If you’re moving goods worth over ₹50,000, you’re required to generate an E-Way Bill before dispatch. It’s more than a GST form. It’s your shipment’s digital gate pass, and without it, your goods can be delayed, fined, or detained.
However, here’s the catch: even if the bill is generated, using the wrong E-Way Bill format, skipping a required field, or entering an invalid vehicle number can still result in being flagged.
In this guide, you’ll learn:
- How to complete the step-by-step process for filling the GST EWB-01
- Avoid errors like invalid vehicle numbers or expired validity
- Get free downloadable templates in Excel, Word, PDF, Docs, and Sheets
- Download Free E-Way Bill Templates
- What Is an E-Way Bill?
- How to Fill the E-Way Bill: Step-by-Step Guide
- Who Needs to Generate an E-Way Bill?
- When Is an E-Way Bill Not Required?
- Benefits of the E-Way Bill Format
- What Goes into the GST EWB-01 Form?
- E-Way Bill Formats: Excel, Word, PDF, Docs, Sheets
- ⚠️ Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- Penalties for E-Way Bill Non-Compliance
- Summary
- Frequently Asked Questions on E-Way Bill Template
- List of Resources
Download Free E-Way Bill Templates
Before you start filling out your next E-way Bill, ensure you’re using a format that suits your workflow. Using the right format will save you time and help you avoid mistakes.
Choose from these editable templates, each designed to match the official GST EWB-01 form.
🟢 Download Free Editable Templates
Excel | Word | PDF | Google Docs | Google Sheets
💡 Here’s when each one works best
- Excel — Use for high-volume entries with formulas and batch updates
- Word — Print and go for single shipments or manual filing
- PDF — Great for finalized records that don’t need edits
- Google Docs — Ideal when multiple team members review or fill fields
- Google Sheets — Best for live updates and syncing with inventory or dispatch data
Best Format for Each Use Case
| Format | Best for | Editable | Printable | Shareable |
Excel |
Bulk entry, formulas, and offline tracking |
✅ |
✅ |
✅ |
Word |
Quick printouts, custom styling |
✅ |
✅ |
✅ |
Final signed copies, fixed format |
❌ |
✅ |
✅ |
|
Google Docs |
Online edits, internal team review |
✅ |
✅ |
✅ |
Google Sheets |
Cloud-based entry, team updates |
✅ |
✅ |
✅ |
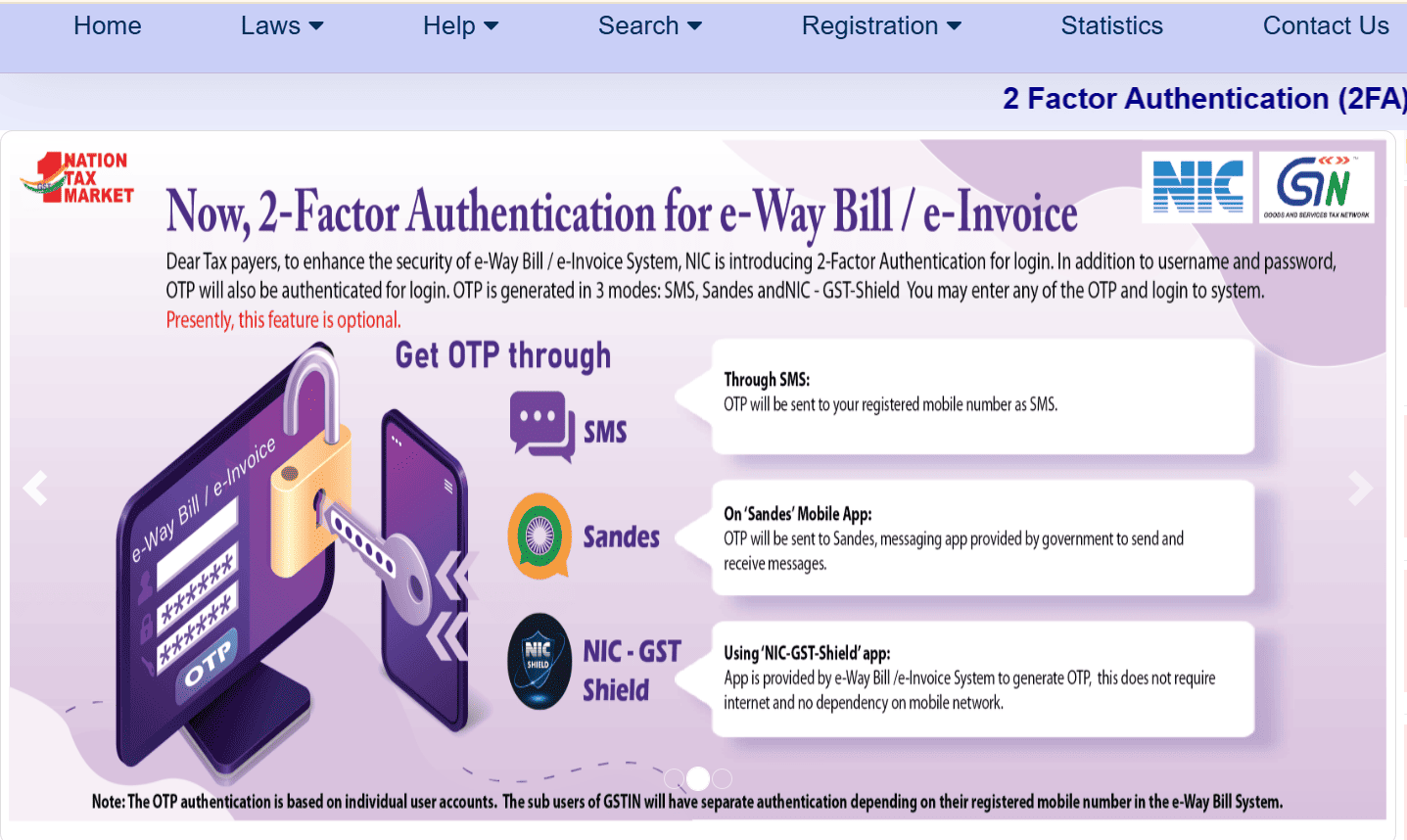
🚨What’s New in the E-Way Bill System? 2025 Update
As per the Official NIC guidelines, the portal now includes:
- 2-Factor Authentication (2FA) for portal logins via OTP
- The transport mode requires consolidation of EWB (EWB-02)
- E-Way Bill auto-generation from e-Invoice is now live for eligible users
- Allows multi-vehicle entries for all transport modes
- Validates entries in bulk Excel uploads
- The Vehicle type field is now required in Part B
What Is an E-Way Bill?
Under the GST framework, if you’re managing any movement of goods valued over ₹50,000, you require an E-Way Bill whether you’re selling, transferring, or returning stock.
It’s a compliance tool that links your shipments to GST records, making them verifiable in transit, whether you’re delivering within a city or across states.
Unlike transport challans or invoices, this document is generated digitally and tracked through the government portal. This mandate applies to both inter-state and select intra-state transactions, depending on your state’s rules.
The bill must be generated before the goods leave your premises, and it becomes part of your tax documentation trail.
The required format is Form EWB-01, which can be generated through the official portal. While you’re usually the one responsible for developing it, that role can also fall to the recipient or transporter, depending on who initiates the movement.
How to Fill the E-Way Bill: Step-by-Step Guide
You can generate the E-Way Bill through the official portal. Here’s how to fill the GST EWB-01 form without missing a field.
Step 1: Log in to the Portal
Visit the E-WayBill System portal and log in using your GSTIN, Username, and Password.
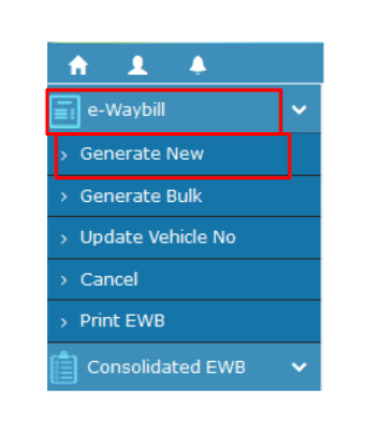
Step 2: Click Generate New
From the dashboard menu, go to E-Way Bill > Generate New to open the form.
Step 3: Fill in Part A — Shipment Details
In this section of the E-Way Bill format, you’ll enter the key consignment details:
- GSTIN of the supplier and the recipient
- Invoice or bill number
- Date of invoice
- Value of goods
- HSN code
- Dispatch and delivery pin codes
- Reason for transportation
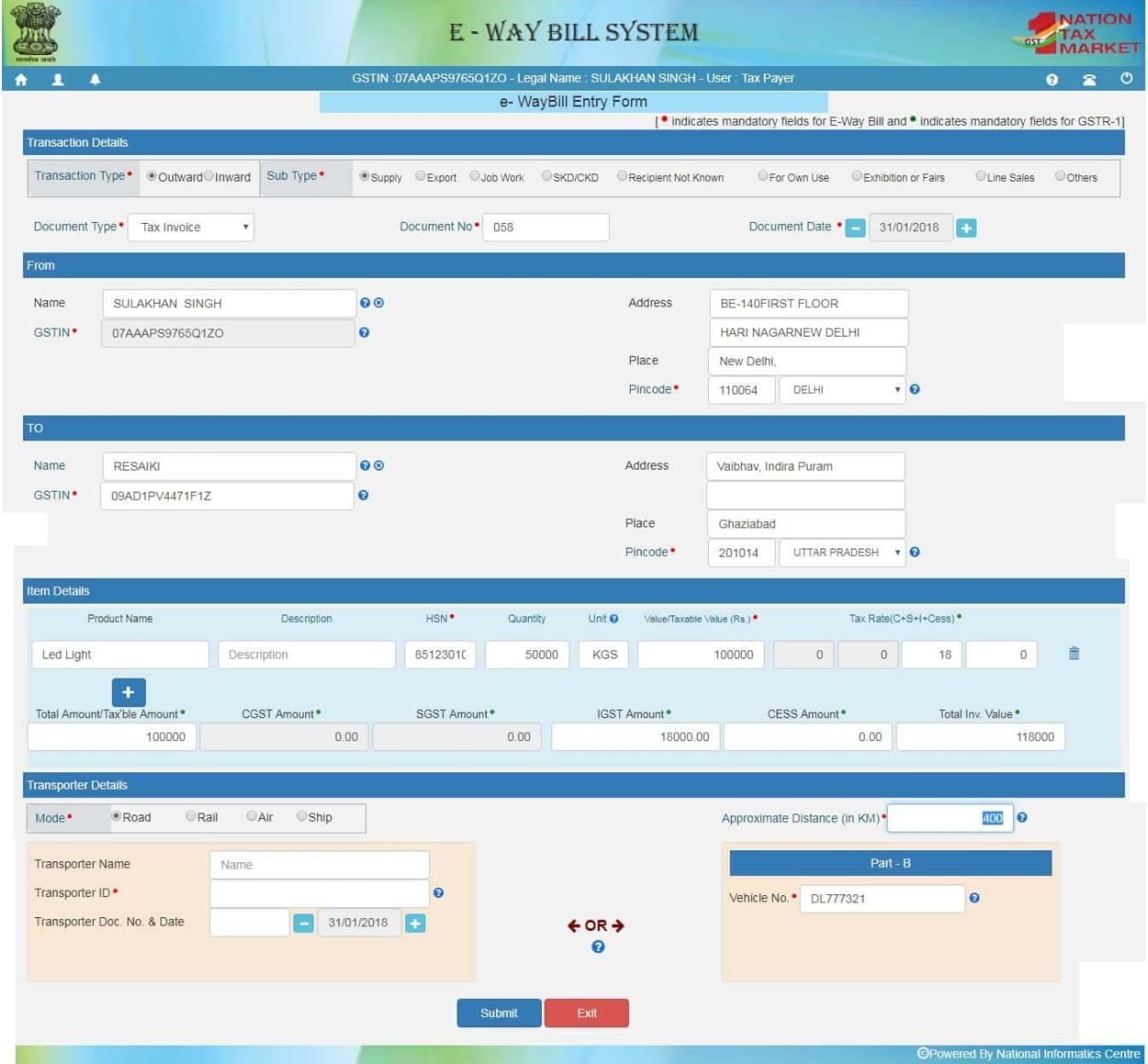
Step 4: Fill in Part B — Transport Details
Next, complete the movement section:
- Vehicle number (mandatory if goods are dispatched)
- Transporter ID or name
- Mode of transport (road, air, rail, ship)
- Document number, such as LR, challan, or bill
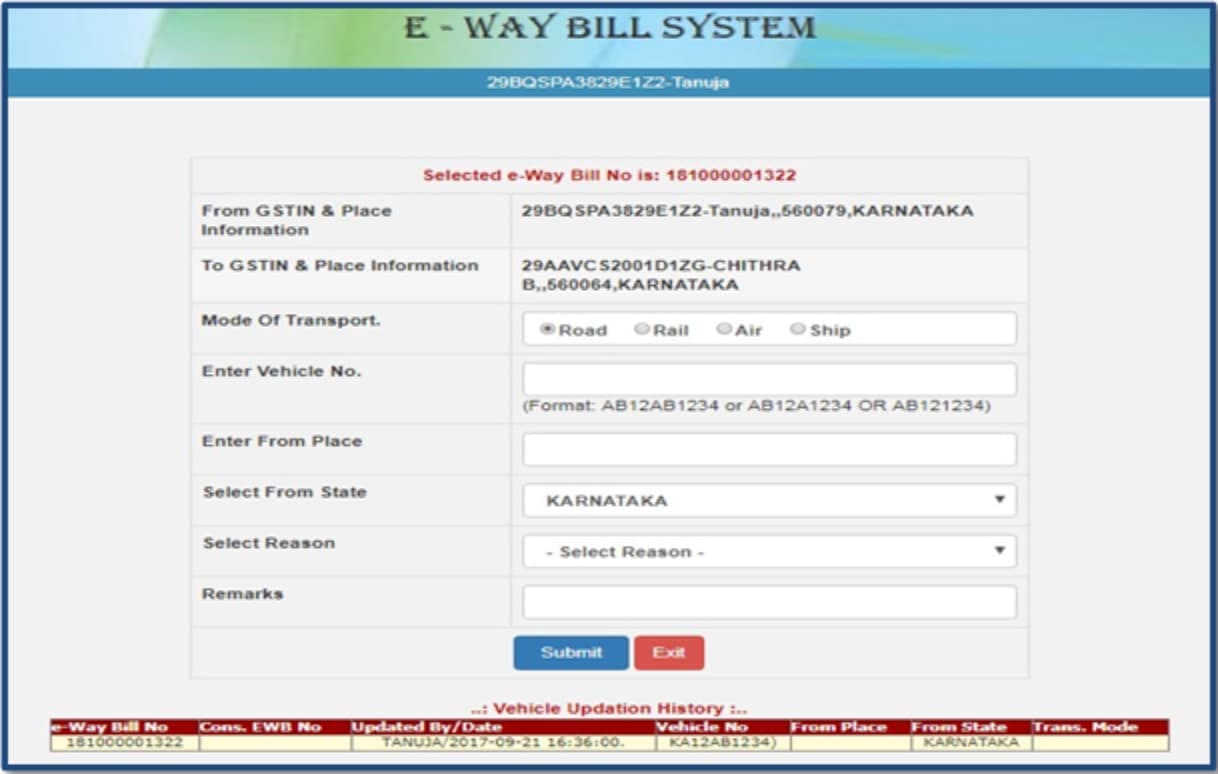
Step 5: Submit and Generate
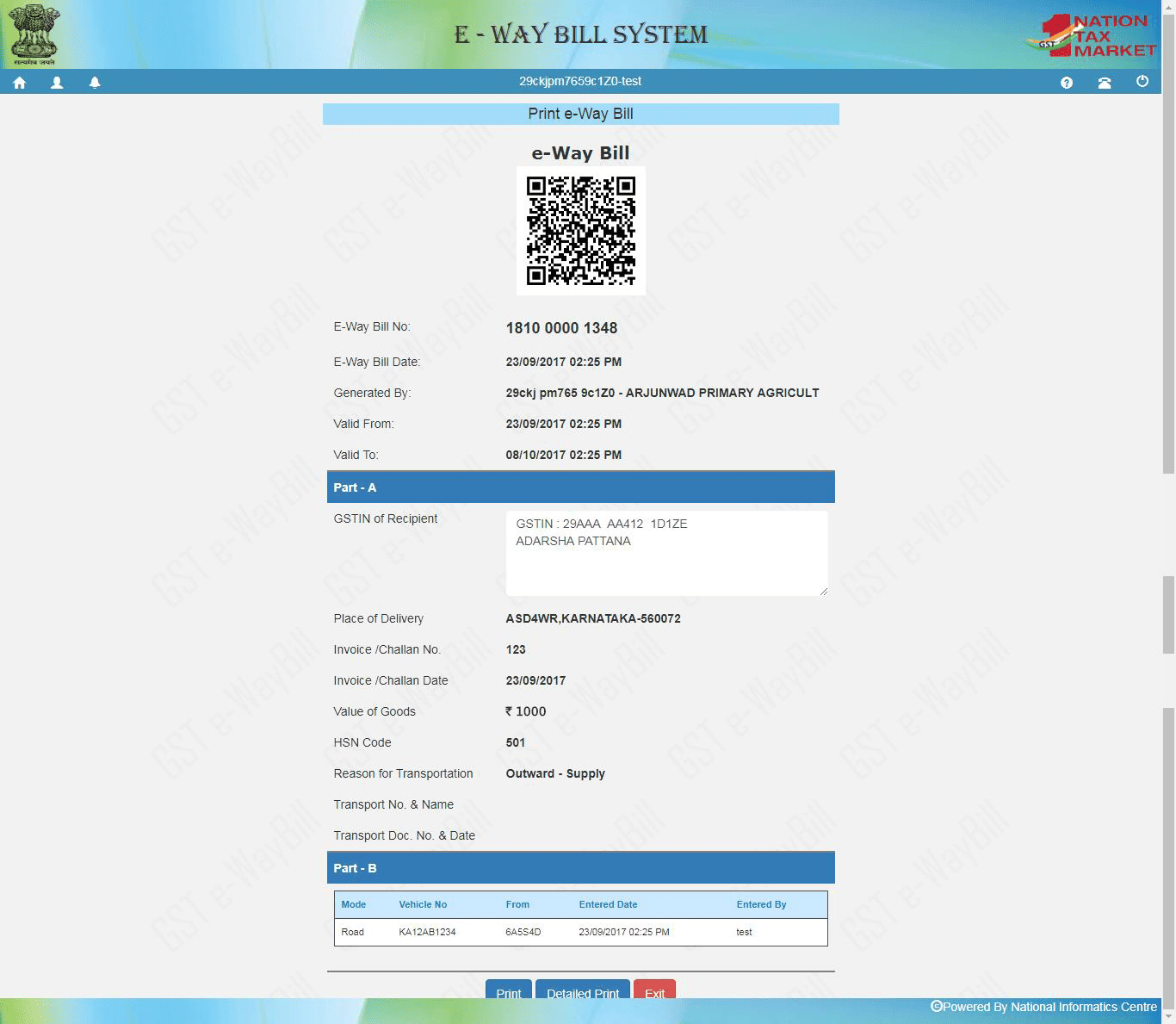
Click submit after reviewing the entries. Once successful, the system will generate a unique E-Way Bill Number (EBN) along with a printable document.
Who Needs to Generate an E-Way Bill?
Depending on your role in the transaction, the responsibility to generate an E-Way Bill changes. Use the below to identify who should initiate it:
| Party Involved | When You’re Responsible | Example |
Registered supplier |
→ Dispatching goods over ₹50,000 |
→ You’re sending goods worth ₹10,000 via your van |
Registered recipient |
→ Supplier is unregistered |
→ You pick up raw materials from an unregistered raw materials supplier |
Transporter |
→ Neither party generated the EWB |
→ You’re hired to move goods via truck, but no EWB was created |
Unregistered supplier |
→ Not required to generate EWB yourself |
→ You’re selling locally to a GST-registered buyer who collects the goods |
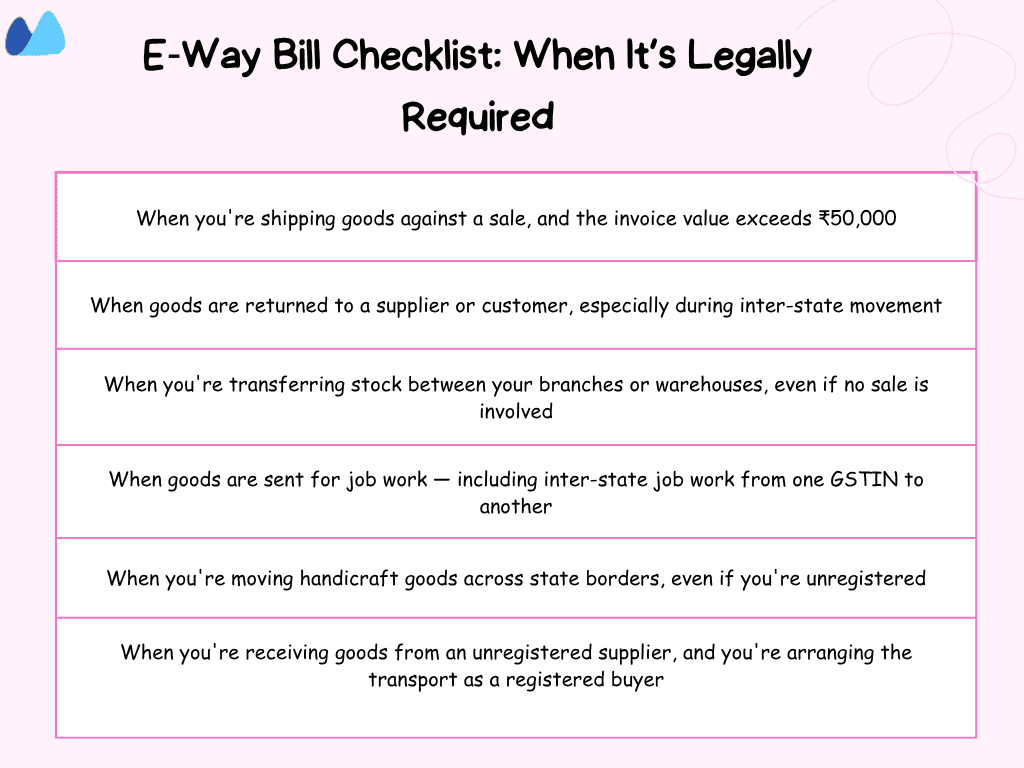
When Is an E-Way Bill Not Required?
There are specific cases where you don’t need to generate an E-Way Bill, even if goods are being transported. Understanding these exceptions helps you stay compliant without wasting time on unnecessary documentation.
1. Consignments under ₹50,000
You don’t need to generate a bill if:
- The total value of goods in a single consignment is below ₹50,000
- You’re not bundling multiple invoices into one transport document
☑️ This rule applies whether you’re the supplier, recipient, or transporter.
2. Transport Using Non-Motor Vehicles
You’re exempt if goods are being moved using:
- A bicycle
- Hand cart
- Push cart
- Other manually operated vehicles
☑️ Motorized transports such as trucks, vans, etc., are not covered under this exemption.
3. Goods Moved under Customs or Government Supervision
No E-way Bill is required when goods are:
- Transferred from a custom port
- Transferred from an airport
- Transferred to the station at an Inland Container Depot
- Moved under customs bond or a transit document issued by the authorities
☑️ This exemption is meant for regulated supply chains involving customs oversight.
4. Exempt Goods and Special Categories
You can skip the bill if the goods fall under these categories:
- GST- exempt items like fresh fruits, vegetables, milk, bread, etc
- Shipments sent by or to defense establishments
- Transport involving government-authorized agencies under special permissions.
💡 Kladana Vs Manual Entry: Automate Your Invoicing Before Dispatch
Auto-fill from invoices or POs. No field mismatches. No rework. Generate GST-compliant E-Way Bill — the smart way
Benefits of the E-Way Bill Format
Using the correct E-way Bill format helps ensure compliance. It’s a tool that supports your business operations, such as:
- When you follow the correct format and meet all the GST documentation rules in one place, you reduce the risk of fines or penalties during transport checks.
- You avoid delays at checkpoints because transporters, suppliers, and recipients are all working from a standardized format that’s easy to verify on the spot
- With a consistent format, you can digitally track every consignment. It makes it easier to respond to audits, track goods in transit, and reconcile deliveries
- You simplify coordination between teams. It helps them from creating the invoice to the transporter
📚 Recommended Read: Generating E-Way Bills from your purchase orders? Use these free PO templates — editable, GST-compliant, and built for dispatch workflow
When should an E-Way Bill be generated?
You must generate the E-Way Bill before dispatch, once the invoice has been issued and the transport details are confirmed. Delays or post-dispatch generation are treated as non-compliance under GST.
What Goes into the GST EWB-01 Form?
The GST EWB-01 form is the standard format used to create your E-Way Bill. It’s divided completely correctly to stay compliant.
Below you can see the breakdown of each field.
Part A — Consignment Details
| Field | What You Need to Enter |
GSTIN of supplier |
Your business’s GST number |
GSTIN of recipient |
The GST number of the buyer or consignee |
Invoice/bill number |
The document number linked to this consignment |
Invoice date |
The commercial document number linked to this consignment |
Value of goods |
The date on which the invoice or bill was raised |
HSN code |
Harmonized System of Nomenclature code for the items being shipped |
Dispatch from/ship toComplete the pin code and state of the dispatch and delivery location |
Complete the pin code and state of the dispatch and delivery location |
Reason for transportation |
Sale, transfer, job work, return, or other applicable reason |
Part B — Transport Details
| Field | What You Need to Enter |
Vehicle number |
Registration number of the vehicle moving the goods (mandatory for road) |
Transporter ID/name |
GST-registered transporter’s ID or name if using a third-party service |
Mode of transport |
Select from road, rail, air, or ship |
Document number |
LR number, bill of supply, challan, or dispatch note reference |
📚 Recommended Read: Need a compliant GST invoice before generating your E-Way Bill? Download GST Invoice Templates In Excel, Word, PDF & Docs — ready to use, editable, and GST rule-aligned
E-Way Bill Formats: Excel, Word, PDF, Docs, Sheets
You can choose from various E-Way Bill formats according to your preferred working style. All formats follow the structure of the GST EWB-01 with a placeholder for both Part A and Part B.
E-Way Bill Format in Excel
Best for bulk entry, editable templates, and offline record-keeping.
- You can download and open the file in Excel or Google Sheets
- You can replace the placeholders with your actual consignment and transport details
- You can use formulas to auto-calculate taxable value or totals
- You can save and print as needed
✅ Pros: Fully editable, great for high-volume dispatches
❌ Cons: Requires manual formatting if printed
E-Way Bill Format in Word
Useful when you need a quick, single-page document in a printable format.
- Open the Doc or DocX file
- Edit your details directly in the template
- Print and share with the transporter
✅ Pros: Simple and print-friendly
❌ Cons: Not ideal for batch entry or reuse
E-Way Bill Format as a PDF
Use this for finalized, non-editable versions.
- Fill the form manually or using PDF editing tools
- Save a locked version for the transporter and audit reference
✅ Pros: Secure and clean layout for submission
❌ Cons: Not editable without a PDF editor
E-Way Bill Format in Google Docs
Great for online collaboration or if multiple users need to edit and review.
- Open the template in Google Docs
- Share with your team or transporter
- Use “comment” or “suggest” mode to review entries
✅ Pros: Easy to share and collaborate in real time
❌ Cons: Requires internet access
E-Way Bill Format in Google Sheets
Perfect for tracking dispatches and collaborating with the logistics team.
- Enter shipment data by row
- Share access with multiple users
- Create one sheet per client, transporter, or region
✅ Pros: Cloud-based and version-controlled
❌ Cons: Not ideal for print formats
⚠️ Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Even if you generate the E-Way Bill on time, minor formatting errors can lead to delays, penalties, or shipment rejection. Here are the most common mistakes businesses make and how to avoid them:
You enter the wrong vehicle number or forget to update part B
⟶ Your E-Way Bill becomes invalid for road checks. You should always verify vehicle details before dispatch
You let the validity expire on long-distance shipments
⟶ If your delivery takes longer than expected, extend the validity period through the portal
Your GSTIN, Invoice number, or item value doesn’t match the invoice
⟶ These must match exactly. Always cross-check against your invoice or auto-generate using ERP tools
You skip required fields like HSN code, transporter ID, or reason for transport
⟶ Leaving any mandatory field blank can block submission. Fill all sections carefully or use pre-valid templates
You upload bulk data with mismatched or duplicate entries
⟶ Use the right Excel format and validate before uploading
You forgot to update the vehicle info after transhipment
⟶ If the goods are shifted mid-route, update Part B immediately to stay compliant
How to Avoid These Issues
- Always verify your master data, such as customer GSTINs, HSN codes, and addresses, before filling the form
- Use a pre-validated invoice or purchase order to avoid manual entry errors
- Double-check vehicle details and mode of transport before submission
- Keep an eye on the validity period, especially for the inter-state or long-distance consignments
Penalties for E-Way Bill Non-Compliance
If you fail to generate or update your E-Way Bill, it’s treated as a GST violation, even if your goods are valid. The consequences affect both your finances and your operations.
What penalties can apply:
- A monetary fine of ₹10,000 or the tax amount (whichever is higher)
- Seizure or detention of goods in transit
- Vehicle confiscation in severe or repeated cases
- Delivery disruption that affects customer experience and downstream operations
Example: What Non-Compliance Looks Like
You dispatch a ₹1.5 lakh consignment with an outdated vehicle number or an expired E-Way Bill. The truck is stopped at a checkpoint, and without a valid bill, your goods are seized. You pay the fine and face delays of 2–3 days, which can damage both your margins and reputation.
Summary
Using the correct E-Way Bill format isn’t just a GST requirement. It’s how you avoid penalties, reduce delays, and maintain trust across your supply chain. When your forms are accurate, your shipment data matches your invoices, and your transport details are verified upfront, you simplify compliance from the start.
Whether you’re handling dispatches daily or scaling operations across multiple states, a straightforward E-Way Bill process supports the effective management of your small business. It keeps your logistics team one step ahead.
Frequently Asked Questions on E-Way Bill Template
What if goods aren’t moved after generating the E-Way Bill?
You can cancel the E-Way Bill within 24 hours if the shipment doesn’t take place. After that, cancellation isn’t allowed.
Can I cancel or modify the E-Way Bill?
✅ You can cancel it within 24 hours if the goods weren’t moved
❌ You can’t modify key fields, such as GSTIN or invoice number. Cancel and regenerate if anything changes
Is the E-Way Bill required for low-value goods?
No. You’re exempt if the consignment’s taxable value is below ₹ 50,000, unless you’re moving inter-state handicraft goods or goods by a registered supplier.
What’s the validity period of the E-Way Bill?
The default validity is based on distance.
Distance: Up to 100km → Validity: 1 day
Distance: Every additional 100 km → Validity: +1 day
Can I generate a consolidated E-Way Bill?
Yes. If you’re moving multiple consignments in one vehicle, you can issue a consolidated E-Way Bill (Form EWB-02). Each shipment still needs its EWB-01.
How many types of E-Way Bills are there?
There are two types based on movement:
- Normal: For a single consignment
- Consolidated: For multiple consignments in one vehicle
And four types based on transaction structure:
- Regular: where billing and shipping are to the same party
- Bill to ship: where one party is billed and another receives the goods
- Bill from dispatch: Where goods are sent from a different location than the seller’s address
- Combination: where all four parties involved in billing and shipping
Can I generate an E-Way Bill without a vehicle number?
Yes. You can generate Part A of the form without vehicle info. However, you must update Part B with the correct vehicle number before the goods are moved.
What is the vehicle that breaks down during transport?
You’ll need to update Part B with the new vehicle number. This ensures the E-Way Bill stays valid during rerouting or transshipment.
Do I need a separate E-Way Bill for returns or replacements?
Yes. Any movement of goods above ₹50,000. It includes returns, repairs, or even replacements, which require a new E-Way Bill with the correct reason selected.
Can transporters generate E-Way Bills?
Yes. If neither the supplier nor the buyer generates it, and you’re handling the shipment (as the transporter), you are responsible for generating the E-Way Bill before the goods move.
List of Resources
- E-Way Bill: Official Log In Portal
- E-Way Bill 2025 Update: E-Invoice Systems and 2-Factor Authentication
Read‑alikes
GST Invoice Template: Download Free Formats in Excel, Word & Google Sheets
4 Free Purchase Order Templates with a Step‑By‑Step Guide: Excel, Word, and Google Sheets Format
How To Create a Quotation Format In Excel, That’s GST Ready, Error-Free, and Built for Scale
Quotation Format In Word: Free Templates for Freelancers, SMEs & MSMEs, Step-By-Step Guide
Sales Report Templates: Tips, Examples, and 4 Free Downloads in Excel, Word, PDF, and Google Sheets