The early days of running a business always felt like controlled chaos — sometimes just chaos. You need to keep track of stock in spreadsheets, approve payments over WhatsApp, and rely primarily on your trustworthy employees who “know where everything is”. At first, it works. Orders go out, clients are happy, and you dream big.
Then, growth hits.
Inventory counts stop adding up. A major client gets the wrong order. Your sales team promises and offers discounts that you disapprove of. Finance can’t close the books because half the numbers don’t match. The business isn’t failing, but it is not scaling either.
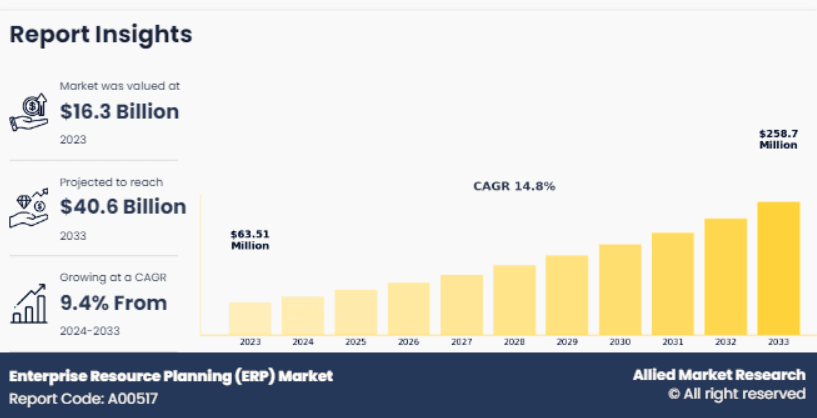
It is a story that thousands of companies live every year. That is why, according to Allied Market Research, businesses globally are projected to spend over $40 billion annually on ERP systems by 2033, not because they are trendy but because managing complexity without the right system will cost more than buying.
ERP is not a one-size-fits-all solution; it depends on the type you choose according to your business requirements. In this guide, you will explore which ERP models exist, how they function, and how to select one that can help you align with your business goals.
What is ERP?
ERP stands for Enterprise Resource Planning. It is software that will help you manage your business operations more smoothly. It is a system that connects cross-functional teams, helps automate tasks, and gives you a complete view of your business. Furthermore, it ensures your data is centralized, easy to use, and consistent.
For example, imagine growing a business where sales, inventory, finance, and HR are using different tools that are not integrated. Sales confirms an order, but the warehouse team is unaware that the stock levels are low.
Meanwhile, the finance team is waiting for manual updates to send out invoices, and payroll is delayed because timesheets are still being collected by mail. Everyone was working hard and doing their job, but the disconnect between the teams led to delays, duplicated work, and time-consuming tasks.
An ERP system brings everything together. Instead of separate systems and constant follow-ups, you manage your core processes, such as sales, inventory, accounts, etc., all in one place.
When you create an order, stock levels update automatically, purchasing gets triggered if needed, finance can invoice instantly, and your management becomes much easier to handle. Once you implement ERP, you can make vast improvements with few errors and a smooth workflow.
Core Features of ERP Software
- WMS & Stock Control: Track inventory levels, procurement, and logistics
- OMS: Manage sales & purchasing orders, conduct receivings, shipments, and related operations
- CRM: Oversee customer relationships, and sales pipelines
- Finance: Maintain financial reporting (e.g., profit & loss), and monitor unpaid invoices
- Team Management: Handle payroll, control user access, assign tasks, and track individual sales performance
- Manufacturing: Manage BOMs & production orders, monitor progress, and oversee shop floor operations
Why Understanding the ERP Types Matters
It is never easy to choose the right ERP software. Different types of ERP have different features. For example, a small e-commerce business might benefit from a lightweight cloud ERP with basic features.
In contrast, a global manufacturer may use different ERP systems, such as on-premise or hybrid ERP systems, that can handle complex operations across multiple locations. Understanding the types of ERP is very important to minimize risk, control the budget, and grow your business.
6 Types of ERP Software
Let’s briefly examine six key types of ERP solutions.
1. On-Premise ERP
This ERP software is installed directly on your company’s servers and handled by your in-house IT team. This model offers you complete control over your data and infrastructure. It helps you maintain the privacy of your data and strict oversight of your system.
For example, a mid-sized electronic manufacturer producing custom circuit boards for medical equipment must store design files, client specifications, and supplier records in-house. Still, they are not allowed to use cloud storage due to regulatory compliance. They also have highly customized workflows that need tight integration with their factory equipment, and cloud ERP software cannot support this high level of customization.
However, if you implement an on-premise ERP system, their IT team will configure the software according to your needs. They will ensure that everything stays secure and maintain integration.
Why Businesses Choose On-Premise ERP Software:
- Control over infrastructure and data
- High customization options
- Smooth integration and better workflow
2. Cloud-Based ERP
This software is mainly hosted online by the vendor and accessed through the Internet. You don’t need an on-site server or IT team to track the updates because the vendor handles it. This type of setup is ideal if your business is a start-up and wants flexibility, scalability, and low cost.
According to a report by Panorama Consulting Group, 65% of companies implemented cloud-based ERP systems in 2023, which shows a clear shift toward more flexible and easy-to-use platforms for better scaling, maintenance, and deployment.
📌 Neytthomes, a high-fashion rug and carpet brand, implemented Kladana cloud-based ERP system to enhance their operations across ten locations. This transition enabled them to perform inventory counts of 270 carpets within an hour, significantly improving stock management efficiency. Additionally, they streamlined store inventory setup to just 30 minutes, allowing for rapid expansion and consistent inventory practices across all outlets.
Why Businesses Choose Cloud-Based ERP:
- No upfront cost is needed
- Easy to scale up or down
- Remotely accessible
- Automatic updates and security handled by the provider
Looking for a cloud ERP made for small and growing businesses?
Kladana is built specifically for SMEs. It’s simpler than enterprise systems and doesn’t require an IT team to set up or manage.
Here’s what you can do with Kladana:
♦️ Inventory & Warehouse — Keep track of your stock to avoid overstocking or running out
♦️ Sales & Purchases — Manage B2B and B2C orders across all your channels
♦️ Production — Monitor raw material use, costs, and progress easily
♦️ Finance — See your cash flow and profits in one dashboard
Why choose Kladana?
- Affordable and transparent pricing — pay only for what you use
- Easy to set up and connect with tools like WooCommerce, Shopify, Xero
- Free 14-day trial included
- 1–3 onboarding sessions + ongoing support whenever you need it
➡️ Try Kladana — simplify your business without breaking the bank
3. Hybrid ERP
This ERP system lets you keep some parts of your ERP system on-premises and move others to the cloud. It is useful when you can’t or do not want to shift everything simultaneously, but still want both benefits.
Let’s say, for example, a family runs a beverage company they own. Their production and finance system runs an old, customized on-premise ERP that was working for them, but is outdated. Replacing it was expensive, and their sales team was rapidly growing. They needed an advanced tool to help them access via phone, sync orders in real time, and not require VPNs.
Finally, they took the hybrid ERP approach: they kept their existing on-premise ERP for production and accounting but connected a cloud-based sales module that let them also submit orders externally. The new system talks to the old one, so inventory stays current, and the accounts team works on their existing tool.
The result? The sales team became faster and more independent while working, and the organisation avoided a complete system overhaul — buying time to upgrade at their own pace.
Why businesses choose hybrid ERP:
- Add on cloud tools where they help the most
- Keeps reliable legacy systems in place
- Avoids full disruption
- Ideal for businesses trying to modernize gradually
4. Open-Source ERP
This ERP system gives you access to the source code to customize everything. You don’t have to pay for any licenses. To maintain and set up, you just need technical skills. It is suitable for micro businesses that do not have the budget to run a proper start-up.
For instance, a custom bike manufacturing startup tailored premium bikes to each customer. Each piece has unique designs, like different frames, components, delivery time frames, and pricing. Their customization is high-end, and standard ERP was too expensive for their needs.
So, instead of going with a typical commercial ERP, they can choose open-source ERP. They can just hire a freelance developer to set up their business. Together, they build custom modules for tracking bike parts, assigning tasks to technicians, and creating build-to-order workflows. Open-source ERP even generates customer updates as each bike moves through production. It will cost less than the traditional ERP.
Why Businesses Choose Open-Source ERP:
- It fits unique business models
- It doesn’t require any license fees
- It has complete customization control
- It is ideal for tech-savvy teams or micro businesses
5. Industry-Specific ERP
Industry-specific ERPs are designed for specific industries, such as garment, food, plastics, or cosmetics. These systems have built-in features that match industry-specific alignments in work and compliance regulations. They help businesses save time without having to customize from scratch.
Why Businesses Choose Industry-Specific ERP:
- It has in-built features and retail modules like inventory, purchasing, and stock transfers
- It minimizes the manual process and gives more visibility
- It helps to standardize operations across multiple branches
6. Two-Tier ERP
This ERP software is used when a company uses an ERP system at the corporate level (Tier 1) and a more straightforward ERP system at its regional offices, branches, or smaller business units (Tier 2). This setup helps maintain and control at the top while allowing local teams to operate at their own pace.
For example, an MNC retail company’s head office handles global finance, supply chain, and compliance through robust ERP software. However, a smaller regional office manages only local sales, inventory, and vendor coordination.
Implementing the same complex ERP for all the branches would be expensive, so they used a tiered ERP. The headquarters continued using the existing one, but for regional use, they started using a lighter, easier-to-manage system according to their needs.
Both systems are connected, so financial and inventory data flow smoothly. This allows their local teams to stay nimble while the headquarters offices still have real-time global performance visibility.
Why Businesses choose two-tier ERP:
- It fits companies with global headquarters and smaller, regional operations
- It makes it easy to use for local workflow
- It helps support efficient reporting and sharing of data
- It provides flexibility by maintaining alignment
ERP System Types: Comparison Table
| ERP Type | Pros | Cons | Best For |
On‑Premise |
✔️ Full control over data and security ✔️ Customizable |
❌ High upfront cost ❌ Requires IT team & infrastructure |
Large enterprises with strong in-house IT teams |
Cloud‑Based |
✔️ Low setup cost ✔️ Accessible from anywhere ✔️ Scalable ✔️ Regular updates |
❌ Less control over data location ❌ Dependent on internet connection |
SMEs, startups, growing companies with remote teams |
Hybrid |
✔️ Combines control of on-premise with cloud flexibility |
❌ Integration challenges ❌ Higher complexity in maintenance |
Businesses with both central and remote operations |
Open‑Source |
✔️ No license fees ✔️ Full customization ✔️ Active community support |
❌ Requires technical expertise ❌ Limited official support |
Tech-savvy SMEs or companies with custom process needs |
Industry‑Specific |
✔️ Tailored features for niche processes ✔️ Faster implementation |
❌ Limited flexibility outside the target industry |
Manufacturing, healthcare, retail, etc. |
Two‑Tier |
✔️ Cost-effective for large enterprises with subsidiaries ✔️ Local control for branches |
❌ Complex integration with Tier-1 system ❌ Data sync issues |
Large corporations with multiple business units or regions |
Types of ERP Deployment Models
| Model | Description | Best use for |
Single‑tenant |
The company is using a private instance of the ERP software |
It is best used for those businesses needing complete control over customization and data security |
Multi‑tenant |
A company sharing the same Infrastructure but separate data |
It is best used for SMEs looking for cost efficiency |
SaaS |
Vendor hosting and managing all online, and you can have access to it |
It is best used by companies that fully manage ERP |
Hosted ERP |
Traditional ERP hosted by the cloud provider |
It is best used for companies that want on-premises ERP but hosted externally |
How To Choose The Right Type of ERP Software
ERP is one of the most important decisions. It will directly affect your operation, employee productivity, and business growth.
1. Understand the Complexity and Your Business Size
You can start by checking your company’s size and complexity. If you run a small business or startup, you don’t need to choose high-end features of ERP at the beginning. Instead, you can go for cloud-based ERP and scale as you grow.
Similarly, suppose you own a big four firm. In that case, it’s better to go for on-premise, hybrid, or even two-tier ERP so that they can handle heavy, complex loads and make your operation smoother without any complications.
2. Identify Industry-Specific Needs
Different sectors will need other types of ERP software. And when you say industry-specific ERP, it is always easy to choose because it will help you manage everything entirely through its inbuilt features and reduce the need for expensive customization later.
3. Evaluate Budget
Your budget will influence the type of ERP software you want or can afford. You should list your needs in the system and choose accordingly instead of choosing everything at once. ERP systems have many hidden costs, such as maintenance, training, customization, etc. So, choose wisely before you face a downfall.
4. IT Capabilities
If you have a strong IT team, you can always choose On-premise, hybrid, or two-tier ERP software. But if you are in the initial phase of your business and cannot afford an IT team, it is best to choose cloud-based or SaaS ERP, which will also allow you to handle updates, security patches, and technical support.
5. Scalability and Flexibility
ERP software is not a one-day solution. It is actually for the long-term growth of your business. You need a system that can scale smoothly to grow and expand your market. Cloud-based ERP is a better option for scalability. Still, for significant upgrades where you want scalability and flexibility, you should choose hybrid and two-tier ERP software models.
ERP Selection Checklist
Start with asking yourself certain questions.
| Questions | Why it matters |
What is the size of the business and future growth? |
SMEs might need ERP, whereas MNCs will need hybrid or on-premises |
Does your industry have a set process for needs or compliance? |
Furniture, clothing, and food manufacturers specifically need specialized ERP features |
What is your initial budget? |
Cloud ERP is less costly compared to high-end ERP software like hybrid or on-premise |
Do you have a proper IT team? |
Without one, it is best to choose an easy-to-master cloud-based ERP |
Do you need to integrate ERP with existing tools? |
You should make sure that ERP supports easy onboarding and third-party integrations |
Have you compared at least 3 ERP vendors? |
It will give you a better idea of pricing and features for your business. |
Then, use our check-list and mark checkpoints step by step.

To Sum up
The right ERP model should fit your business needs while preparing you for growth and change. Do not rush the selection process. You should involve key decision makers from IT, operations, finance, and even end users. Choose your ERP software carefully because it will streamline your operations and give you a competitive advantage for years.
Frequently Asked Questions on Types of ERP Software
Still unsure which ERP model suits your business? You’re not alone. Below are common questions asked by business owners exploring different types of ERP systems, from cloud ERP to hybrid and industry-specific solutions.
1. What is ERP software and how does it work?
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) software connects your core business functions — like sales, inventory, production, and finance — into one system. It helps streamline workflows, reduce manual work, and enable better data-driven decisions.
2. What are the different types of ERP systems?
The most common ERP models include:
- On-Premise ERP — installed locally on your company’s servers
- Cloud-Based ERP — hosted online by the vendor, accessible via internet
- Hybrid ERP — combines on-premise and cloud-based features
- Open-Source ERP — flexible and customizable, requires technical skills
- Industry-Specific ERP — tailored to manufacturing, retail, healthcare, etc.
- Two-Tier ERP — used by large companies to manage HQ and subsidiaries separately
3. Which type of ERP software is best for small businesses?
Cloud ERP is often the best choice for small and growing businesses. It’s cost-effective, easy to scale, and doesn’t require in-house IT support. Platforms like Kladana are designed with SMEs in mind.
4. What are the key benefits of ERP implementation?
Top benefits include:
- Real-time data access across departments
- Better resource planning and inventory control
- Enhanced financial reporting and forecasting
- Faster order processing and reduced operational delays
5. What is cloud ERP and how is it different from on-premise ERP?
Cloud ERP is hosted by a provider and accessed online. It requires no internal servers, offers scalability, and includes regular updates.
On-premise ERP is installed and maintained on your company’s physical infrastructure, giving full control but higher maintenance costs.
6. Is cloud ERP secure for storing sensitive business data?
Yes. Most cloud ERP vendors use high-level encryption, role-based access, and compliance certifications (like ISO, GDPR) to protect your data. Just ensure your provider meets your specific security requirements.
7. How do I choose the right type of ERP for my business?
Start by assessing your company size, budget, industry, and technical resources. Cloud ERP suits fast-growing SMEs, while on-premise may work better for large firms with IT teams. Use checklists or consult vendors for demos.
8. What is the cost difference between ERP models?
- Cloud ERP: Monthly/annual subscription, lower upfront cost
- On-Premise ERP: High setup and hardware cost, long-term investment
- Open-source ERP: Free license but development and support costs apply
The right choice depends on your budget and how much customization you need.
9. Can ERP systems integrate with my existing tools?
Yes. Most modern ERPs (especially cloud-based and hybrid) support integrations with platforms like Shopify, WooCommerce, Xero, Zoho, and CRMs. Always check available APIs or native connectors before you choose.
List of Resources
- Allied Market Research — ERP Market Size Report
- Panorama Consulting Group — Implementing Cloud-based ERP
- Research Gate — Case Study on Cloud ERP
- Research Gate — Case Study on ERP Implementation

