Manufacturing cost estimating is more than just adding up bills. For manufacturers, it’s the process of forecasting how much it will cost to produce a product before and after it’s made. By applying structured costing approaches, businesses can set accurate prices, protect margins, and plan resources effectively.
Without reliable estimates, companies risk underpricing, overpricing, or losing control of their finances. This guide explains key manufacturing costing methods, techniques, and systems that help small and medium-sized businesses improve cost accuracy and decision-making.
- What is Manufacturing Cost Estimating?
- Why Cost Estimation Matters (Profitability & Decision-Making)
- Core Cost Components
- Common Costing Methods in Manufacturing
- Costing Techniques & Tools
- Cost Estimation Systems: Automation & Software
- Costing in Practice: Step-by-Step Product Costing Flow
- Common Mistakes in Manufacturing Cost Estimation
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions on Manufacturing Costing
📊 Automate Cost Calculation with Kladana ERP
Manual costing can be time-consuming and often inaccurate. Kladana helps you avoid this by automatically calculating your production costs — both before and after manufacturing.
💸 Planned Cost Report
Plan your production budget with confidence. Kladana creates a planned cost report using the details from your production order — like the list of materials (BOM) and operation rates. This report shows how much it should cost to make a product.
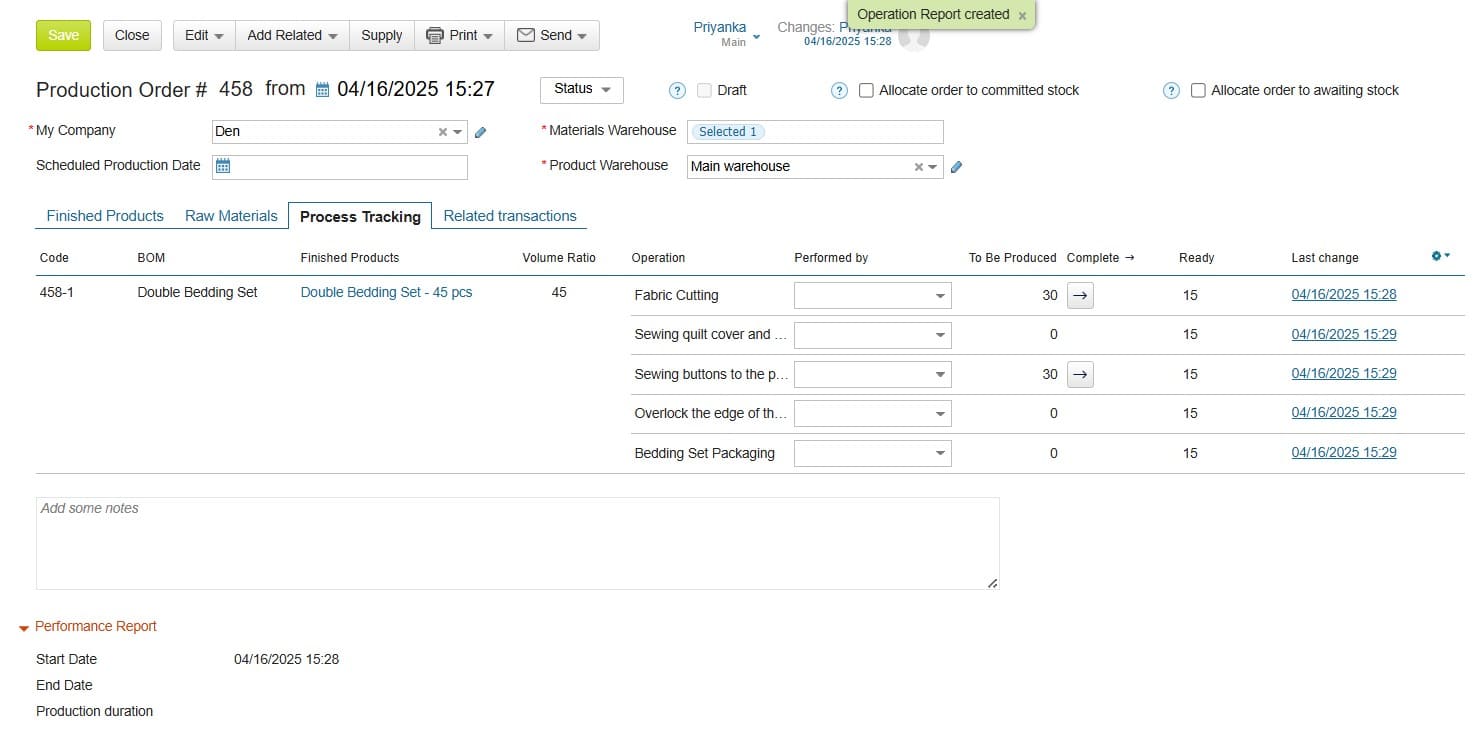
What is Manufacturing Cost Estimating?
Manufacturing cost estimating means calculating the expected expenses involved in producing goods. It includes direct costs like raw materials and labor, as well as indirect costs such as utilities, rent, and machine maintenance. A good manufacturing cost estimation balances these elements into a clear product costing model.
Businesses use this process to understand the true cost per unit, track profitability, and plan production more confidently. Different product costing methods — such as job costing, process costing, or activity-based costing — fall under this broader approach. In practice, cost estimation serves as the foundation for budgeting, pricing, and long-term financial planning in manufacturing.
Why Cost Estimation Matters (Profitability & Decision-Making)
Accurate manufacturing cost estimation directly affects a company’s profitability. If costs are underestimated, products may be sold too cheaply, cutting into margins. Overestimation, on the other hand, can make pricing uncompetitive and reduce sales. Reliable costing procedures help strike the right balance.
Cost estimation also supports smarter decision-making beyond pricing. Managers can evaluate whether to produce in-house or outsource, adjust production volumes, or negotiate better supplier contracts. A structured cost estimation system highlights where resources are being consumed and where savings are possible. This financial clarity makes it easier to plan budgets, set profit targets, and respond to market changes.
In short, cost estimation is not just an accounting exercise — it’s a strategic tool. Businesses that adopt strong costing approaches gain tighter control over expenses, improved efficiency, and long-term competitiveness.
🧮 Try the Free Break-Even Point Calculator
Looking for a practical way to connect costing with profitability?
Kladana’s Break-Even Point Calculator shows exactly how many units you need to sell to cover fixed and variable costs — and when your business starts generating profit.
- Enter your production costs, price, and volume assumptions
- Instantly see the break-even point and revenue threshold
- Test scenarios to refine pricing and cost strategies
Core Cost Components
A clear product costing process starts with understanding the main cost components.
Direct costs are tied directly to production. These include raw materials, packaging, and wages of workers who make the product. Direct costs are easy to trace and form the base of any product costing system.
Indirect costs are necessary for production but harder to link to a specific item. Examples are electricity, machine repairs, and quality inspections. Though not as visible, these costs influence overall manufacturing cost calculation.
Overheads combine a wide range of expenses that keep production running —administration, rent, insurance, and equipment depreciation. Businesses often use a product costing model to distribute these expenses fairly across products.
By identifying and separating these components, manufacturers gain a clearer view of where money is spent. This improves cost accuracy, helps avoid underpricing, and ensures pricing reflects the true effort behind production.
📘 Recommended Read: Thinking about automating cost estimation? Discover how ERP Inventory Management streamlines costing, improves accuracy, and connects your entire production workflow.
Common Costing Methods in Manufacturing
Businesses rely on different types of costing methods in manufacturing to track expenses, set prices, and plan production. The choice depends on product type, production volume, and business goals.
Job Order Costing
Used when products are custom-made, such as furniture or machinery. Costs for materials, labor, and overhead are tracked for each job, giving precise control over profitability per project.
Process Costing
Best for mass production of identical items, like food or chemicals. Costs are averaged across all units, simplifying production costing methods and ensuring consistent unit pricing.
Activity-Based Costing (ABC)
Assigns costs to specific activities, such as machine setups or quality checks. This detailed approach shows where resources are consumed, helping reduce inefficiencies.
Standard Costing
Applies predetermined costs for labor, materials, and overhead. Variances between standard and actual costs highlight areas for improvement and tighter financial control.
Hybrid Methods
Combine elements of different systems. For example, a manufacturer may use process costing for standard goods and job order costing for custom orders.
💸 Actual Cost of Goods
Track what your product really costs after production.
Kladana calculates the actual cost automatically by collecting data from all related transactions:
- Shipments
- Receivings
- Transfers
- Sales Returns
- Stock & Profit Reports
This helps you analyze profit margins, fine-tune pricing, and better control inventory value.
Costing Techniques & Tools
Costing techniques can be managed either manually or with digital systems. The choice impacts accuracy, speed, and overall efficiency.
Manual spreadsheets are still common in small businesses. They allow basic cost estimation techniques, such as calculating direct material and labor costs. While spreadsheets are inexpensive and flexible, they can quickly become complex, error-prone, and difficult to update as operations grow.
Digital tools such as ERP or MRP systems automate manufacturing cost estimation. These systems integrate data from production orders, inventory, and sales to calculate real-time costs. A cost estimation system inside ERP ensures consistency, reduces human error, and provides insights for decision-making.
For scaling manufacturers, digital costing approaches save time, improve accuracy, and enable proactive financial control compared to manual methods.
Cost Estimation Systems: Automation & Software
A cost estimation system goes beyond basic calculations. It integrates all cost data — materials, labor, overhead, and inventory movements—into one platform. This automation improves accuracy and saves time compared to manual costing procedures.
ERP software plays a central role in modern manufacturing costing methods. It connects production orders, bills of materials (BOMs), and inventory records to provide both planned and actual cost reports. Managers can compare estimates with real expenses, spot inefficiencies, and adjust pricing or purchasing strategies.
Some systems also support scenario planning, allowing businesses to model different production costing methods or pricing approaches before making decisions. This flexibility helps manufacturers stay competitive and financially prepared in changing markets.
For small and medium enterprises, adopting automated product costing systems ensures transparency, consistency, and stronger control over profit margins.
📘 Recommended Read: Need a deeper breakdown of manufacturing costs? Explore our guide on the Cost of Goods Manufactured (COGM) — complete with formulas, components, and examples to sharpen your cost analysis.
Costing in Practice: Step-by-Step Product Costing Flow
A structured product costing process helps manufacturers turn raw data into clear financial insights. Here’s how it typically works:
- List Materials and Labor — Identify raw materials, components, and direct labor required for production.
- Add Overheads — Allocate indirect costs such as utilities, rent, and machine depreciation using a fair costing approach.
- Choose a Method — Apply suitable production costing methods (job order, process, or standard costing) based on the product type.
- Estimate Unit Cost — Divide total costs by production volume to calculate per-unit manufacturing cost.
- Review Variances — Compare estimated costs with actual expenses to refine future calculations.
This step-by-step flow turns manufacturing cost estimation into a repeatable, reliable process. With digital tools, the flow becomes faster and less prone to error, giving businesses a consistent product costing system that supports smarter pricing and planning.
Common Mistakes in Manufacturing Cost Estimation
Even with the right costing methods in manufacturing, errors can distort results and hurt profitability.
Ignoring indirect costs is one of the most common mistakes. Utilities, equipment wear, and administrative expenses often get overlooked, leading to underpriced products.
Inconsistent costing procedures create confusion in financial records. Switching between different cost methods without clear rules makes it difficult to compare results or plan effectively.
Relying only on outdated data can also mislead estimates. Material prices, labor rates, and overheads change often. Without regular updates, the product costing system quickly becomes inaccurate.
Finally, depending too heavily on manual spreadsheets increases the risk of errors. Automated cost estimation systems reduce mistakes and provide real-time insights.
Avoiding these pitfalls ensures more reliable manufacturing cost calculations and stronger decision-making.
Stop spreadsheet chaos: Automate your cost estimation today.
Conclusion
Manufacturing cost estimating is more than a financial exercise — it’s the foundation of profitable decision-making. By applying structured costing approaches and reliable product costing methods, businesses gain visibility into where money is spent, how resources are used, and what each unit truly costs to produce.
Modern cost estimation techniques combined with ERP software give manufacturers the accuracy and speed that manual processes lack. This ensures competitive pricing, tighter control over margins, and stronger long-term planning.
For small and medium-sized manufacturers, adopting a clear costing approach is not optional — it’s essential for growth. Investing in automated costing systems like Kladana helps avoid errors, improves efficiency, and turns cost estimation into a strategic advantage.
Frequently Asked Questions on Manufacturing Costing
What is manufacturing cost estimating?
Manufacturing cost estimating is the process of forecasting expenses involved in producing goods. It covers materials, labor, and overhead costs. Accurate estimates help businesses set competitive prices, manage budgets, and improve profitability.
Why is cost estimation important in manufacturing?
Cost estimation supports better pricing, budgeting, and decision-making. Without reliable calculations, businesses risk underpricing, overpricing, or losing profit margins. A structured costing approach ensures financial clarity and competitiveness.
What are the main costing methods in manufacturing?
Common costing methods include job order costing, process costing, activity-based costing, standard costing, and hybrid methods. Each suits different production scenarios depending on volume, customization, and complexity.
What are the components of a product costing system?
A product costing system includes direct costs (materials, labor), indirect costs (utilities, repairs), and overheads (administration, rent, depreciation). Together, these components form the basis of accurate manufacturing cost calculation.
How do costing procedures affect pricing?
Costing procedures define how expenses are allocated to products. Clear methods ensure prices cover all costs while keeping margins healthy. Inconsistent procedures can distort pricing and profitability.
What are common costing techniques?
Cost estimation techniques include analogous estimation, parametric estimation, and bottom-up estimation. These techniques vary in detail and accuracy, helping businesses plan projects and production costs effectively.
Can small businesses use advanced costing systems?
Yes. Even small manufacturers benefit from automated product costing systems. ERP software makes complex calculations simple, reduces manual work, and provides accurate real-time cost data.
What is the difference between costing methods in accounting and manufacturing?
Costing methods in accounting cover broader financial reporting, while costing methods in manufacturing focus on tracking production expenses. Both overlap but serve different decision-making needs.
How often should costing systems be reviewed?
Ideally, businesses should review costing systems quarterly or at least annually. Regular reviews ensure that changes in raw material prices, labor rates, or overheads are reflected in cost models.
How does ERP software improve manufacturing cost estimation?
ERP automates the product costing process by integrating data from BOMs, production orders, and inventory. It generates planned and actual cost reports, reduces errors, and improves decision-making speed.
Read‑alikes
Understanding the Production System in Manufacturing: Types, Benefits, and Examples
Discrete Manufacturing: Key Elements, Insights, and Benefits
Piece Rate Pay — A Complete Guide for Employers & Workers
Understanding the Cost of Goods Manufactured: Formula, Components, Examples & Importance


