-commerce warehouses focus on fast picking, packing, and returns.
- Cold storage warehouses store food, pharmaceuticals, or perishables under controlled conditions.
No matter the type, the goal is the same: make sure goods are in the right place, at the right time, and in the right condition.
📖 Recommended Read: If you’re selling on Shopify, you may have specific requirements for the solution that’ll help you manage your warehouse operations. Read our guide to choose the system that best suits your needs.
Core Functions of Warehouse Operations
The main functions of warehouse operations ensure products move smoothly from arrival to dispatch. All the types of warehouse operations support efficiency, cost control, and customer satisfaction:
- Receiving goods: verifying shipments against purchase orders, checking product quality, and recording items in the system. A thorough receiving process prevents errors from spreading through the supply chain.
- Put-away and storage: placing items in their correct location, using clear labeling and slotting strategies. Good storage planning improves space utilization and reduces the time needed to find items later.
- Picking and packing: selecting products for customer orders and packaging them safely. Efficient picking methods, like batch or zone picking, speed up fulfillment and reduce mistakes.
- Shipping and dispatch: preparing orders with correct labels and documentation, then handing them to carriers on time. Reliable shipping processes ensure faster deliveries and fewer returns.
- Inventory control: tracking stock through cycle counts, audits, and real-time updates. Accurate inventory records prevent stockouts, overstocking, and lost sales.
Strong control over these warehouse activities minimizes delays, reduces costs, and builds a reliable fulfillment system. Together, they form the core of daily warehouse operations.
Warehouse Operations Process Flow
The warehouse operations process moves goods step by step from inbound to outbound. Each stage begins after the previous one is completed:
- Receiving: suppliers deliver goods, they are checked and logged.
- Put-away: items are moved to assigned storage locations.
- Storage: goods are kept in the warehouses until needed.
- Picking: items for customer orders are selected.
- Packing: products are packed and labeled for delivery.
- Shipping: carriers collect and dispatch orders.
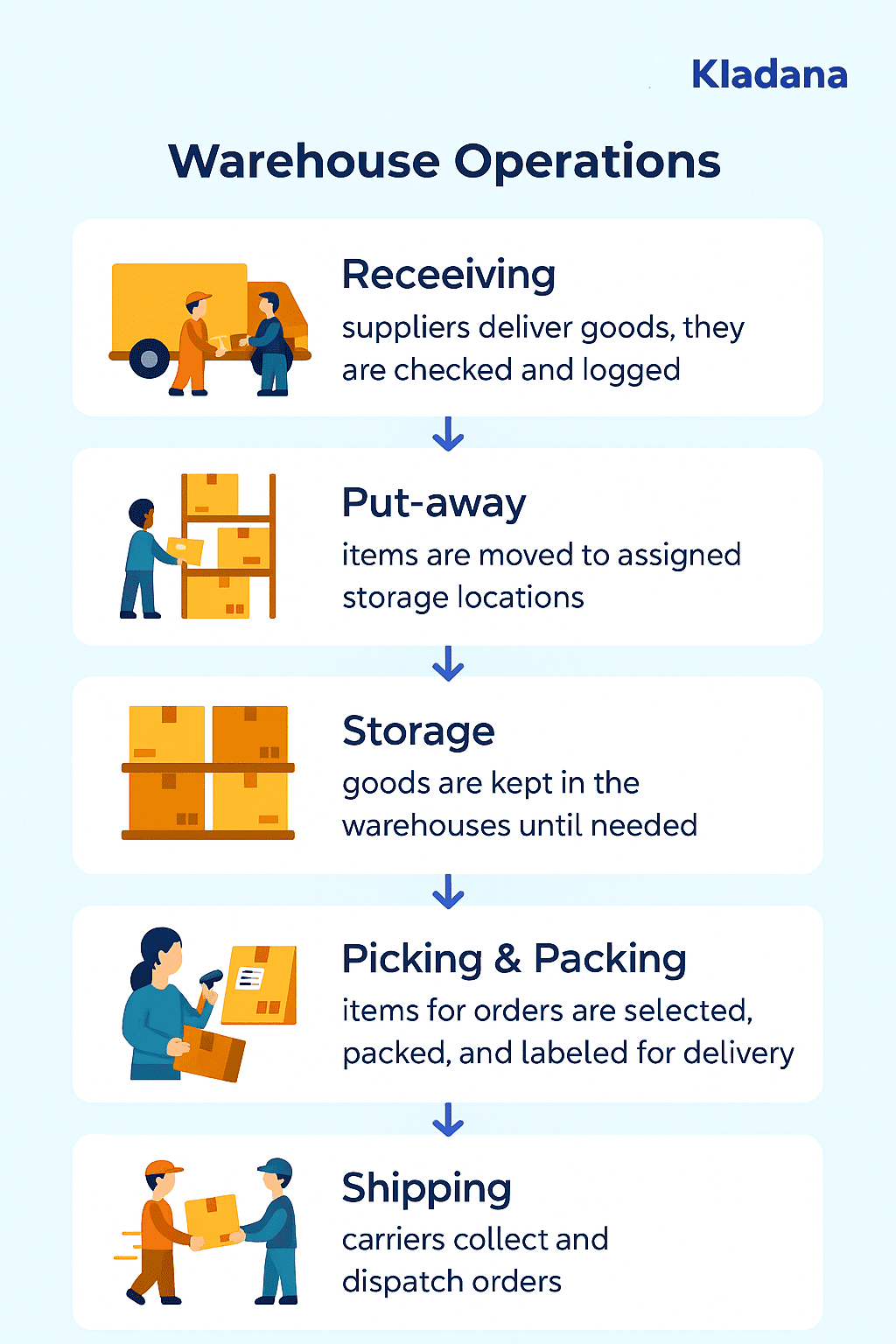
A clear process provides accuracy and helps avoid bottlenecks. When each stage runs smoothly, fulfillment is faster, inventory data stays correct, and customers receive their orders on time.
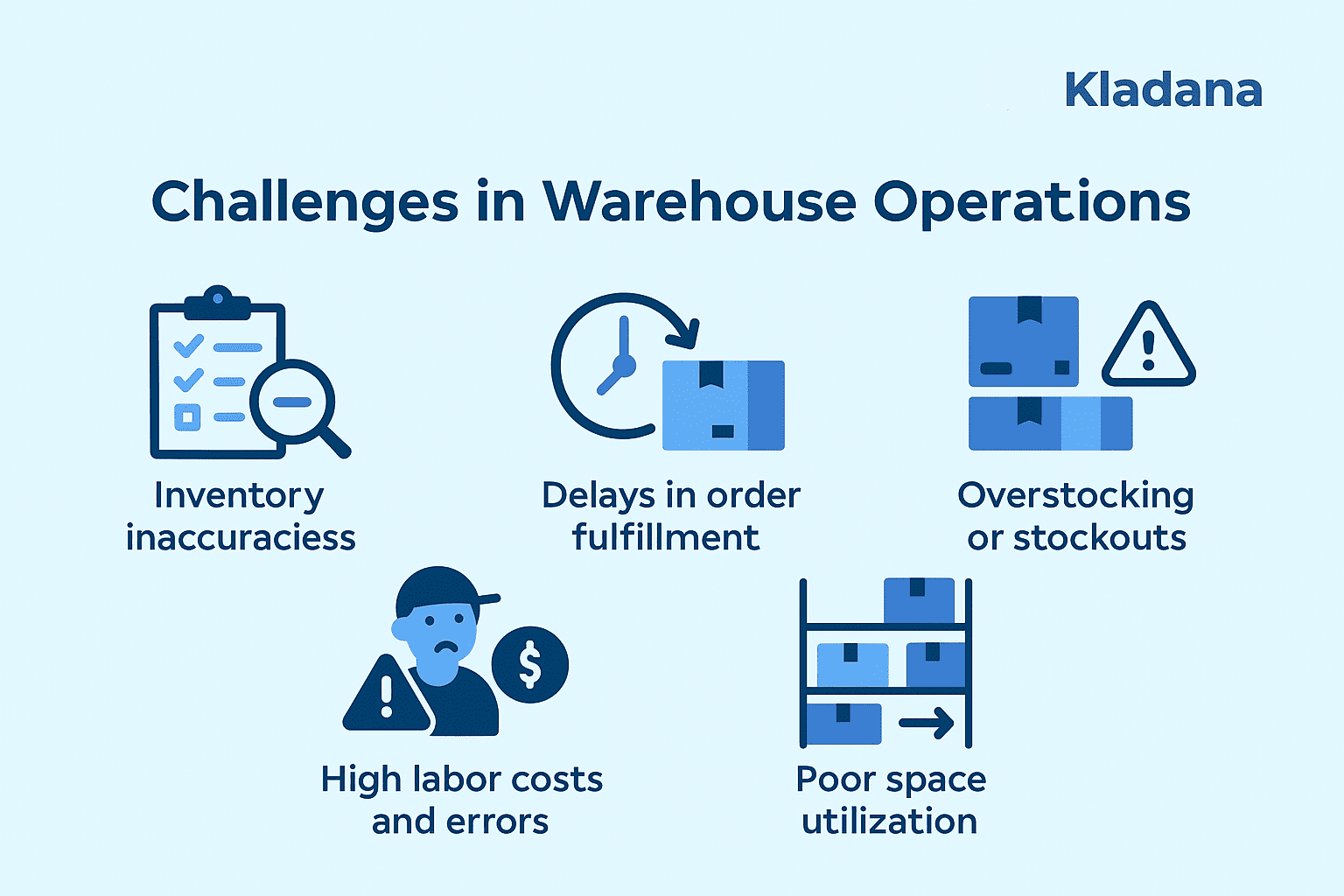
Challenges in Warehouse Operations
Even best-designed warehouses are challenged with issues that delay efficiency. Typical issues are:
- Inventory inaccuracies — counts or data-entry errors lead to stockouts or overstocking.
💡 Solution: Employ barcode or RFID technologies that are connected with a WMS to record movements of stock automatically and keep records up to date.
- Late order fulfillment — slow picking or slower boxing for slower shipping.
💡 Solution: Redesign layout to keep fast-moving goods close to picking locations and use batch or zone picking methods.
- Overstocking or stockouts — poor demand forecasting ties up capital or misses out on sales.
💡 Solution: Employ forecasting tools or ERP modules that calculate plans for maximum stock levels from historic sales.
- High labor cost and errors — labor that proceeds slowly tends to be error-prone.
💡 Solution: Use handheld scanners, conveyors, or part-automation to minimize manual task dependency.
- Inefficient space usage — poor layout increases lead times and wastes capacity.
💡 Solution: Employ slotting strategies and vertical storage systems to maximize usable space.
By having well-structured warehouse ops management in place, businesses can turn these problems into opportunities to improve efficiency and minimize costs.
Best Practices for Efficient Warehouse Operations
Warehouse efficiency improvement comes from a mix of technology, planning, and people management. Some proven practices are:
- Set up Warehouse Management System: receive, pick, and ship automatically for real-time control.
- Use barcode or RFID tracking: reduce manual errors and increase inventory visibility.
- Warehouse layout optimization: relocate fast-selling goods close to picking locations.
- Train staff and simplify processes: increase quality and speed every time.
- Apply lean and just-in-time practices: eliminate waste and carry the right amount of inventory.
These practices make operations smoother, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction. Relatively small changes over time add up to huge savings.
Technology and Automation in Warehouse Operations
Modern warehouses rely on technology to boost speed and accuracy. A Warehouse Management System provides real-time visibility of stock and automates daily tasks like receiving, put-away, and picking.
Automation is transforming warehouse management operations:
- Robots and AGVs transport goods without human intervention.
- IoT devices track temperature, movement, and stock levels.
- AI-powered forecasting tools predict demand based on sales history and market trends.
ERP integration connects warehouse data with purchasing, sales, and finance for full supply chain control.
These technologies reduce labour costs, increase precision, and better-informed decision-making. Firms that implement automation may experience accelerated order processing as well as greater satisfaction among customers.
📖 Recommended Read: We recommend implementing barcoding if you haven’t done so already. Our detailed guide will help you get started and walk you through six initial steps.
KPIs to Measure Warehouse Efficiency
Tracking the right KPIs helps assess how well warehouse operations perform and where improvements are needed. These metrics give managers visibility into costs, productivity, and customer service levels.
- Order accuracy rate — measures the percentage of error-free orders shipped. A higher rate means fewer returns and better customer satisfaction.
- Inventory turnover — shows how often stock is sold and replenished. A healthy turnover indicates strong demand forecasting and prevents dead stock.
- Receiving and put-away cycle time — tracks how quickly goods move from delivery to storage. Faster cycles reduce congestion at docks and keep products ready for sale.
- Picking efficiency — counts lines picked per hour or per worker. It helps identify if layout, training, or automation changes are needed.
- Order lead time — measures the full time from order creation to shipment. Shorter lead times directly improve customer experience.
- Space utilization percentage — evaluates how well available warehouse space is used. High utilization lowers storage costs per unit.
Monitoring these KPIs regularly highlights weak spots and shows whether warehouse optimization strategies are working. Linking KPIs with WMS or ERP dashboards allows businesses to act quickly, reallocate resources, and maintain service quality.
Warehouse Operations vs Warehouse Management
Although related, warehouse operations and warehouse management are not the same. Operations focus on execution, while management takes a broader, strategic role.
| Aspect | Warehouse Operations | Warehouse Management |
| Focus | Day-to-day tasks | Strategic planning and oversight |
| Activities | Receiving, storing, picking, packing, shipping | Policy design, layout planning, staffing, process improvement |
| Scope | Tactical — deals with immediate needs | Strategic — ensures long-term efficiency and scalability |
Strong warehouse operations management combines both. Smooth daily workflows depend on clear policies and smart planning, while management relies on accurate execution data for optimization.
In short, operations are the “doing,” management is the “planning.”
Real-time inventory visibility for better decisions.
Ensure you accurately track the exact quantities of every item in your warehouse. Avoid unpleasant surprises, such as unexpected raw material shortages, failed shipments, and unplanned emergency supplies at higher costs.
Case Example: Optimizing Warehouse Operations in an SME
The Challenge:
A mid-sized e–commerce retailer faced constant delays in shipments and rising costs. Manual picking slowed down fulfillment, and frequent stock count errors frustrated both staff and customers.
The Solution:
To fix this, the company implemented a WMS integrated with the ERP solution. The system introduced real-time inventory tracking, automated picking lists, and barcode scanning. Staff no longer wasted time searching for products, and order errors dropped significantly.
The Results:
Within just three months:
- Order accuracy improved by 25%
- Fulfillment time was cut by 50%
- Storage space was optimized for faster access
- Customers enjoyed quicker deliveries and began placing more repeat orders
| Aspect | Before WMS Implementation | After WMS Implementation |
| Order accuracy | Frequent errors due to manual picking and stock mismatches | Improved by 25% with barcode scanning and real-time tracking |
| Fulfillment speed | Delayed shipments; staff wasted time locating items | Fulfillment time reduced by 50% with automated picking lists |
| Storage efficiency | Poor space use led to congestion and delays | Optimized layout with better put-away strategies |
| Customer satisfaction | Complaints about late deliveries and errors | Faster deliveries led to more repeat purchases |
The Takeaway:
Even small and mid-sized businesses can see quick gains from structured warehouse operations management. With the right tools, efficiency improvements translate directly into lower costs and higher customer satisfaction.
Conclusion
Strong warehouse operations are the essence of any supply chain. Each step affects costs, delivery speed, and reputation among clients. Mistakes in one area can ruin the entire process.
Adopting best practices like clear workflows, optimized layouts, and staff training ensures smooth daily operations. Adding warehouse optimization such as WMS, ERP, and other automation tools helps reduce errors, improve visibility, and cut costs.
✔️ For growing businesses, the next step is to review current processes. Identify bottlenecks, measure performance with KPIs, and consider how automation could help. Streamlined warehouse operations not only improve efficiency but also create a competitive edge.
Start by auditing your warehouse processes today — small changes can make a big difference.
Frequently Asked Questions on Warehouse Operations
What are warehouse operations?
Warehouse operations are the activities inside a warehouse that handle goods from receiving to shipping. They include storage, picking, packing, and inventory control.
What are the main functions of warehouse operations?
The core functions of warehouse activities are receiving goods, put-away and storage, picking and packing orders, shipping, and maintaining accurate inventory records.
What are the steps in warehouse operations?
The process flow includes receiving, put-away, storage, picking, packing, and shipping. Each step ensures goods move correctly through the warehouse.
What types of warehouses exist?
Common types are distribution centers, e–commerce fulfillment warehouses, cold storage for perishable goods, and bonded warehouses for imports and exports.
What are common challenges in warehouse operations?
Typical challenges include stock inaccuracies, delayed fulfillment, high labor costs, poor space use, and risks of overstocking or stockouts.
How do businesses optimize warehouse operations?
Businesses use WMS software, barcode scanning, lean principles, optimized layouts, and standardized workflows to improve efficiency.
What is the role of technology in warehouse management?
Technology like ERP, WMS, IoT devices, and robotics reduces errors, automates processes, and provides real-time visibility.
What is a warehouse management system (WMS)?
A WMS is software that manages warehouse tasks such as receiving, picking, packing, and shipping. It improves accuracy and speed.
How do warehouse operations impact supply chain efficiency?
Efficient operations ensure on-time deliveries, accurate stock data, and cost savings, all of which strengthen the supply chain.
What is the difference between warehouse operations and logistics?
Warehouse operations cover internal activities, while logistics includes transportation, distribution, and coordination across the supply chain.
List of Resources
Tech.co. Marketing VF Ltd. — Logistics Statistics 2025: Industry Numbers You Need to Know