Every manufacturing floor faces a prime challenge of managing the schedule. Without one, there can be chaos. And that’s why there’s a need for production planning.
Because efficient production for manufacturing operations can save a lot.
A PPCexpo report mentions that manufacturers optimizing their production planning can achieve up to a 30% increase in operational efficiency.
Small and mid-sized factories can use Excel and Google Sheets. These are basic tools where operations managers map out what needs to happen, when, and with what resources.
To use those effectively, you need a well-built template production plan so teams can align tasks, reduce wasted time, and deliver on deadlines.
You can manage garment batches, food production lines, or electronics assembly; it doesn’t matter. You only need a reliable production schedule template to avoid surprises and make faster decisions.
Read on to explore free, editable templates designed for real factories, plus step-by-step tips on using them effectively.
What Is a Production Schedule?
A production schedule is a structured document that lays out what products will be made, when they will be made, and which resources will be used. Overall, you’ll use it as a roadmap for turning raw materials into finished goods.
When it comes to the manufacturing process, your production schedule sits right between production planning (which decides what’s needed) and execution (where machines, people, and processes get moving).
Why does it matter so much?
It matters because you need a schedule for repetitive activities. Also, a production template can be a great help, especially by helping you avoid idle time, meet promised deadlines, and maximize your resources.
You’ll risk missing orders, overrunning costs, or overloading machines and teams without it.
What to Include in a Production Scheduling Template
A template production plan is only as valid as the details inside it. You’ll need to capture just enough to track everything that matters. Do not make it so jammed that it becomes impossible to update or read.
Here’s what should always go into a solid production schedule template:
Date/Week/Shift
Every task should be time-stamped, whether by week, day, or shift (especially if you run 24/7 operations). This organizes the timeline and ensures nothing slips.
Production Order ID
Assign a unique identifier to each production job so it becomes easier to trace the order through planning, execution, and delivery.
Product/Batch
Include what is being produced in terms of item name, product code, or batch reference. Batch numbers are essential to track compliance or quality in industries like food and chemicals.
Quantity Required
Clearly state how many units are expected per run. This helps match raw material needs, machine settings, and labor allocations.
Estimated Time Per Unit
Estimate how long it takes to produce a unit. Multiply this across the quantity to get a realistic timeline, which is a ‘must’ for accurate capacity planning.
Assigned Machine or Work Center
Map each job to a specific machine, assembly line, or workstation so that you can balance workloads, avoid overloading, and identify where there’s idle capacity.
Start and End Time
Add precise time slots to avoid overlaps and conflicts. These slots help synchronize parallel processes, minimize downtime, and track progress during the shift.
Remarks (e.g., Delays, Hold-ups)
Leave room for notes on issues, adjustments, or dependencies. Tracking disruptions can help improve the next round of planning.
Download Production Schedule Templates (Free)
Sometimes building a template production plan from scratch takes more time than you can spare, especially when deadlines loom and your team waits for instructions.
That’s where ready-to-use templates come in handy.
Below, we’re offering a curated set of free production schedule template downloads designed for different manufacturing inventory setups.
Each is available in Excel and Google Sheets formats, so you can choose what works best for your team.
A. Weekly Schedule Template
This sheet is ideal for small factories or workshops that plan weekly. It breaks down production tasks by week, helping you match output to demand forecasts.
OR
B. Shift-Based Sheet
You can choose this if you’re running operations across multiple shifts. It helps track which team or crew is responsible for what batch, machine, or workstation. This includes columns for start/end times, shift leaders, and any carryover notes between teams.
OR
C. Job Order-Based Planning
Download this for operations across multiple shifts, as it lets you track which team or crew is responsible for what batch, machine, or workstation. This template will include columns for start/end times, shift leaders, and any carryover notes between teams.
OR
D. Gantt-Style Production Calendar
Want a visual? Check out this template that uses conditional formatting and bars that mimic a Gantt chart for production. It’s perfect for mapping dependencies, overlapping tasks, or seeing the entire month at a glance.
OR
How to Use the Template in Real Production Planning
You may get the template production plan ready, but it’s only the first step. You also need to learn how you will use it daily on the shop floor, and that can make all the difference.
The templates we shared are helpful when you integrate them into your team’s routine. It’ll help you guide production from order intake to final output.
Step-by-Step Use Case
Now, let’s start loading your production orders into the template.
This includes:
- Order ID or reference number
- Product name or batch details
- Quantity to be produced
- Required completion date
- Assigned machine or line
Once you enter all the necessary details, you must arrange tasks by date, shift, or priority. Leverage the template’s timeline or calendar view to check for overlaps or bottlenecks.
For example, you may encounter two jobs competing for the same machine. Now you can reassign or reschedule in advance.
Who Updates It (Planner, Supervisor)
You can choose who can update the template and draw some accountability.
Planner/Operations Manager: They’ll be responsible for entering the initial schedule, production targets, and capacity plans.
Supervisor/Shift Lead: Anyone in this position will update the progress on the floor, mark completed tasks, flag delays, or even note machine issues.
QA or Production Head: It includes reviewing for the final sign-off, especially when dealing with high-value or export orders.
It starts with assigning clear ownership to update the sheet, or the key details can go missing.
Color Coding or Formula Tips
Color cues can make your production schedule template more visually appealing and simplify tasks.
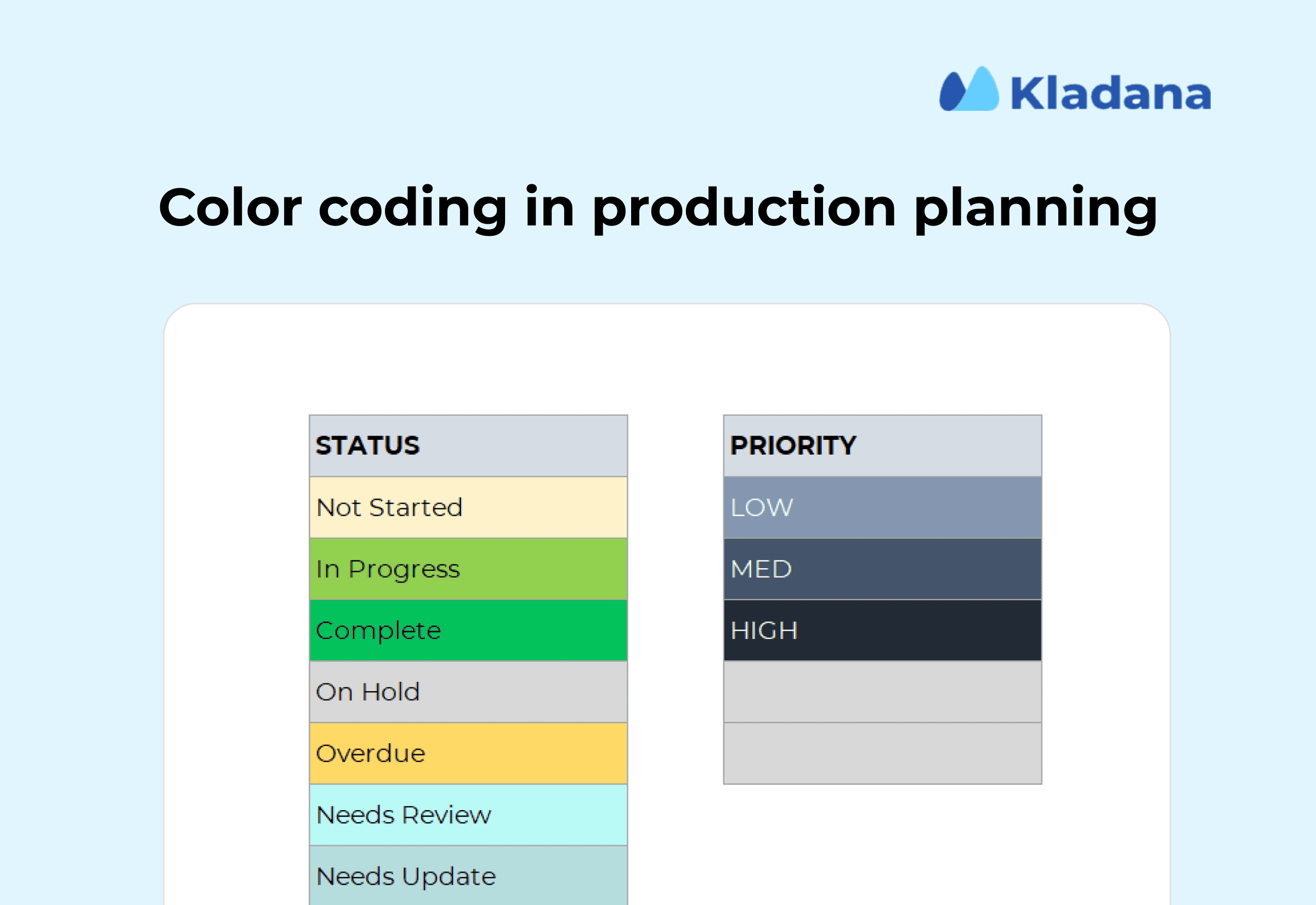
For example, some of the color coding will involve colors like:
- Green: On track
- Yellow: Minor delays or rescheduled tasks
- Red: Critical delays or machine downtime
Apply Excel or Google Sheets’ conditional formatting to automate this.
Simple formulas also help: for example, =IF(CompletionDate<TODAY(),"On Time","Late") can auto-flag tasks.
Summing up quantities (=SUM), calculating shift loads, or using VLOOKUP to reference part numbers from a catalog can streamline data handling and reduce manual errors.
Integrate with Tools Like Kladana
If you want to take it further and drive automation, you can also leverage Kladana. You can simply connect your spreadsheet with Kladana’s production management module:
- Push production orders directly from Kladana into your scheduling sheet.
- Sync BOM (bill of materials) data for material availability checks.
- Pull real-time WIP (work-in-progress) status into your schedule for live tracking.
Such a blended approach of flexible spreadsheets and Kladana for automation gives your team the best of both worlds.
This way, you don’t need to abandon your familiar template, but you can speed up and improve accuracy by linking it to live systems.
⚡ Still scheduling production in Excel?
Kladana automates orders, materials, and costs — all in one system
Manual Spreadsheet vs. Automated Scheduling Tools
As a manufacturing business, you have two choices: stick with manual tools like Excel and Google Sheets or upgrade to automated scheduling software.
What manual spreadsheets offer
Manual spreadsheets remain a popular starting point because they’re practical and easy to set up. You don’t need fancy software, complex onboarding, or long-term commitments.
It offers the following:
Flexibility
Get a custom layout that matches your process. You can add columns, reorder rows, or adjust formats based on what works best for your shop.
Low cost
You only need tools like Excel or Google Sheets, which do not require investing anything more.
Fast start
Build and implement your production template in hours, as there’s no waiting for IT or vendor support.
Familiarity
Most team members already know the basics of spreadsheets, reducing training needs.
Simple updates
For small operations, it’s often fastest to type in changes directly, especially when only one or two people manage the plan.
Where manual spreadsheets struggle
When operations grow, you must think beyond the manual sheets to keep up with the increasing demands. Updates lag, and errors creep in, leading to coordination issues and costly delays.
Version control
When several team members update the sheet, there’s a high risk of overwriting changes or working with outdated data.
Delayed updates
Shop floor scheduling can adapt to quick changes such as machine breakdowns and supply delays. However, updating a shared sheet in time is rarely realistic.
Limited visibility
Spreadsheets don’t automatically pull data from machines, WIP (work in progress), or inventory systems, creating blind spots.
Manual data entry
Every update requires human input, increasing workload and the risk of entry mistakes, especially as orders multiply.
Lack of integration
Standalone sheets operate in isolation, meaning there’s no seamless link to order systems, BOM (bill of materials), or warehouse updates.
| Feature | Manual Spreadsheet (Excel/Sheets) | Automated Scheduling Tools (e.g., Kladana) |
Setup time |
Instant, user-built template |
Needs software setup and integration |
Cost |
Minimal (often free) |
Software subscription or licensing fees |
Scalability |
Suitable for small teams, tricky for larger operations |
Designed to scale with team and process growth |
Data accuracy |
Relies on manual updates |
Real-time sync from the production floor and systems |
Integration with BOM/WIP |
Manual or partial |
Complete integration across orders, materials, and WIP |
Reporting |
Requires manual compilation |
Automated reports and dashboards |
Where Kladana fits in
Returning to the core question: Are you planning to integrate automation?
If yes, how do you fit in Kladana beyond static templates?
Why SMEs Trust Kladana as Their ERP Solution:
✅ Production Order Management — Plan and track every stage of production with clear visibility into operations, from raw materials to finished goods.
✅ Material Requirement Planning — Estimate raw material needs in advance to avoid last-minute procurement delays and stock shortages.
✅ Smart Task Scheduling — Schedule production tasks based on priority, capacity, and resource availability to keep operations running smoothly.
✅ Real-Time Inventory Sync — Monitor inventory levels throughout the production cycle, including raw materials, WIP, and finished goods.
✅ Employee Assignment Tracking — Assign tasks to specific team members and monitor progress to improve accountability on the shop floor.
✅ Production Cost Calculation — Automatically calculate production costs based on consumed materials and operations to fine-tune pricing and margins.
Now, for a small factory, you can start with Excel or Google Sheets, which makes sense.
But, as your production complexity rises, you’ll need to bring in an automated tool like Kladana to save time. It’ll eventually drive coordination and even reduce costly errors.
FAQs on Production Schedule Templates
Got questions?
Here’s a quick roundup of what many planners ask.
What is a production schedule template?
It’s a structured sheet (Excel or Google Sheets) to organize production tasks, timelines, and resources.
How do I create a production schedule in Excel?
Start with a blank sheet, define key columns (order, product, quantity, machine, dates), and apply formulas for tracking totals or shifts.
What should be included in a manufacturing schedule?
Include order IDs, products, required quantities, assigned machines, start/end times, and any remarks.
Is there a free Excel or Google Sheets production schedule template?
Sure… see our downloadable templates section above.
How is a production schedule different from a production report?
A schedule plans upcoming work; a report summarizes completed work.
Can I use a template for both batch and continuous production?
Yes, with some adjustments for how you track time and quantities.
How do I manage shift-wise or weekly production planning?
Use dedicated templates with shift-based or weekly layouts.
Can production schedules be automated using ERP software?
Yes! Tools like Kladana automate scheduling, task tracking, and inventory sync.
What’s best to plan production when delays or downtime hit?
Update your schedule in real time and reassign tasks based on available capacity.
Are there industry-specific templates (e.g., garments, food, furniture)?
Definitely! You’ll find specialized layouts designed for different sectors in the download section.
Kladana offers an all-in-one solution for manufacturers who want more than just a template production plan.
There’s built-in production management, BOM tracking, real-time inventory sync, and automated scheduling that cuts manual work and boosts on-time delivery.
Gain More Efficiency by Switching to Kladana from Excel
Kladana gives you real-time control, fewer errors, and faster workflows.
No more copy-paste chaos.
List of Resources
PPCexpo — Production Planning in Manufacturing Industry: Key Insights