Businesses often have their employees wasting a lot of time doing repetitive, mundane tasks. A Clociky study estimates that 90% of workers feel overwhelmed by the sheer volume of tedious tasks they face daily. A solution to this issue is — business process automation (BPA).
The term BPA is often used to highlight the way businesses use different technologies to automate processes. It contributes to ensuring the smooth running of business processes without the constant need for manual input, saving time and cost.
In this article, we’ll explore the need for business process automation and discuss its importance, examples, benefits, and use cases.
- What is Process Automation?
- What is Business Process Automation?
- Why is Business Automation Important?
- Exploring BPA With Practical Examples
- Challenges of Business Process Automation
- 10 Benefits of Business Process Automation
- A Step‑by‑Step Process to Implementing Business Process Automation
- Tools, services, and software for Business process automation
- Features of Business Process Automation
- Best Practices for Business Process Automation
- FAQs on Business Process Automation
What is Process Automation?
Process automation is a method that involves the use of technology (in terms of tools) to execute repetitive, rule‑based tasks. It needs zero to minimum human intervention with an intent to drive efficiency, accuracy, and cost savings.
With process automation, businesses can streamline tasks by using technology to handle complex processes. It focuses on three key areas: automating tasks, organizing information in one place, and minimizing the need for manual input. This system is built to eliminate delays, and reduce mistakes and data loss while also improving transparency, communication between teams, and overall efficiency.
Here’s how automation can streamline onboarding a new employee. Once a candidate accepts the job and sets their start date, the HR recruiter enters this information into the onboarding system. This triggers several automated actions:
- A unique portal is created for the new hire, and an automated email is sent to them. The new employee then enters their details and uploads the necessary forms.
- Based on the employee’s role and department, business rules determine what IT equipment and access they’ll need. The IT department prepares a laptop and ensures it’s ready for the employee’s first day.
- The facilities manager receives an automated email notifying them of the new hire. They assign a workspace, and the system logs this information on the new employee’s portal so they know where to go on day one.
- AI technology extracts tax and banking information from the employee’s forms, and integration with the company’s systems sends this data to payroll and expense management.
Automation like this can be applied to many areas of an organization, including supply chain, acquisitions, and customer onboarding. It saves time, reduces errors, and creates a better experience for both employees and customers.
What is Business Process Automation?
Business Process Automation refers to using technology to automate repetitive, time-consuming tasks within your business to drive efficiency across the organization. BPA orchestrates complex workflows by automating repetitive tasks, routing information, and triggering actions to minimize manual intervention. This needs a blend of software and predefined rules to streamline business processes.
At its core, BPA typically involves –
- Workflow engines that define and manage the sequence of tasks and decision points within a process.
- Integration tools that are connected to different systems to enable seamless data exchange between them.
- Business rules engines that automate decision-making based on predefined criteria.
- Data analytics which monitors and optimizes process performance.
Note that business process automation (BPA) is one part of a more extensive area of BPM (business process management), which focuses on only a few operations. This area often includes Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Digital Process Automation (DPA).
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Automates individual tasks that are typically repetitive and rules-based. Here’s how BPA vs RPA differs when compared head‑on.
Digital Process Automation (DPA)
A step beyond BPA that optimizes and automates end‑to‑end processes involving customer interaction.
Intelligent Process Automation (IPA)
This is an advanced form of automation that blends RPA with AI and machine learning (ML) to automate tasks and also learn and adapt over time. Here’s how IPA differs from Robotic Process Automation (RPA).
Let us further explore the significant terms used in automation — BPA, RPA, DPA, IPA, and more — and compare those.
| Feature | BPA | RPA | DPA | IPA |
Focus |
Automates structured processes |
Automates individual tasks |
Automates end‑to‑end processes |
Automates complex, decision-driven processes |
Scope |
Broader, multi-step workflows |
Narrow, specific tasks |
Cross-functional, enterprise-wide |
End‑to‑end, often involving unstructured data |
Technology |
Workflow orchestration, integration, Workflow engines, software |
Rule‑based, screen scraping, Bots, scripts |
AI, ML, RPA, analytics, AI, UI/UX improvements |
AI, ML, NLP, RPA, cognitive automation |
Implementation |
Moderate IT involvement, Focus on workflow improvements |
Quick, low‑code/no‑code options |
Complex IT and business collaboration, focus on digital business transformation |
Complex, requires specialized expertise, adjusting to real‑time data |
Benefits |
Improved process visibility, control |
Increased efficiency, cost reduction |
Enhanced customer experience, agility |
Transformative, strategic impact |
Example |
Purchase order approvals |
Data entry, invoice processing |
Customer onboarding, loan processing |
Claims processing, fraud detection |
Visual |
Gears representing a workflow |
Robot interacting with a single UI |
Network connecting systems |
Brain symbolizing intelligence |
Why is Business Automation Important?
Business automation is essential because it can execute repetitive, time-consuming tasks that were traditionally performed manually. Business process automation acts as a force multiplier, empowering various departments to achieve more with the same resources, driving both efficiency and innovation.
Here’s why BPA is important —
- Provides improved accuracy and consistency across different tasks and processes
- Ensure better customer experience through automated services
- Enable improved accuracy with machine-driven task performance
- Drives employee satisfaction by freeing them up for critical tasks
- Reduces reliance on manual labor to cut down operational costs
Read‑alikes
Revolutionizing WMS Efficiency: Smart Warehouse Barcoding
Full Guide to MRP Solutions: Core Features, Advantages and Pitfalls
ERP Inventory Management: 12 Benefits for Your Business in Full Guide
Exploring BPA With Practical Examples
Now that we’ve covered the basics and the importance of business process automation (BPA) let’s explore its workings with a few examples.
Different industries and business verticals automate critical processes to significantly improve efficiency, reduce errors, and save valuable time across various businesses.
Wholesalers For Inventory Management and Order Processing
Wholesalers can automate managing inventory and processing orders to keep up with demand while minimizing human error. A study by Deloitte revealed that BPA can reduce processing time by 50‑75%. This means manufacturers holding inventories can provide faster order fulfillment and fewer stockouts.
Kladana empowered Vitaly’s sales reps with real-time inventory tracking and automated order processing, eliminating manual tasks. This streamlined operation led to a significant increase in turnover within seven months, showcasing Kladana’s ability to drive business growth.
Explore Kladana helped Vitaly Rizov’s business to automate its inventory and order processing and achieved positive results within 7 months.
One of Kladana’s features is inventory counting. It helps stock takers to keep tabs on their inventory, enabling them to quickly pull data of their existing stock and plan their purchases accordingly.
Production Planning for Manufacturers
The ideal automation for manufacturers will integrate sales data, production capacity, and supplier information to provide optimized production plans.
McKinsey’s study found that automating 64% of manufacturing tasks can save 749 billion work hours. Business process automation will eventually adjust schedules in real time based on unexpected events, like a machine breakdown or a sudden spike in demand.
A typical example would be a mid-sized manufacturer integrating Kladana.
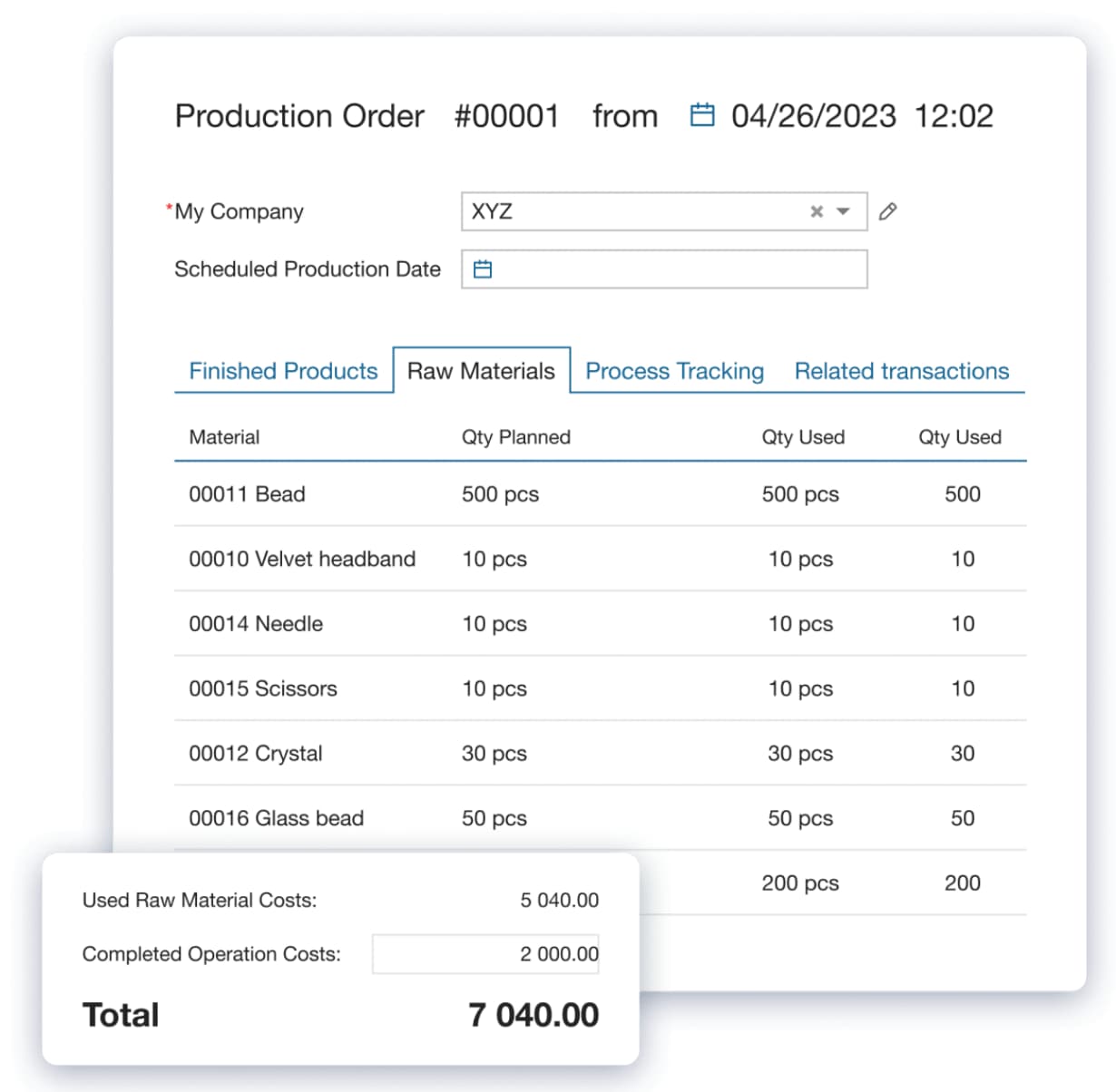
For example, Metako used Kladana to enhance its manufacturing and transform a loss-making business into a market leader. It did so by leveraging Kladana to identify areas of waste and improve efficiency. They also changed their product focus to target the premium segment.
Explore how Kladana’s powerful ERP features rescued a struggling business by turning around its troubled financial operations and making them more streamlined.
In 2024, we hosted a webinar to dive deep into exploring how you can automate your manufacturing using Kladana’s advanced ERP features:
Construction Project Management With Workflow Automation
Construction industry workers need help managing multiple projects simultaneously. Automating project management workflows improves communication, reduces delays, and ensures that the project runs on schedule.
Logistics Companies Can Save Time Using Kladana
One of our clients — am4u.ru, operates a chain of 25 convenience stores. They needed to track sales and replenish inventory efficiently across multiple locations.
As a solution, we implemented an automation system that analyzes real-time sales data, predicts demand, and automatically distributes goods to each store directly from Kladana.

The logistics expert’s workload was dramatically reduced, freeing up 70% of their time for more strategic tasks. Inventory levels were optimized, stockouts were minimized, and overall efficiency soared.
Explore Andrey’s story on how his partnership with Kladana helped him develop in‑app integrations, automate business, and create tailored solutions using the API
Finance Industry Can Optimize Their Workforce Efficiency
Financial institutions must deal with a lot of paperwork, manual data entry, and time-consuming compliance checks, which can lead to delays and potential errors.
Gartner found that accounting departments experience an average of 30% avoidable rework. Implementing robotic process automation in the finance industry can unlock efficiency in various applications, as mentioned below.
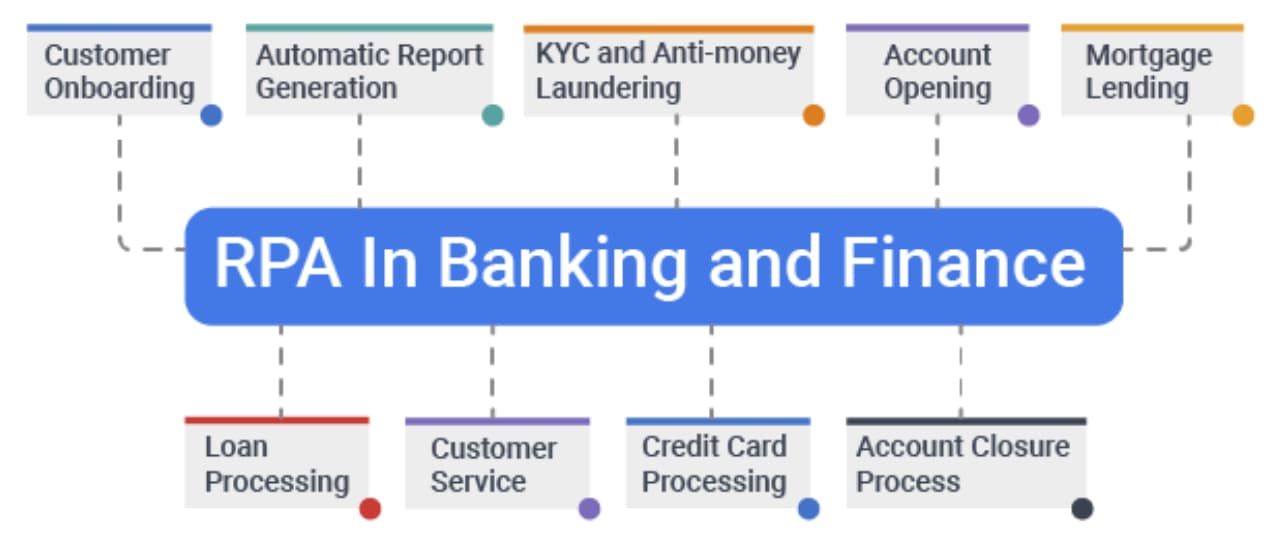
Challenges of Business Process Automation
The benefits of business process automation (to be discussed later) are numerous, but you should anticipate some challenges when implementing BPA.
Knowing these will help you navigate potential issues head‑on.
Initial Investment and Ongoing Maintenance
Automation can unlock cost savings in the long run, but there are upfront costs for software, implementation, and training.
Resistance to Change
People in an organization may naturally resist change as they have to alter familiar work routines or fear job losses due to new technologies. Hence, these concerns need to be addressed proactively through open communication and training programs.
Complexity in Integration
Integrating BPA with existing systems and workflows can be complex, requiring significant effort and expertise. Else, any misalignment can disrupt operations rather than streamline them.
Data Security and Compliance
Automating processes will involve handling sensitive data. Make sure that the data is secure and compliant with relevant regulations, which demand upfront investments in robust cybersecurity measures.
Lack of Expertise
Implementing and managing BPA will demand a certain level of technical expertise. Without skilled personnel, you may struggle with the automation efforts, leading to subpar results or even failures.
10 Benefits of Business Process Automation
It’s not just about doing things faster; it’s about doing them smarter, more accurately, and with less stress. And that’s where business process automation (BPA) will enable multiple advantages, as mentioned below, that go beyond simply streamlining tasks.
#1. Freeing Up Your Workforce
Automation takes the burden of mundane, repetitive tasks off your employees’ shoulders. They can use this time to perform more strategic and goal-specific tasks, leading to enhanced job satisfaction, improved morale, and reduced employee turnover.
Automated technologies like Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Optical Character Recognition (OCR) can extract key information from emails, chats, or even handwritten forms. These are automatically populated into the CRM system, eliminating the need for manual data through intelligent routing.
#2. Bring Down Operational Cost
Automation ensures significant cost savings by reducing the need for manual labor, minimizing errors, and optimizing resource allocation. It can also help you avoid hefty fines and penalties due to non-compliance.
A manufacturing company automates its invoice processing to eliminate the need for manual data entry. RPA further automates invoice validation and approval workflows to reduce the risk of human error and accelerate payment cycles.
#3. Enhanced Accuracy and Reduced Errors
Manual processes are prone to human error, which can lead to costly mistakes, especially in data-sensitive tasks like financial reporting or inventory management. BPA tools ensure that these processes are carried out consistently and accurately, reducing the likelihood of errors and improving the overall quality of work.
A finance department might use robotic process automation (RPA) to read invoices, extract relevant data, and input it into accounting software. Here’s an example of the same.
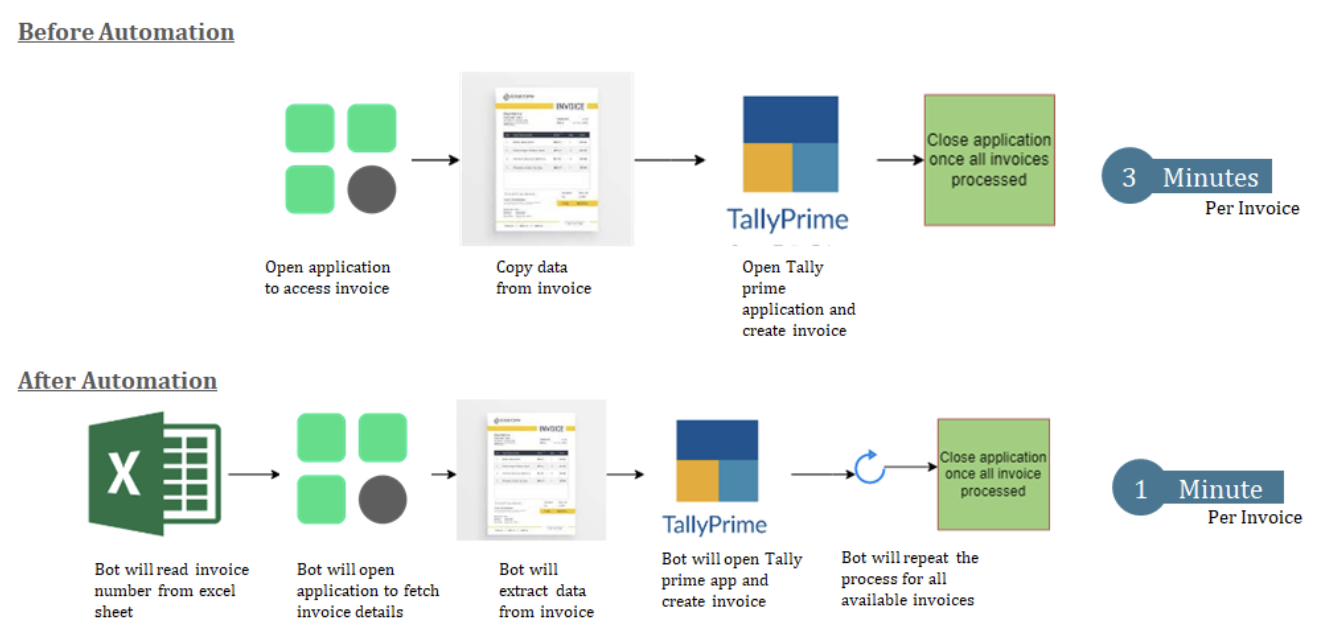
This eliminates the risk of data entry errors and ensures that financial records are accurate and up‑to‑date.
#4. Improved Compliance and Auditability
Automation can help ensure adherence to industry regulations and internal policies by automating tasks like document management, approvals, and audits. This reduces the risk of non‑compliance and protects your business from potential fines and penalties.
A healthcare provider implements a Document Management System (DMS) that provides robust access control and encryption features. The image below explains this briefly.
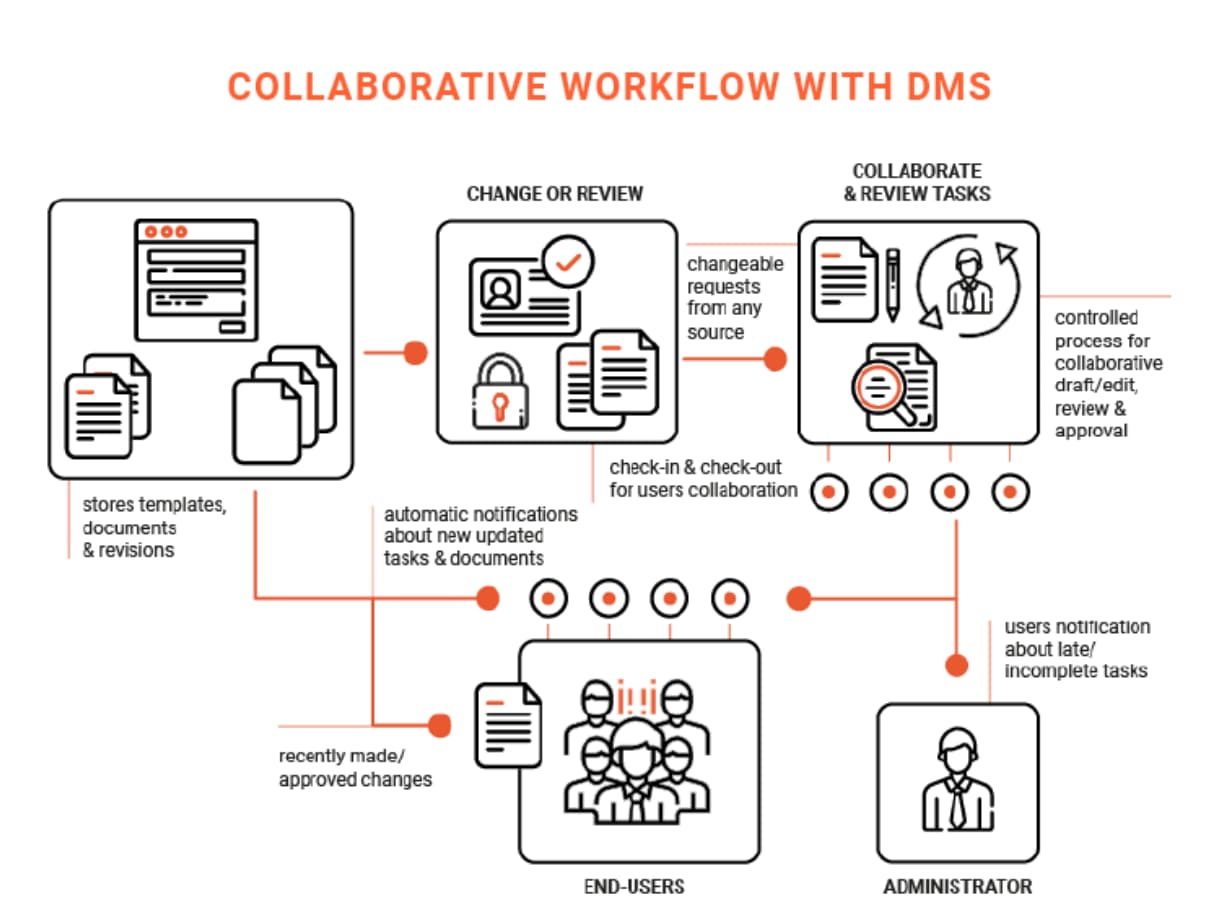
It automates the storage, retrieval, and sharing of patient records, wherein sensitive information is accessible only to authorized personnel. This facilitates compliance with HIPAA regulations and maintains patient confidentiality.
#5. Increase Customer Satisfaction
Automation can improve the speed and accuracy of customer interactions, leading to higher levels of customer satisfaction. Whether it’s through faster response times, more accurate order fulfillment, or personalized communication, BPA helps businesses meet and exceed customer expectations.
A retail company can deploy an AI‑powered chatbot that utilizes Natural Language Processing (NLP) to understand and respond to customer inquiries in a conversational manner. The chatbot can also access the company’s Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system to provide personalized responses, track orders, and even initiate returns.
#6. Gain Real‑Time Visibility
Cloud‑based BPA tools provide real‑time dashboards and analytics, giving you a comprehensive view of your operations. This enables you to track progress, identify bottlenecks, and make informed decisions based on data, not guesswork.
A logistics company utilizes a cloud‑based Transportation Management System (TMS) integrated with GPS tracking and Internet of Things (IoT) sensors to monitor shipments in real‑time.
#7. Achieve Competitive Advantage
Businesses that effectively implement BPA are more agile and responsive to market changes, giving them a significant competitive edge. Automation allows companies to operate more efficiently, reduce costs, and respond quickly to new opportunities or challenges.
A company can implement an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system with integrated supply chain automation tools, among other things (as mentioned below).
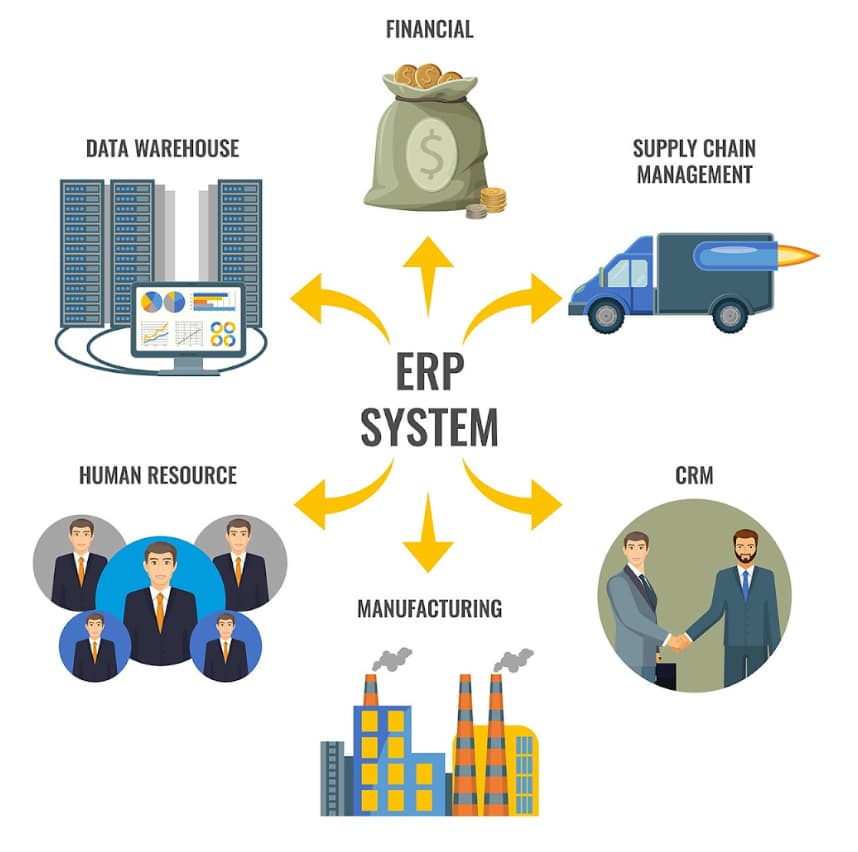
This system provides real‑time visibility into the entire supply chain, from procurement to delivery. In case of disruptions like supplier delays or sudden demand spikes, the system can automatically trigger alerts to recommend alternative suppliers or adjust production schedules.
#8. Enable Faster Time to Market
By automating critical business processes, companies can expedite their product development cycles, bringing new products or services to market more quickly. This speed is crucial in competitive industries where being first to market can make a significant difference.
A software development company utilizes Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipelines to automate code deployment and testing. Streamlining these tasks and reducing manual intervention can significantly shorten the development cycle and allow the company to release updates and new features faster than competitors.
#9. Drive Data‑Driven Decisions
Automation tools can gather and analyze vast amounts of data, providing valuable insights that inform strategic decision-making. This allows businesses to identify trends, anticipate customer needs, and make proactive adjustments to their operations.
A retail chain implements a Business Intelligence (BI) platform that integrates data from various sources, such as point‑of‑sale systems, customer feedback surveys, and social media analytics.
#10. Improve Collaboration and Workflow Efficiency
Streamline workflows and enhance collaboration by automatically routing tasks to the right team members at the right time. This reduces delays and miscommunications and allows teams to work together more effectively.
For instance, a marketing team can leverage an automated project management tool to assign tasks, track deadlines, and send notifications when a team member completes a task. This keeps everyone on the same page as the projects move forward without bottlenecks.
Kladana’s ERP solution helps you automate your business operations. Make your processes more streamlined and efficient.
A Step‑by‑Step Process to Implementing Business Process Automation
Though there are challenges involved in business process automation, adopting a step‑by‑step and thoroughly careful approach could help you journey towards this tech‑driven transition.
Below, we have covered the key steps that help implement business process automation with ease.
A. Implementing BPA for Manufacturing
If you are in the production business (industries like cement production or heavy machinery), your manufacturing department forms the backbone of your business. So, starting off the BPA with manufacturing will set the stage for a smoother, more productive operation.
For instance, when you choose Kladana for manufacturing automation, you can easily integrate it with your existing manufacturing systems. This offers real‑time visibility and control over your production processes.
Steps to implement manufacturing business process automation
Let us explore some of the major steps involved in implementing automation in the manufacturing department.
Step 1: Identify Key Processes
Pinpoint repetitive, time‑consuming tasks like production scheduling, work order management, and quality control.
Step 2: Choose the Right Tools
Select automation software that integrates seamlessly with your existing manufacturing systems and offers features like real‑time monitoring, data analytics, and predictive maintenance.
Step 3: Implement and Integrate
Carefully deploy your automation solutions, ensuring proper training for your team and smooth integration with your existing infrastructure.
Step 4: Monitor and Optimize
Track key performance indicators (KPIs), gather feedback to identify areas for improvement, and fine‑tune your automated workflows.
B. Inventory Automation
Once you automate the manufacturing department, pivot the investments to inventory, which takes care of your products so that you have the right products available in the right quantities at precisely the right moment. This saves you from costly stockouts and overstocks.
Kladana provides your inventory management an edge over others with the inventory management module.
Leverage its real‑time tracking and automated reordering features to keep your inventory optimized, reduce carrying costs, and prevent stockouts.
Steps to implement inventory automation?
Step 1: Centralize Data
Gather all your inventory data into a single, accessible platform. Implement Real‑Time Tracking: Utilize barcodes, RFID tags, or other technologies to track inventory levels in real‑time.
Step 2: Automate Reordering
Set up automated reordering processes based on predefined stock levels and demand forecasts.
Step 3: Optimize Warehouse Layout
Strategically organize your warehouse to streamline picking and packing processes.
C. Warehouse Management Automation
It’s now time to shift your focus on logistics by automating warehouse management. Effective warehouse management leads to storing products, getting them picked up, and shipping them effectively — all while reducing errors and speeding up delivery times.
Kladana’s warehouse management system can automate picking and real‑time shipment tracking.
It ensures your warehouse operations are streamlined and error‑free, resulting in faster order fulfillment and increased customer satisfaction.
Steps to implement warehouse automation?
Step 1: Implement a Warehouse Management System (WMS)
Choose a WMS that supports automation and integrates with your other systems.
Step 2: Automate Picking and Packing
Utilize technologies like pick‑to‑light systems, voice picking, or even robotics to improve accuracy and efficiency.
Step 3: Optimize Storage and Retrieval
Employ automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS) to maximize space and minimize manual handling.
Step 4: Streamline Shipping and Tracking
Integrate with shipping carriers and provide real‑time tracking information to customers.
Tools, services, and software for Business process automation
Business process automation (BPA) uses various tools and technologies to streamline operations and boost efficiency.
As automation evolves, businesses are combining both established and new technologies to meet their needs.
Workflow Automation Tools
The modern workflow automation tools are designed for business users with limited coding experience.
Examples include Zapier and Microsoft Power Automate, which automates repetitive tasks across different applications.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Software robots mimic human interactions with digital systems by performing tasks like data entry, invoice processing, and customer support.
For instance, tools like UiPath and Automation Anywhere enable the integration of solutions into various business processes, reducing the need for manual intervention.
Intelligent Automation
AI‑driven intelligent automation combines RPA with artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to automate tasks while learning and improving over time.
AI tools like IBM Watson and Google Cloud AI can be integrated into business automation systems for predictive analytics, enhance decision-making, and optimize workflows.
Digital Process Automation (DPA)
DPA reflects the integration of BPA strategies into broader digital transformation efforts to enhance customer experiences, improve operational efficiency, and enable greater agility in business processes. Banking businesses can use platforms like Bizagi or IBM’s Business Automation to let customers submit claims online, submit documents automatically routed for review, and swiftly process payments.
No‑Code/Low‑Code Platforms
These platforms empower non‑developers to automate workflows and develop custom applications quickly, reducing the dependence on IT departments.
Tools like Mendix and OutSystems provide user‑friendly interfaces, making it easier for business users to create and deploy automated solutions without deep technical expertise.
Business Process Management Software (BPMS)
Use centralized process management, such as BPMS platforms, which combine workflow management, automation, and analytics into a centralized hub.
Tools like Appian and Pega offer comprehensive BPMS solutions that integrate automation with analytics to provide real‑time insights and optimization opportunities.
Features of Business Process Automation
The features below create a synergistic effect to ensure that businesses achieve unprecedented levels of efficiency and agility.
Data Integration
Business process automation can seamlessly connect disparate systems and applications. It facilitates the flow of information and eliminates data silos.
Real‑Time Data Analysis
Drive informed decision-making with real‑time insights and analytics so that businesses can make data‑driven decisions quickly and accurately.
Reporting and Analytics
Your BPA should also be able to generate detailed reports and dashboards to track key metrics and measure the impact of automation.
Customizable Dashboards
Gain enhanced visibility with tailored dashboards for specific roles or needs. It offers clear visibility into key performance indicators (KPIs) and workflow statuses.
Collaboration Tools
Ensure top‑notch communication and collaboration among team members when implementing BPA so that every team member is connected to a singular idea of automation.
Scalability
Futureproof your business with automation, which will help employees adapt and grow as your business expands and your automation needs evolve, allowing you to handle increased complexity and volume.
Security Features
Ensure data protection as you implement BPA with robust security protocols to protect sensitive information while staying compliant with industry standards.
Audit Trails
Accountability and compliance should stay at the center of BPA to keep a record of all automated processes. This will provide transparency and help businesses meet regulatory requirements.
AI and Machine Learning Integration
Drive continuous improvement by leveraging AI and machine learning to optimize workflows and adapt to changing business needs over time.
Best Practices for Business Process Automation
BPA’s features lay the groundwork, but you need to maximize its potential by following some of the best practices that reflect a strategic approach.
Here are some of those.
Define Your Goals
Identify the specific outcomes you want to achieve through automation. Whether it’s reducing costs, improving efficiency, or enhancing customer experience.
Identify and Prioritize Processes
You need to focus on high‑impact areas by identifying and automating repetitive, time‑consuming processes prone to human error. Prioritize tasks that, when automated, will have the most significant impact on your overall operations.
Involve Key Stakeholders
Engage employees from different departments early in the process. Their insights and feedback are crucial for successful implementation and adoption.
Choose the Right Tools
Select BPA tools and technologies that best suit your business needs. Consider factors like ease of integration, scalability, and user-friendliness to ensure the tools you choose can grow with your business. Consider factors like scalability, ease of use, and integration capabilities.
Provide Adequate Training
Invest in training programs to equip your employees with the skills and knowledge needed to use the new automation tools effectively.
Monitor and Optimize Continuously
Improve iteratively, as BPA requires continuous monitoring of automated processes, feedback collection, and necessary adjustments to optimize performance.
Document Processes and Learnings
Documenting automated processes, including workflows, challenges, and solutions, to create a knowledge base adds value for future automation efforts.
Explore the Power of Seamless Kladana ERP Software Integration
- Easy connectivity
- Tailored data sync
- Dependable and fast automation
- Custom fields for your workflows
FAQs on Business Process Automation
Let’s explore some of the common questions around BPA with answers to help you make the right decisions for your business.
Q. What is the difference between business process automation and business process management?
A: While they sound similar, business process automation (BPA) and business process management (BPM) are different. BPA focuses on using technology to automate repetitive tasks within a process, while BPM is a broader discipline that involves analyzing, designing, and optimizing entire business processes.
Q. What is robotic process automation (RPA)?
A: RPA is a type of BPA that uses software robots to automate repetitive, rule‑based tasks that are challenging to do when using traditional programming methods.
Q. What are the key benefits of using BPA tools?
A: BPA tools improve efficiency, accuracy, scalability, and compliance while also reducing costs and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Q. Can business process automation be used by small businesses?
A: Absolutely! In fact, BPA can be especially beneficial for small businesses, helping them compete with larger organizations by streamlining their operations and increasing efficiency.
Q. How can I choose the right business process automation software?
A: Before choosing BPA software, consider your specific needs and budget. Then, choose the one that’s easy to use, scalable, and integrates well with your existing systems.
Q. How can BPA improve collaboration among teams?
A: BPA tools provide centralized platforms for managing processes, which enhances transparency and communication across teams, leading to better collaboration and fewer misunderstandings.
Q. How does BPA impact data security?
A: BPA tools often include robust security features to protect sensitive data. However, you need to implement proper security measures and regularly audit systems for data protection.
Q. Is business process automation a one‑time project?
A: No, business process automation is an ongoing process. As your business grows, you’ll need to adapt and optimize your automated processes continuously.
Q. Can BPA tools be customized to fit specific business needs?
A: Yes, many BPA tools are highly customizable, allowing businesses to tailor workflows, dashboards, and automation rules to meet their unique operational requirements.
Q. What are the advantages of using BPA tools?
A: BPA tools offer many benefits, such as efficiency, accuracy, scalability, compliance fulfillment, and cost reduction.

